Question
Question: Write the structural formula of Chloro-Ethane....
Write the structural formula of Chloro-Ethane.
Solution
The IUPAC (International System of Pure and Applied Chemistry) system is the most rational and widely used system of nomenclature in organic chemistry. The IUPAC name of any organic compound consists of three parts namely: word root, suffix (primary or secondary) and prefix (primary or secondary).
Complete answer:
Chemical structure of an organic compound represents the actual number of atoms, nature of bond (saturated or unsaturated) and functional group present in one molecule of the compound i.e., it shows the real formula of its one molecule.
In Chloro-ethane,
The word root ‘eth’ suggests that there are 2 carbon atoms in the parent chain, the prefix indicates that a halogen atom chlorine is substituted at 1 - position, the suffix ‘ane’ indicates that the parent chain is saturated and is an alkane. There is no functional group present here.
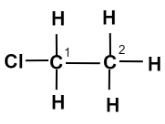
Note:
Prefix is used before the word root and it denotes the substituent and non-functional group attached to the organic compound. The word root indicates the number of carbon present in the longest continuous parent chain and suffix indicates the functional group present in the organic compound. If a carbon containing functional group is present, this carbon atom will also count in the parent chain. Naming of organic compounds is determined according to the naming guideline of IUPAC -Suffix-ane- is used in the IUPAC naming of alkane, and suffix-oic acid -is used in the IUPAC naming of carboxylic acids having functional group (-COOH). Suffix-al - is used in the naming of aldehyde having functional group (-CHO), while Suffix-one -is used in the IUPAC naming of ketone having functional group-(C=O)-
