Question
Question: Write the state of hybridization of carbon in following compounds and shapes of each of the molecule...
Write the state of hybridization of carbon in following compounds and shapes of each of the molecules
A) CH3Cl
B) HCONH2
Solution
The IUPAC nomenclature of CH3Cl is 1-chloromethane and the common name is chloromethane. It is toxic gas and is commonly used as a refrigerant and also as a local anaesthetic. HCONH2 has the IUPAC name as formamide and the common name is methanamide. It is used in the manufacture of formate esters and as an ionizing solvent.
Complete answer:
To find the hybridisation of any compound we will use this simple formula:
Hybridisation=2no.of valence electrons in the central atom+no.ofHydrogen Atoms+no.of Halide Atoms±Formal Charge
If the answer obtained is:
| Answer Obtained/Steric Number | Hybridisation | Geometry |
|---|---|---|
| 2 | sp | Linear |
| 3 | sp2 | Trigonal Planar |
| 4 | sp3 | Tetrahedral |
| 5 | sp3d | Trigonal Bipyramidal |
| 6 | sp3d2 | Octahedral |
Consider the first molecule given:
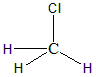
A) CH3Cl : Using the formula to find out the hybridisation of the molecule.
Hybridisation=24+3+1=4
Hence the hybridisation would be sp3 with the geometry to be tetrahedral. There are zero lone pairs in the Carbon atom of the molecule hence the shape of the molecule will also be tetrahedral itself. The structure of the molecule is as follows:
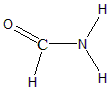
B) HCONH2 : This is an organic molecule, hence we can find the hybridisation using steric numbers. The formula for finding steric number is:
S.N=Lone Pairs on Central Atom+No.of atoms bonded to the central atom
The Carbonyl carbon in Formamide has zero lone pairs, since all four valencies of carbon are occupied. The steric number for Carbon in Formamide is =0+3=3
From the table above the hybridisation of Carbon in Formamide would be sp2 and the geometry would be trigonal planar. The structure of Formamide is:
Therefore, the hybridisation of Carbon in CH3Cl and HCONH2 is sp3 and sp2 respectively.
Note:
If there are lone pairs present on the central atom, the Hybridisation and geometry of the molecule will remain the same, their shape will change accordingly. For example, the shape of a molecule having Tetrahedral geometry with one L.P will be Pyramidal shaped. Similarly, molecules with Trigonal Planar geometry and one L.P will have angular shape.
