Question
Question: Write the structural formula and IUPAC name of the given compound with a terminal acid. Molecular ...
Write the structural formula and IUPAC name of the given compound with a terminal acid.
Molecular formula: C4H8O2 .
Solution
The given compound is a terminal acid which means that it contains the carboxyl functional group - COOH at the end of the chain.
Since the molecular formula is given to be C4H8O2 and there is a carboxyl - COOH group present, therefore, the remaining part of the compound has the C3H7 group.
Complete step by step answer:
The compound is a carboxylic acid having the formula C3H7 - COOH .
The C3H7 group is propyl group which can also be written as CH3CH2CH2 group.
Therefore, the structural formula of the given compound is
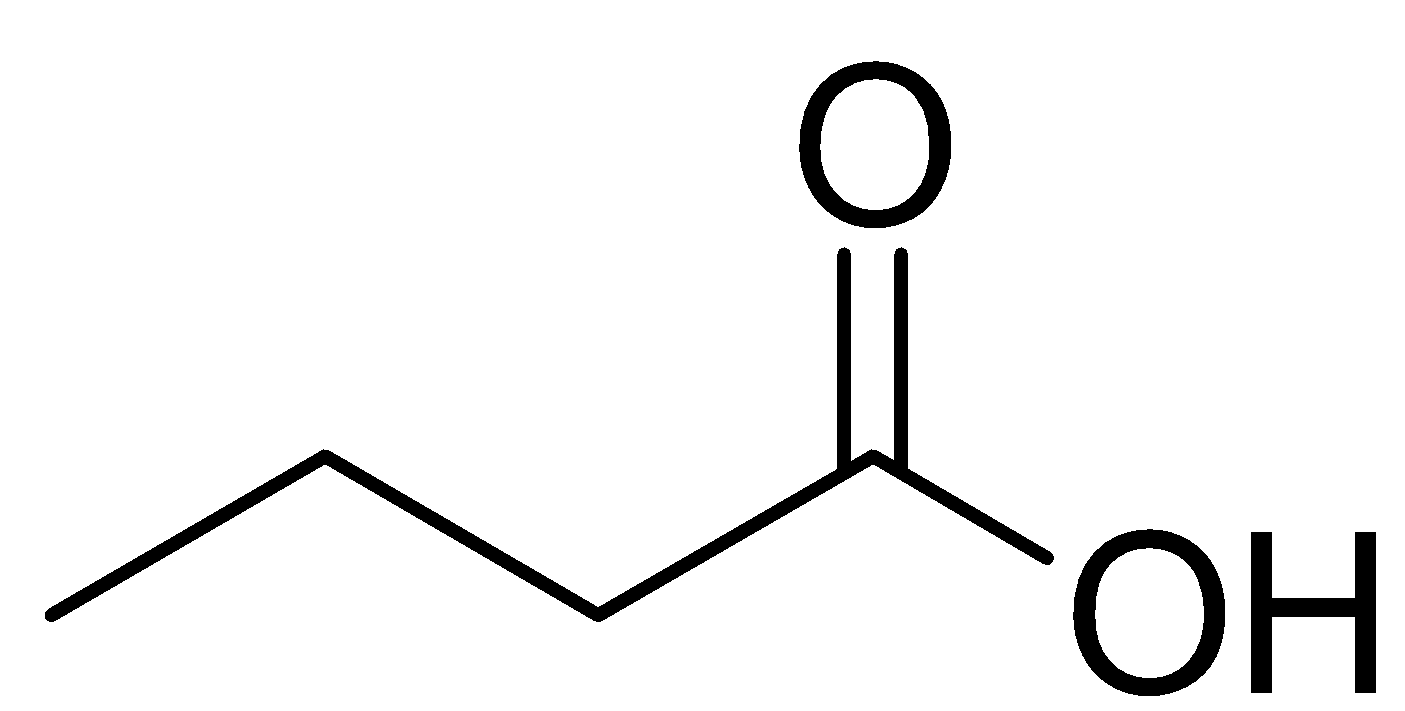
Or,
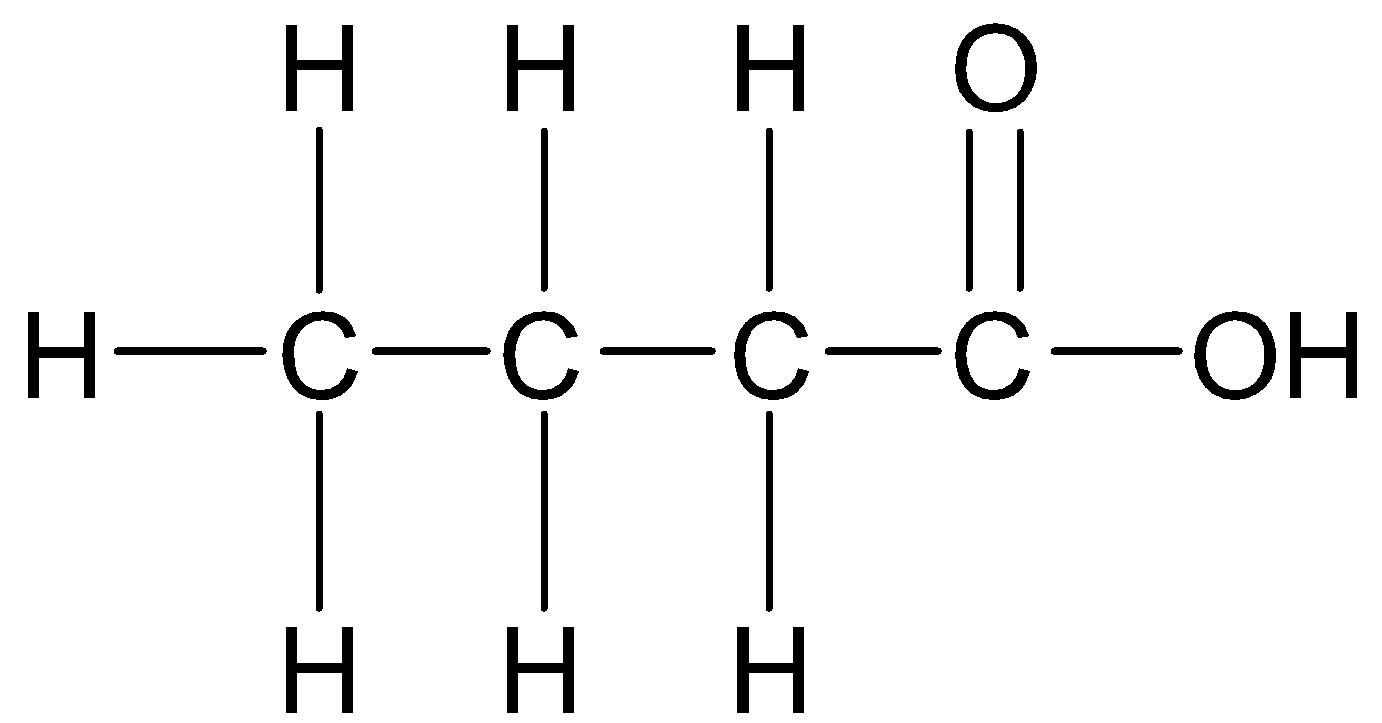
-According to IUPAC nomenclature, if organic compounds contain one principal functional group, then the longest continuous chain of carbon atoms containing the principal functional group is selected.
-If the functional group is such that a carbon atom is already present in it, such as the carboxyl functional group, then the numbering of the carbon chain is done in such a way that this functional group gets the lowest position of 1. While naming the compound, the position 1 is not written with such a group.
-For unsubstituted monocarboxylic acids, the IUPAC name is obtained by changing the suffix ‘ane’ of the corresponding alkane to ‘oic acid’ or in other words, it is ‘alkanoic acid’.
-Now, let us see the structure of the given acid. The carboxyl group is given the position 1 which is omitted while naming. Numbering in this way, we see that there are total 4 carbon atoms involved and so we get:
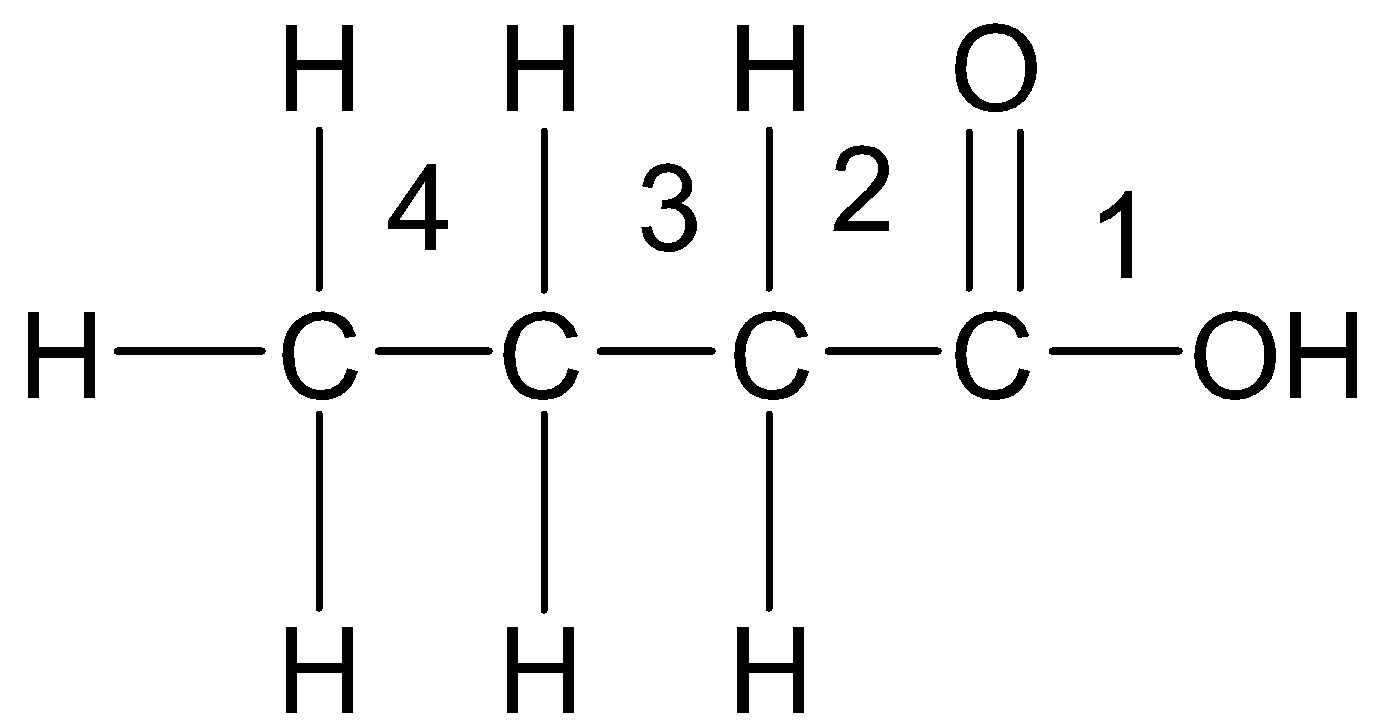
So, the IUPAC name is Butanoic acid.
Note:
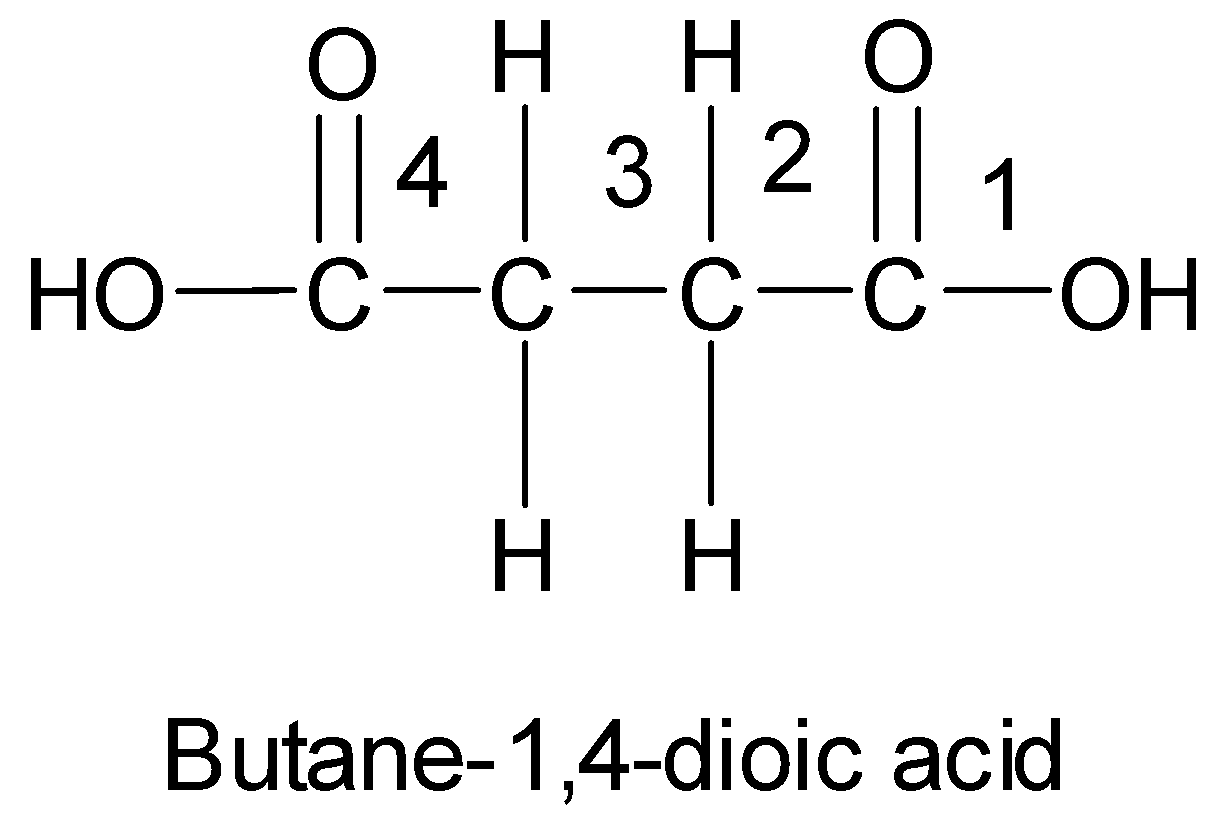
-In case of dicarboxylic acids, the IUPAC names are obtained by adding the suffix ‘dioic acid’ to the name of the parent alkane.
-The position of the carboxyl groups is indicated by Arabic numerals. For example, the following dicarboxylic acid is butane-1, 4-dioic acid.