Question
Question: Write the MO electronic configuration of a diatomic molecule having a bond order of three....
Write the MO electronic configuration of a diatomic molecule having a bond order of three.
Solution
MO electronic configuration means the molecular orbital electronic configuration of a molecule. As we have to write the MO electronic configuration of diatomic molecules having bond order 3 we will be dealing with nitrogen.
Complete step by step answer:
Molecular electronic configuration depends upon the molecular orbital theory. Molecular orbital theory describes the distribution of electrons in the same way as the distribution of electrons in atoms is defined by using atomic orbitals.
We will consider the molecular orbitals in molecules composed of two identical atoms such as H2 or Cl2. Such molecules are known as homonuclear diatomic molecules.
Molecular orbital theory actually uses a linear combination of atomic orbitals to represent molecular orbitals resulting from bonds between atoms. They are generally divided into three types: bonding, antibonding and non-bonding. Common bonding orbitals are sigma orbitals that are symmetric about the bond axis and π orbitals with a nodal plane along the bond axis. Antibonding orbitals are shown by the addition of asterisk (*). For example, an antibonding pi orbital may be shown as π∗.
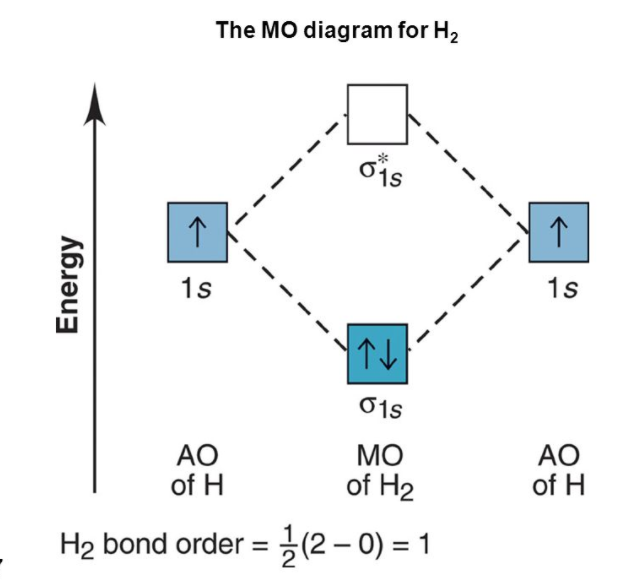
This is the representation of the molecular orbital diagram of molecules.
Now, as according to the question we will deal with the diatomic molecule with bond order 3 that is N2.
The molecular orbitals of N2 are formed by overlapping the atomic orbitals of the N atoms.
The new molecular orbitals are formed as:
1. The 1s orbitals form a bonding sigma 1s and an antibonding one.
2. the 2s orbitals form a bonding sigma 2s and are the same as an antibonding one.
3. the 2p orbitals directed along the internuclear axis form a bonding sigma 2pz and an antibonding molecular orbital.
4. the 2pxand 2pyorbitals from each atom form bonding π2pxand π2pybonding molecular orbitals and antibonding π∗2pxand π∗2py molecular orbitals.
Each Natom contributes seven electrons so we use the Aufbau principle to fill the molecular orbitals starting at lowest level.
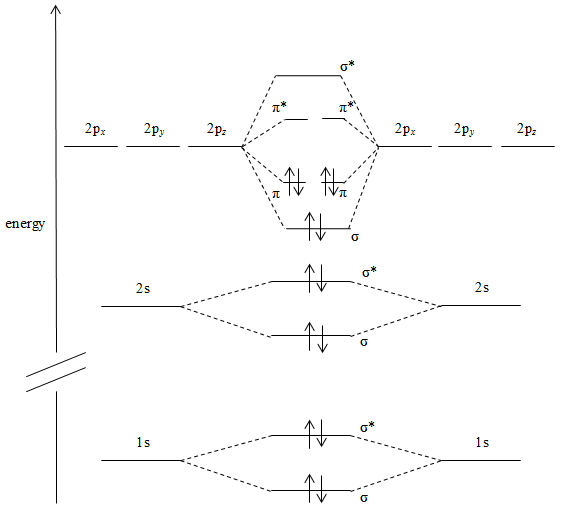
The above diagram represents the molecular electronic configuration of nitrogen atoms.
Note:
The filling of electrons should be done carefully according to the Aufbau principle. The orbitals should be filled according to that the lowest energy orbital should be filled first and so on.
