Question
Question: Write the preparation of salicylic acid with mechanism...
Write the preparation of salicylic acid with mechanism
Solution
Salicylic Acid is a small aromatic acid whose chemical name is mono hydroxybenzoic acid. It is lipophilic in nature.
Complete Step-by-Step Answer:
Before we move forward with the solution of the given question, let us first understand some important basic concepts.
The preparation of salicylic acid is done via a process known as Kolbe’s Reaction. This reaction involves phenol as the major reactant. The mechanism of this reaction can be discussed as follows:
We need to first increase the reactivity of the phenol functional group. For this purpose, we make the phenol molecule react with sodium hydroxide, which is a strong base. This causes the displacement of the hydrogen atom in the hydroxyl group, with the sodium atom. The compound thus formed is known as a phenoxide ion. We now carry out electrophilic substitution with carbon dioxide. This results in the formation of a salicylate compound. In the end, we react it with a strong acid line sulphuric acid to substitute the sodium atoms with hydrogen atoms, which results in the formation of salicylic acid. The entire chemical equation for the same can be given as follows:
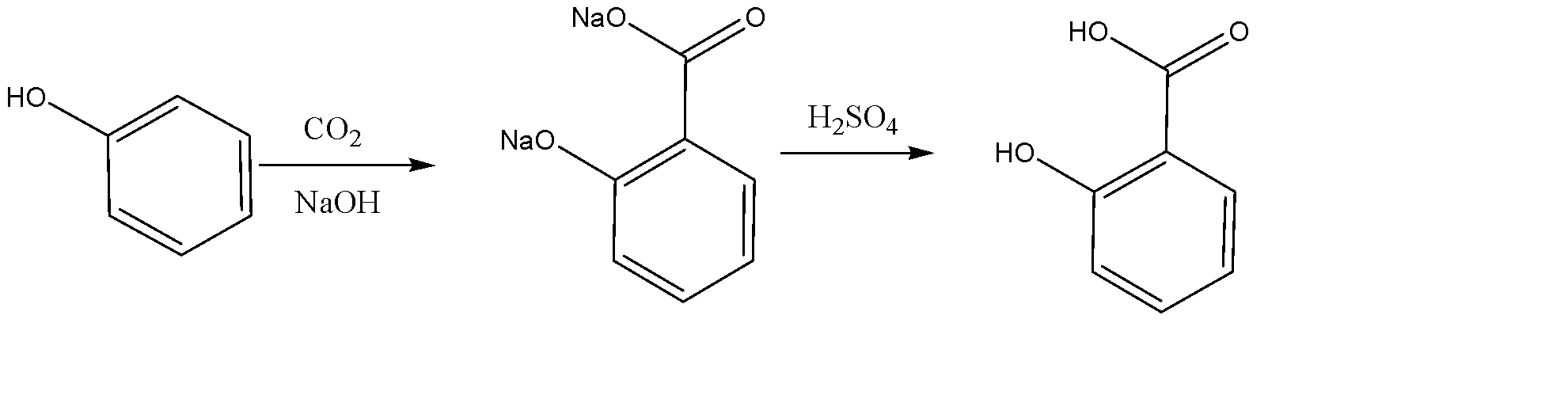
Also, the mechanism for Kolbe’s reaction can be given as follows:
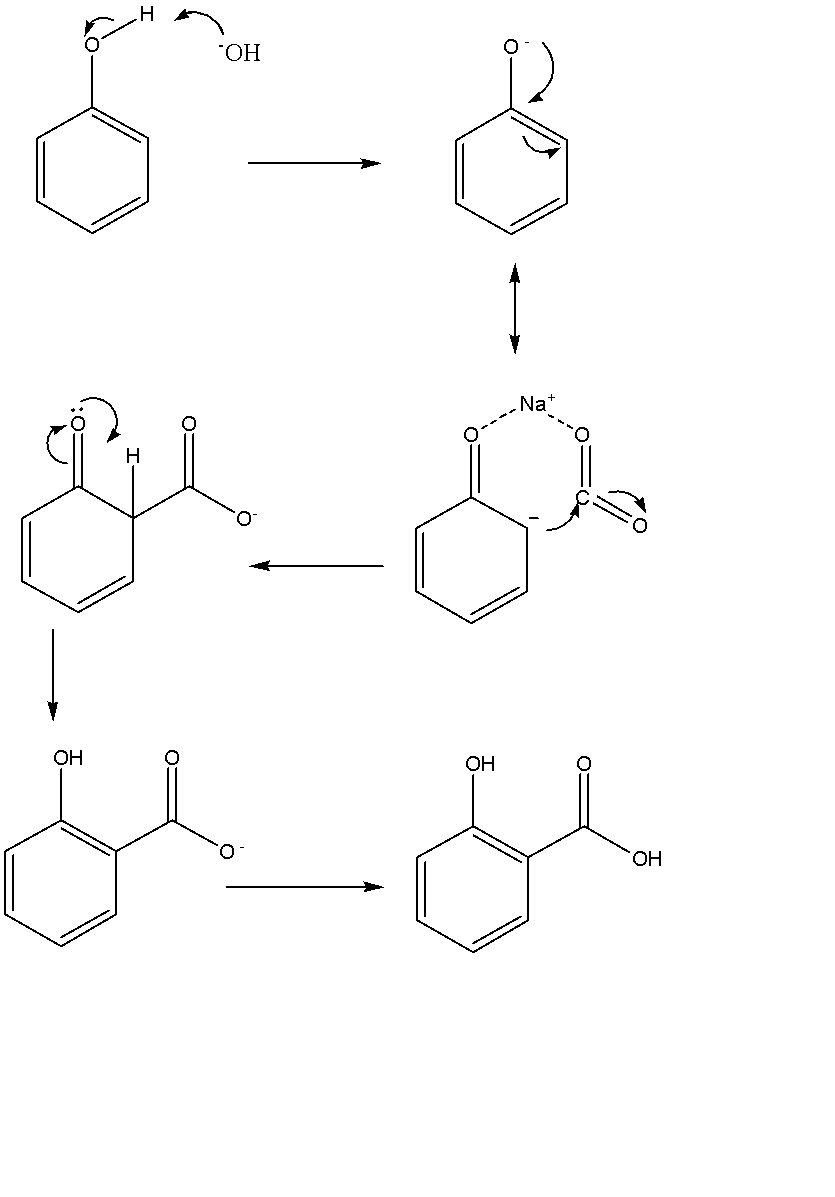
Note: It was first derived from the bark of Willow Tree. It derives its common name from a variety of sources related to it with a similar name, e.g., it is derived as a metabolic product of silicon (an alcoholic B-glycoside obtained from plants) and also it is an active metabolite produced from acetylsalicylic acid (aspirin). In nature, it occurs as clear and colourless crystals of an organic acid. The salt and ester derivatives of this compound are also widely used in organic chemistry and are known as salicylates. In plants, it occurs naturally as a growth hormone.
