Question
Question: Write the function of each of the following. (a) Seminal vesicle (b) Scutellum (c) Acrosome of...
Write the function of each of the following.
(a) Seminal vesicle
(b) Scutellum
(c) Acrosome of human sperm
Solution
Two of them are related to the human male reproductive system. One is a gland that secretes essential nutrients for the motility of sperm while another is present on the head of the sperm. Scutellum is found in monocot seeds.
Complete answer:
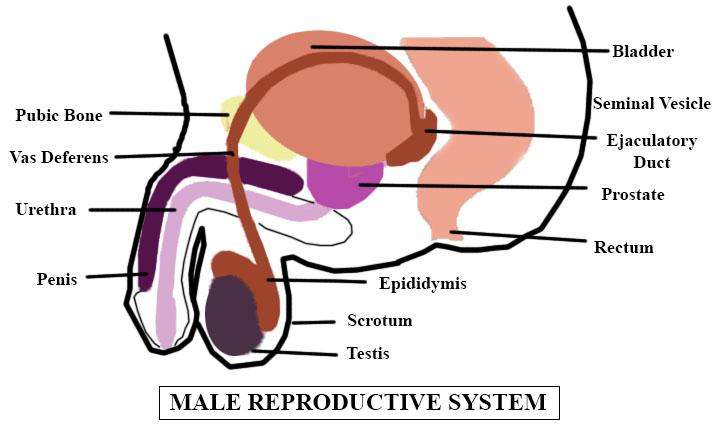
(a) Seminal vesicle: Its secretion comprises fundamental plasma which is wealthy in fructose, calcium, and enzyme.
(b) Scutellum: Papery cotyledon of the monocot seed and goes about as a section for the development of supplements from the endosperm to the creating embryo.
(c) Acrosome: During fertilization, it contains hydrolytic enzymes that help in the penetration of eggs.
The seminal vesicles secrete a big proportion of the fluid that ultimately becomes semen. The liquid is emitted from the ejaculatory channels of the vesicles into the vas deferens, where it turns out to be important for semen. This at that point goes through the urethra, where it's discharged during a male sexual reaction. Supplements help uphold sperm until fertilization happens; prostaglandins may likewise help by softening mucous of the cervix, and by causing reverse withdrawals of parts of the female reproductive tract, for example, the fallopian tubes, to ensure that sperm are more averse to be removed.
The scutellum additionally can request the proportionality from a thin cotyledon in monocots (particularly individuals from the grass family). It is very thin with a high area and serves to soak up nutrients from the endosperm during germination.
The acrosome of human sperm is a cap-like structure derived from the Golgi apparatus.
Note:
Inflammation of the seminal vesicles is named seminal vesiculitis, most frequently is thanks to bacterial infection as a result of a sexually transmitted disease or following a surgery. Seminal vesiculitis can cause pain inside the lower mid-region, scrotum, penis, or peritoneum, painful ejaculation, and blood inside the semen. It is typically treated with antimicrobials, despite the fact that may require surgical drainage in complicated cases.
