Question
Question: ‘X’ can be 
(A) N2H2/OEt, Δ
(B) RedP/HI
(C) HS-CH2-CH2-SH(dithiol), DryHCl/RaneyNi/H2
(D) All of these
Solution
Carbonyl compounds can be converted into respective hydrocarbons by treating with áZn/HCl and N2H2(hydrazine)/C2H5ONa, these reagents known as Clemmensen and Wolff-Kishner reagent respectively.
- Raney nickel (Ni) is like palladium on carbon (Pt/C) reducing agent, which is mainly used for the hydrogenation of alkene and alkynes. Raney nickel is mainly used for the reduction of C-S bond to C-H bond. This reagent can be used as an alternative means for the conversion ketone to alkane.
- Red phosphorus with hydrogen iodide acts as a strong reducing agent by producing nascent hydrogen atoms.
Complete step by step answer:
(A) Aldehyde and ketone are reduced by hydrazine (NH2-NH2) in the presence CH3-CH2ONa and form hydrocarbon, this reaction is known as Wolff-Kishner reduction. So buten-2-one reacts with hydrazine in the basic medium gives n-butane. This reaction is represented by following reaction-
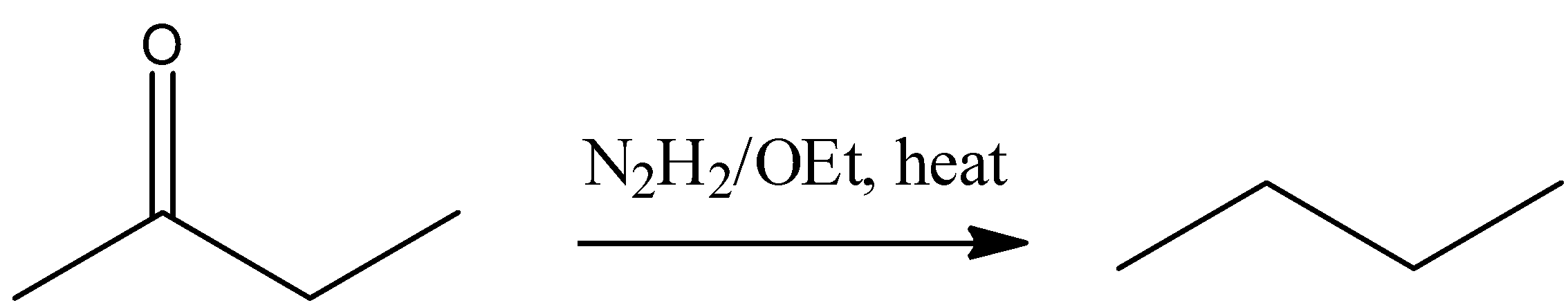
(B) RedP/HI, acts as a powerful reducing agent, it will give alkane (n-butane) after the complete reduction carbonyl group of buten-2-one . This reaction is represented by following reaction –
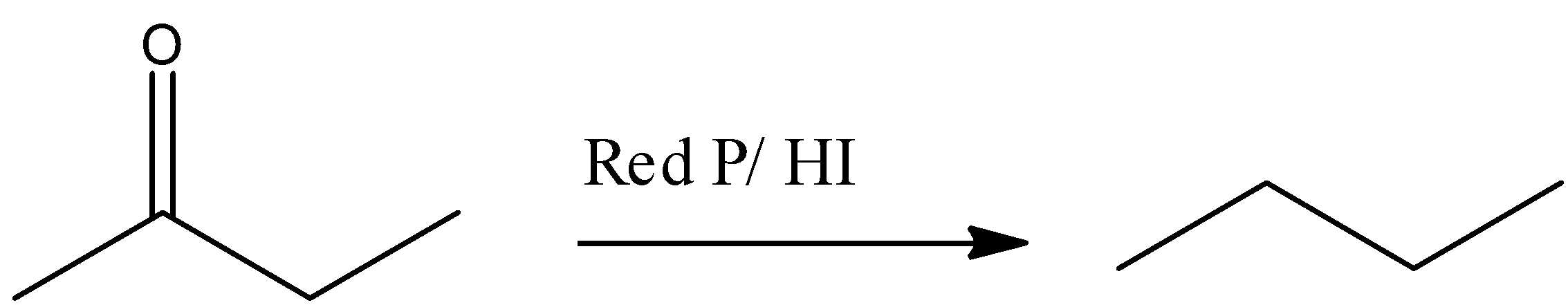
(C) Thiols will react in the acidic medium with the carbonyl group of buten-2-one (ketone) to form thioketal. After reacting with Raney nickel removal of the sulphur group takes place and finally forms n-butane. This reaction is represented in the following reaction.
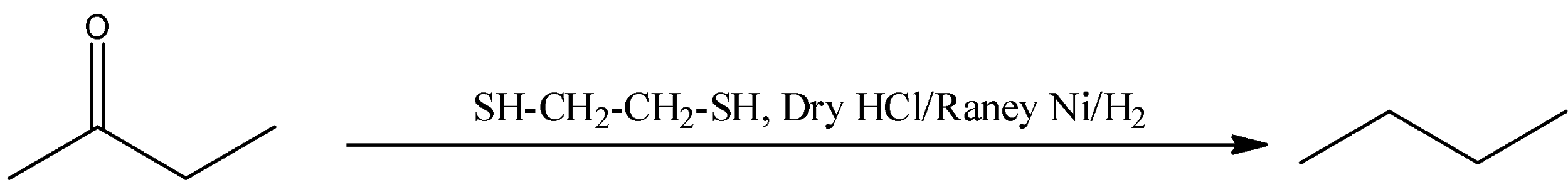
The correct answer is option “D” .
Note: In RedP/HI , Red phosphorus acts as a catalyst and this reducing agent reduces carbonyl compounds to respective alkane. In this reduction process red phosphorus reacts with HI and forms PI3 . It is the reaction controlling agent. It removes iodine which is necessary because iodine is highly reactive. It will react with hydrocarbon and form haloalkane.
