Question
Question: Write the mechanism of acid dehydration of ethanol to yield ethene....
Write the mechanism of acid dehydration of ethanol to yield ethene.
Solution
In a dehydration reaction, the water molecule is lost from the compound called alcohol and results in an unsaturated compound like alkene. Alcohol dehydration is an example of elimination reaction in which a molecule is removed which leaves multiple bonds between the carbon atoms.
Complete step by step answer:
Dehydration reaction is a type of chemical reaction in which water molecules are formed from the extraction of the components of water (hydrogen and oxygen) from a single reactant such as alcohol. When dehydration of an alcohol is performed, an alkene is produced.
We can write the basic chemical equation involved as the following:
C2H5OH→C2H4+H2O
Dehydration of ethanol takes place in presence of an acid because acid provides a proton so that oxygen from the ethanol can be attracted towards it and then the proton gets attached to it to form oxonium ion. This is the first step in the mechanism of acid dehydration of ethanol.
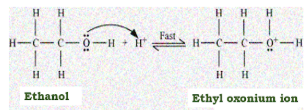
Second step involves formation of an intermediate i.e. carbocation. It is a rate determining step because it is a slow step by eliminating the water molecule. A carbocation is a stable intermediate in which a carbon atom has a positive charge and three bonds. We can also call it as carbon cation pr carbonium ion.
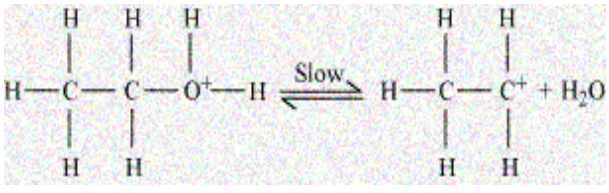
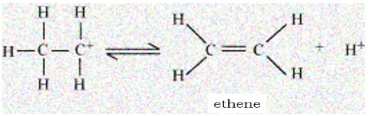
The last step is the elimination of a proton to form an ethene. The acid which was consumed in step 1 is released in step 3. After the formation of ethene, the proton is removed to shift the equilibrium in a forward direction.
Note:
The rate of dehydration depends on the stability of an intermediate i.e. carbocation. The carbocation is very much stable in case of tertiary alcohols and therefore, the rate of dehydration is highest for tertiary alcohols than the secondary and primary ones.
