Question
Question: Write the structures of the products when \({\rm{Butan - 2 - ol}}\) reacts with the following: a. ...
Write the structures of the products when Butan−2−ol reacts with the following:
a. CrO3
b. SOCl2
Solution
The given alcohol is a secondary alcohol that would get oxidized upon reacting with CrO3 and halogenated on reacting with SOCl2.
Complete answer
We are given an alcohol namely butan−2−ol as the reactant so before proceeding to the specific reactions, let’s have a look at the structure of butan−2−ol that can be drawn as follows:
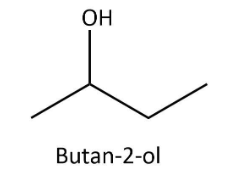
As we can see that, in butan−2−ol, hydroxyl group is attached to a carbon that has two alkyl substituents and thus it is a secondary alcohol. Now, let’s consider the reaction of butan−2−ol with given reagents one by one:
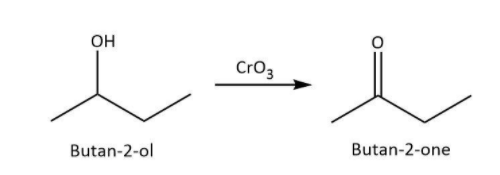
a. We know that chromic anhydride or CrO3 is an oxidizing agent that can oxidize a hydroxyl group to a carbonyl group. So, in case of primary alcohol, the hydroxyl group is attached to a carbon that has only one alkyl or aryl substituent. Upon oxidation, the carbonyl group will be attached to one hydrogen and one alkyl or aryl group thus giving an aldehyde.
However, in a secondary alcohol, the hydroxyl group is attached to a carbon that has two alkyl or aryl substituents. Therefore, we can say that its oxidation will give a ketone.
Let’s write the reaction for oxidation of butan−2−ol on the basis of above understanding along with the structure of the product as follows:
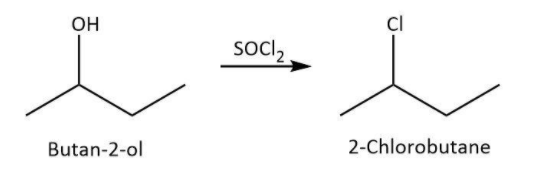
We know that thionyl chloride or SOCl2 can be used for chlorination of alcohols. Let’s write the reaction for chlorination of butan−2−ol along with the structure of the product as follows:
Note:
In oxidation of alcohols, one O−H and one C−H bonds are broken whereas in halogenation, only C−O bond is broken.
