Question
Question: Write the products formed as Y? \({{(C{{H}_{3}})}_{3}}C-CH(OH)-C{{H}_{3}}\text{ }\xrightarrow{Conc...
Write the products formed as Y?
(CH3)3C−CH(OH)−CH3 Conc. H2SO4 X (Major) reductiveozonolysis Y
A.Acetone
B.Methanal
C.Dimethylpropanal
D.(B) and (C)
Solution
Concentrated Sulphuric acid acts as a dehydrating agent. A dehydrating agent means the substance which eliminates a water molecule from the compound. Dehydration converts a saturated compound into an unsaturated compound. The given reactant is a secondary alcohol that will form an alkene on the elimination of a water molecule.
Complete answer:
The first reactant compound is 3,3-dimethyl-Butan-2-ol. It reacts with concentrated Sulphuric acid to eliminate a water molecule. This water molecule is formed from the –OH group and one Hydrogen from the Hydrocarbon chain. The resultant product formed is a cation.
The dehydrating reaction of 3,3-dimethyl-Butan-2-ol is as follows:
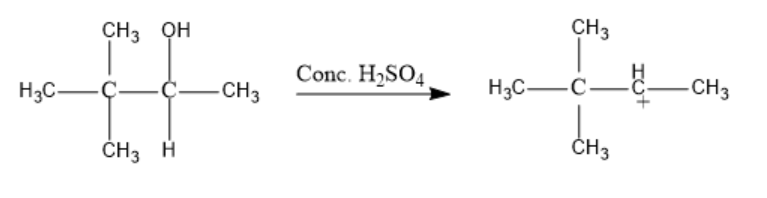
Now, a methyl shift occurs from the third carbon to the second carbon atom in the formed cation.
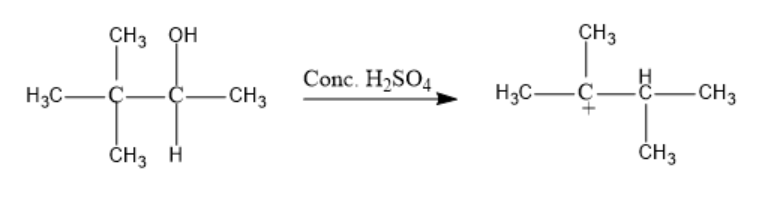
Further, H+ is lost from the hydrocarbon chain and But-2-ene is formed as the major product.
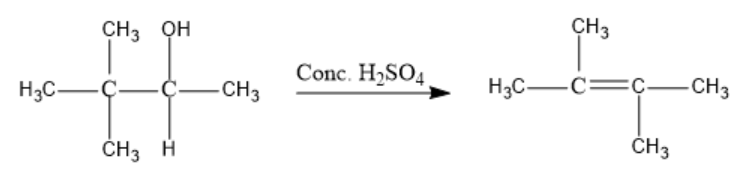
Compound (X) is But-2-ene [C(CH3)2= C(CH3)2]
In reductive Ozonolysis, the unsaturated bonds are cleaved to form either alcohols or carbonyl compounds. Ozone is used as a reactant along with reducing agents like dimethyl sulphide or zinc.
But-2-ene undergoes reductive ozonolysis with O3, to form a carbonyl compound. The double bond is cleaved and two compounds are formed.
Let’s see the reaction of reductive ozonolysis of But-2-ene:
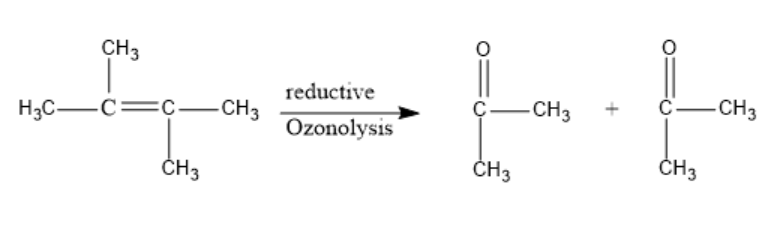
The products formed after reductive ozonolysis are two molecules of Acetone.
Thus, the Compound (Y) is Acetone (CH3COCH3).
Final answer: The correct answer is Option A: Acetone.
Note:
Ozonolysis is an oxidative reaction that occurs with O3 molecules but reductive Ozonolysis also takes place. The resultant carbonyl compounds have half the number of carbon atoms than the alkene. The addition of the Ozone molecule in the double bond is an electrophilic reaction.
