Question
Question: Write the products of the following reactions: i. \(C{H_3} - \mathop C\limits_{}^{\mathop \paralle...
Write the products of the following reactions:
i. CH3−C∥O−CH3Zn−HgConc.HCl
ii. CH3−CO−ClH2Pd/BaSO4
iii. 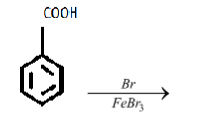
Solution
i. The given reaction is a name reaction, and as the name suggests reduction of a carbonyl group is taking place.
ii. The given reaction is undergoing hydrogenation (addition of hydrogen) followed by reduction.
iii. The reagent in the given reaction is filled with bromine, therefore bromine atom must be added to the product molecule. But to which site?
Complete step by step solution:
i. The given reaction contains a ketone (methoxymethane) undergoing Clemmensen reduction. Where the carbonyl group is reduced to the hydrocarbon group. Now, let’s complete the reaction.
CH3−C∥O−CH3Zn−HgConc.HClH3C−CH2−CH3
Additional information:
1. In a Clemmensen reduction, the carbonyl group of aldehyde and ketone gets reduced to the corresponding hydrocarbon.
2. Erik Christian Clemmensen was a Danish- American chemist, known for the very reaction we just learned.
ii. In the given chemical reaction the -Cl group will get hydrogenated and the carbonyl group is reduced to aldehyde (-CHO). This is also a name reaction, known as Rosenmund reduction.
CH3−C∥O−ClH2Pd/BaSO4H3C−C∥O−H
Additional information:
1. When an acyl chloride (-C=O- Cl) is hydrogenated over a catalyst, palladium on barium sulfate. The reaction is called Rosenmund reduction.
2. Karl whelms Rosenmund was a German chemist, known for the discovery of the reaction you just solved.
iii. In the specified reaction the benzoic acid is getting brominated (bromine atom is being added). Let’s continue with the reaction;
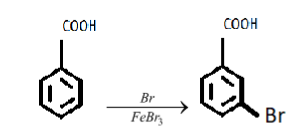
A carboxylic acid is an electron-withdrawing group(attracts the electron density from the benzene group towards itself, because of the two oxygen atoms).
Note:
i. Remember the carbonyl group reduced to the corresponding hydrocarbon in the Clemmensen reduction, and not to the corresponding alcohols.
ii. Try to avoid confusion with other reduction reactions, know that every name reaction has its unique reagents and conditions.
iii. Be careful with the reagents of bromination and Friedel-craft-alkylation, both of them have FeBr3 but there is an alkyl group present in the alkylation reaction (just like its name suggests).
