Question
Question: Write the resonance structure that would result from moving the electrons as the curved arrows indic...
Write the resonance structure that would result from moving the electrons as the curved arrows indicate. Be sure to include formal charges if needed.
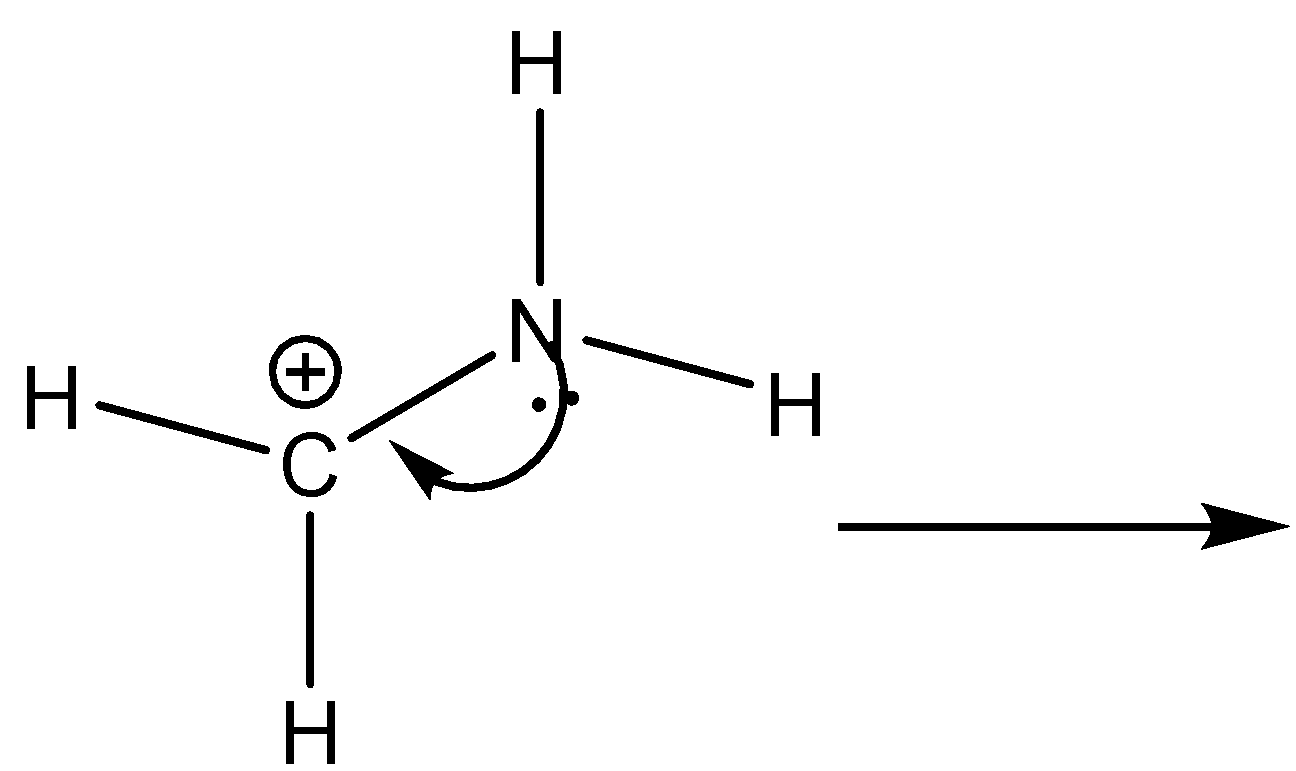
Solution
Let us first discuss resonance hybrid structures. In any given molecule or ion or atom which exhibits resonance, there exist a few resonance forms that can be understood as the average of two or more resonance structures that define the given species. They are represented as separate structures from the other resonance structures by using double-headed arrows.
Complete step by step answer:
Resonance structures are two or more Lewis structures that describe the delocalization of electrons in a molecule or polyatomic ions. Resonance in chemistry describes the bonding in particular molecules or ions by merging many contributing forms, referred to as canonical structures or resonance structures as per the theory of valence bonding into a hybrid resonance or structures.
The delocalization of electrons takes place by fractional bonds and formal charges in a resonance hybrid. Not all resonance structures are equivalent and we need to determine which one is best describing the actual bonding. To predict which resonance structures are favored, we use formal charges.
Let us look at the carbocation which is given. Due to the presence of nitrogen, the lone pair electrons can undergo conjugation with the carbocation. As a result, a new resonating structure is formed as below,
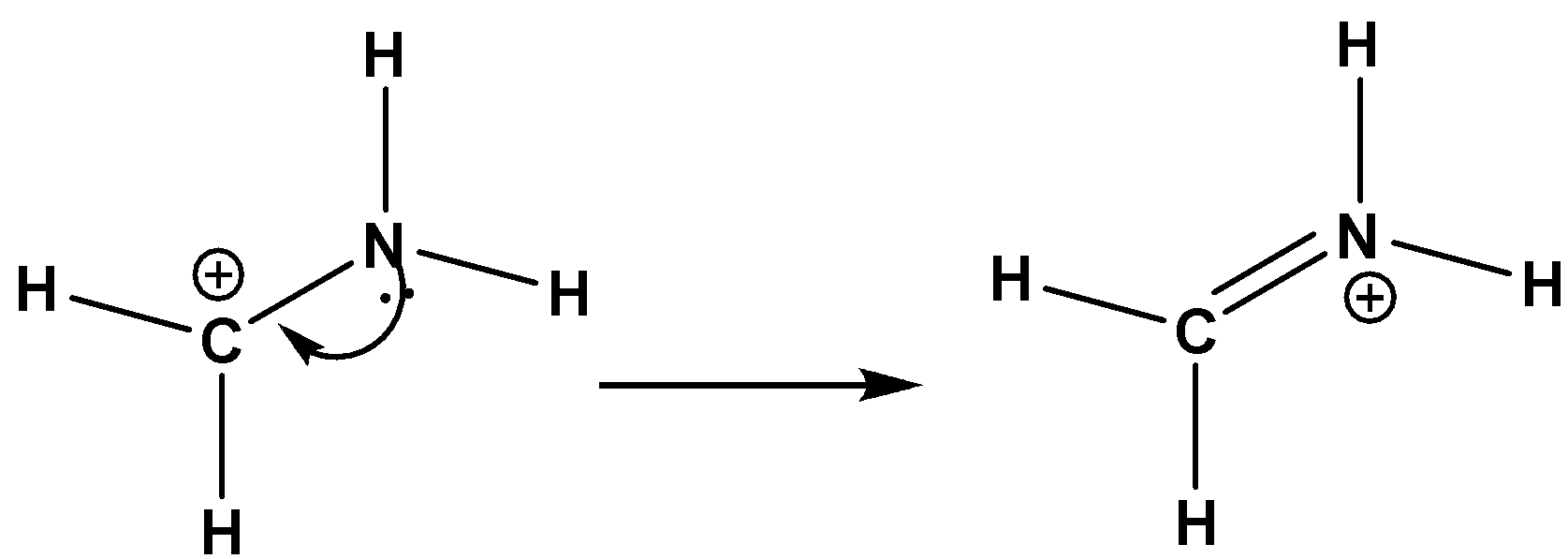
Now, Formal charge is valence electrons – (lone pair of electrons + 21 bounded electrons). We can calculate it for an individual atom. For example, on the nitrogen atom, a formal charge on a nitrogen atom will be 5−(4+0)=+1. So, a positive charge will be developed on nitrogen shown above.
Note: Out of the two resonance structures of the enolate ion that we have drawn above, the one which places the positive charge on the carbon is the least stable and more reactive. This is because the positive charge will be destabilized more by the greater due to incomplete octane of the carbon atom. But in the next structure octane of carbon is complete which stabilizes that structure more than before.
