Question
Question: Write the IUPAC name of the compound 
Solution
IUPAC stands for International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry. It is the world authority on the chemical nomenclature as well as terminology. Thus, IUPAC nomenclature is basically a method of naming organic compounds according to certain rules.
Complete step by step answer
IUPAC provides consistency to the names of organic compounds. It enables every compound to possess a unique name, which otherwise is not plausible with the common names. Let us have a look at the important rules that need to be followed during naming of a compound:
1. To determine the suffix of the compound name, recognise the functional group present in the compound (as listed in table).
| Functional group | Suffix |
|---|---|
| Alkane | -ane |
| alkene | -ene |
| Alkyne | -yne |
| Alcohol | -ol |
| Aldehyde | -al |
| Ketone | -one |
| Carboxylic acid | -oic acid |
| ester | -oate |
In the given compound, we have carboxylic acid and alcohol as functional groups. As we know that carboxylic acid has higher priority than alcohol, suffix in our case will be –oic acid.
2. To determine the prefix of the name of compound, identify the longest and continuous chain of carbon containing the functional group and count the number of carbon atoms in the chain as shown in table below.
| Number of carbon atoms | Prefix |
|---|---|
| 1 | Meth- |
| 2 | Eth- |
| 3 | Prop- |
| 4 | But- |
| 5 | Pent- |
| 6 | Hex- |
| 7 | Hept- |
| 8 | Oct- |
| 9 | Non- |
| 10 | Dec- |
In the given compound, the number of carbon atoms in the longest chain is 4. That means prefix in our case is but-.
3. Numbering of the carbons in the longest chain of carbon (Remember that If the organic molecule is not an alkane (and has a functional group) you have to initiate numbering such that the functional group is placed on the carbon having the lowest possible number). So, start with the carbon at the end which is closest to the functional group.
In the given compound, we will start numbering from right as shown below:
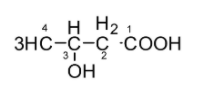
4. Check if there are any branched groups, name them and allocate the number of the carbon atom to which that group is linked. The branched groups must be mentioned before the name of the main chain in an alphabetical order.
In the given compound, alcohol on the third carbon will be treated like a branched group. It will be written as 3-hydroxy- before the main chain name.
5. Finally, combine the elements of the compound name in the specified order as: branched groups, prefix, suffix according to the functional group and its location along the longest carbon chain.
**Therefore, the given compound will have IUPAC name as: 3-hydroxybutanoic acid
Note:**
IUPAC nomenclature creates a standardized method to name the chemical compounds. Common nomenclature employs the older names for organic compounds rather than using the prefixes for the carbon chain. IUPAC nomenclature even provides certain rules for the naming of ions as well.
