Question
Question: Write the structural formula and the IUPAC names of all possible names of the compounds with the mol...
Write the structural formula and the IUPAC names of all possible names of the compounds with the molecular formula C3H8O.
Write two uses of phenol.
What happens when glucose is treated with (a) bromine-water (b) dilute nitric acid (c) Hydrogen Cyanide(HCN).
Solution
To solve this question knowledge on the IUPAC nomenclature and the reaction of carbohydrates is required. The functional group attached to the carbon chain is written as a suffix which replaces the e at the end of the name of the carbon chain. The reactions of glucose given are tests for its structural determination.
Complete step by step solution:
The structural formula of the compounds with molecular formula C3H8O are as follows:
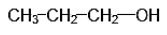
IUPAC NAME: 1-Propanol
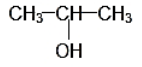
IUPAC NAME: 2-Propanol
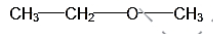
IUPAC NAME: Ethoxy methane.
The two uses of phenol are as follows:
- Phenol is used in diluted concentrations as intermediates as disinfectants.
- In industries, phenol is used as the starting material to make explosives such as picric acids, and drugs such as aspirin.
When glucose is treated with:
(a) Bromine-water: The bromine water oxidises glucose to gluconic acid. This is a mild oxidising agent and is a test to show the presence of the carbonyl group in the glucose.
(b) On treatment of the glucose with nitric acid, oxidation of glucose takes place to form D-glucaric acid.
(c) On reaction with hydrogen cyanide, the glucose molecules form the cyanohydrin.
Note:
Isomers are compounds with similar molecular formula but difference in chemical structure distinctly arranged in space.
Phenol is a class of organic compounds that is categorized by a hydroxyl group to the carbon atom that is a part of the aromatic ring. Besides phenol, the other names of it are benzenol and carbolic acid.
Bromine-water is an intense red coloured solution of bromine gas in water which is mainly used for the halogenation of unsaturated compounds containing double bonds, triple bonds, enols, acetyl groups, aniline, and glucose. The reaction is considered to be complete when the colour of the solution disappears.
