Question
Question: Write the structures and IUPAC names of the cross-aldol condensation products only of ethanal and pr...
Write the structures and IUPAC names of the cross-aldol condensation products only of ethanal and propanal.
Solution
Understand the reaction aldol condensation. Write down the reaction mechanism for cross aldol condensation so that you will understand the working. Draw the expanded structures of ethanal and propanal and then perform cross aldol condensation only on the compounds.
Complete step-by-step answer:
Aldol condensation occurs in aldehydes that have αhydrogen with a diluted alkali to form β hydroxy aldehydes that are also called aldols. When the reaction takes place between two different carbonyl compounds it is called crossed aldol condensation.
The rate determining step in the formation of aldol is the formation of enolate ion as it is the slowest step of the reaction mechanism.
We will now write the reaction mechanism for the aldol condensation of ethanal and propanal.
The structure of ethanal is : CH3CHO
The structure of propanal is :CH3CH2CHO
Reaction mechanism:
- The aldehyde is deprotonated by the incoming hydroxide ion.
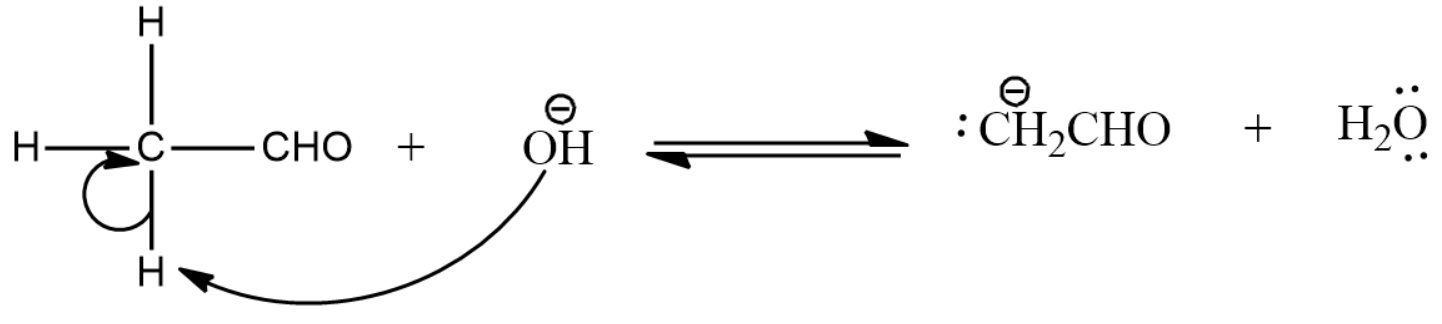
- Here the enolate ion formed in the above step reacts with the next aldehyde molecule which can be identical or different from the first molecule.
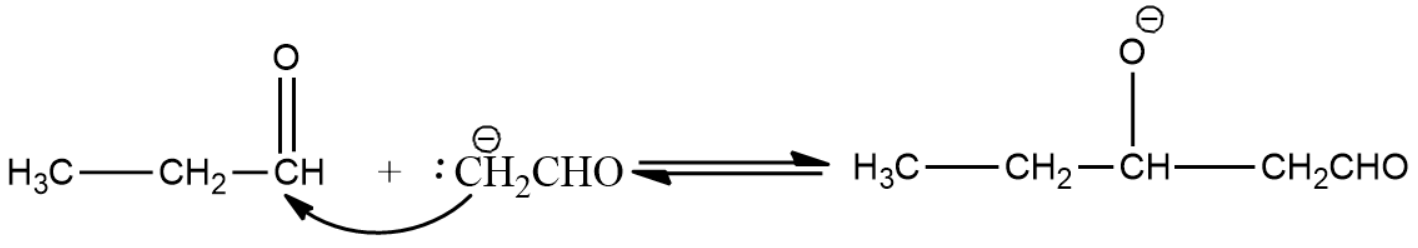
- Alkoxide ion formed is then protonated by water molecules and thus leads to the formation of aldol.
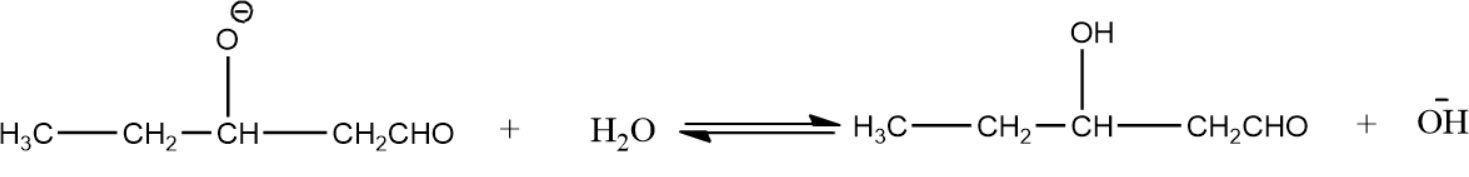
In the same way, when we use propanal as the first aldehyde molecule and ethanal as second aldehyde molecule we get the product as,
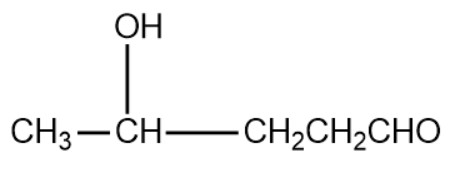
After removal of 1 water molecule from the above 2 compounds we get the following compounds:
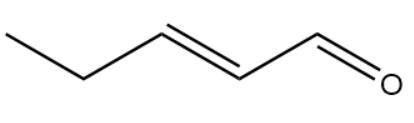
IUPAC Name : Pent-2-enal
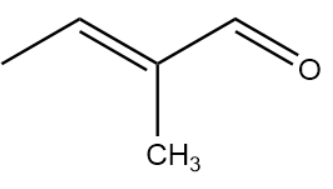
IUPAC Name : 2-methylbutenal
Note: When a carbonyl compound does not have α hydrogen and a concentrated base is used, the reaction that takes place instead of aldol reaction is called cannizzaro reaction.
