Question
Question: Write the electron dot structure of \( Na \) and \( Cl \) atoms, how do these atoms form a chemical ...
Write the electron dot structure of Na and Cl atoms, how do these atoms form a chemical bond? Name the type of bond so formed. Why does a compound so form have a high melting point?
Solution
In order to answer this question, we should know the electronic configuration of sodium ( Na ) and chlorine ( Cl ). From this, we come to know about their valence electrons. We also know that Sodium chloride ( NaCl ) forms an ionic compound.
Complete Step By Step Answer:
Let us understand the solution in complete detail.
The atomic number of sodium ( Na ) is 11 . The valence electrons of sodium is 1 .
On the other hand, the atomic number of chlorine ( Cl ) is 17 . The valence electrons of chlorine is 7 .
The electron dot structure of sodium and chlorine is as follows:
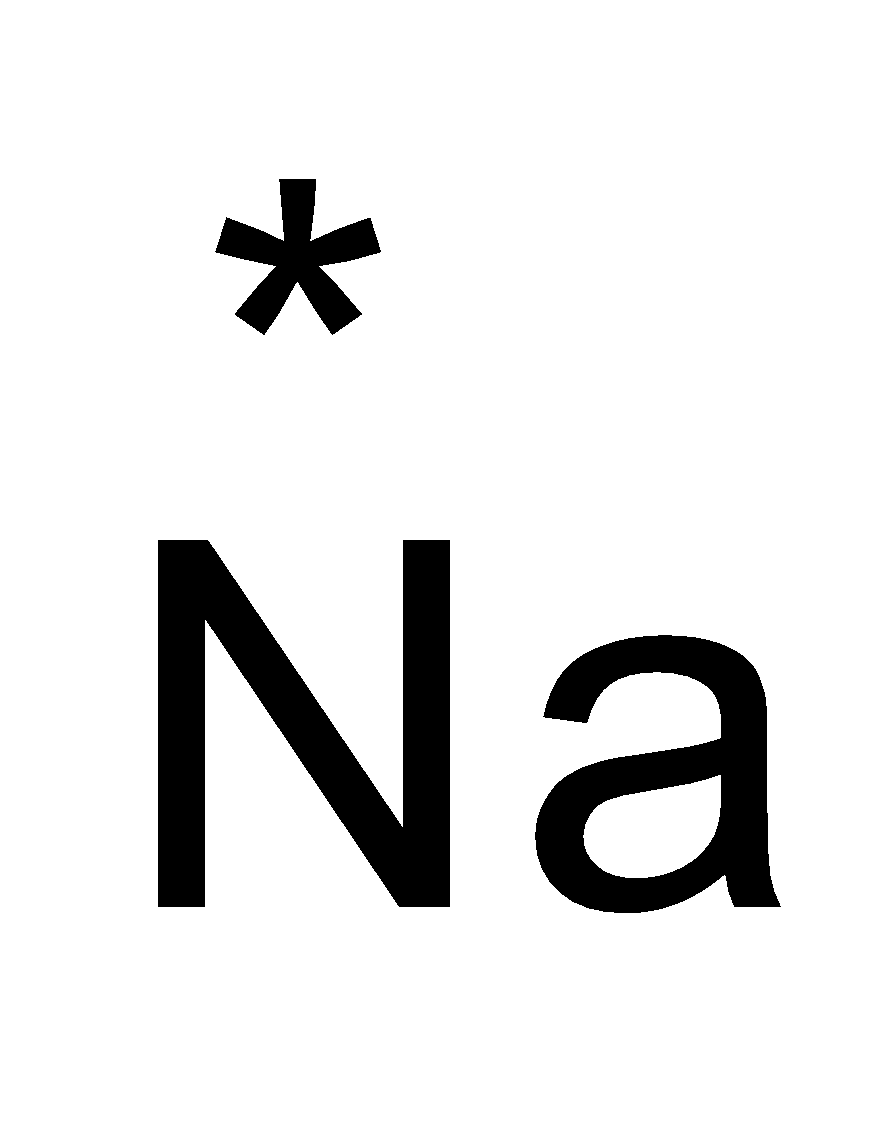
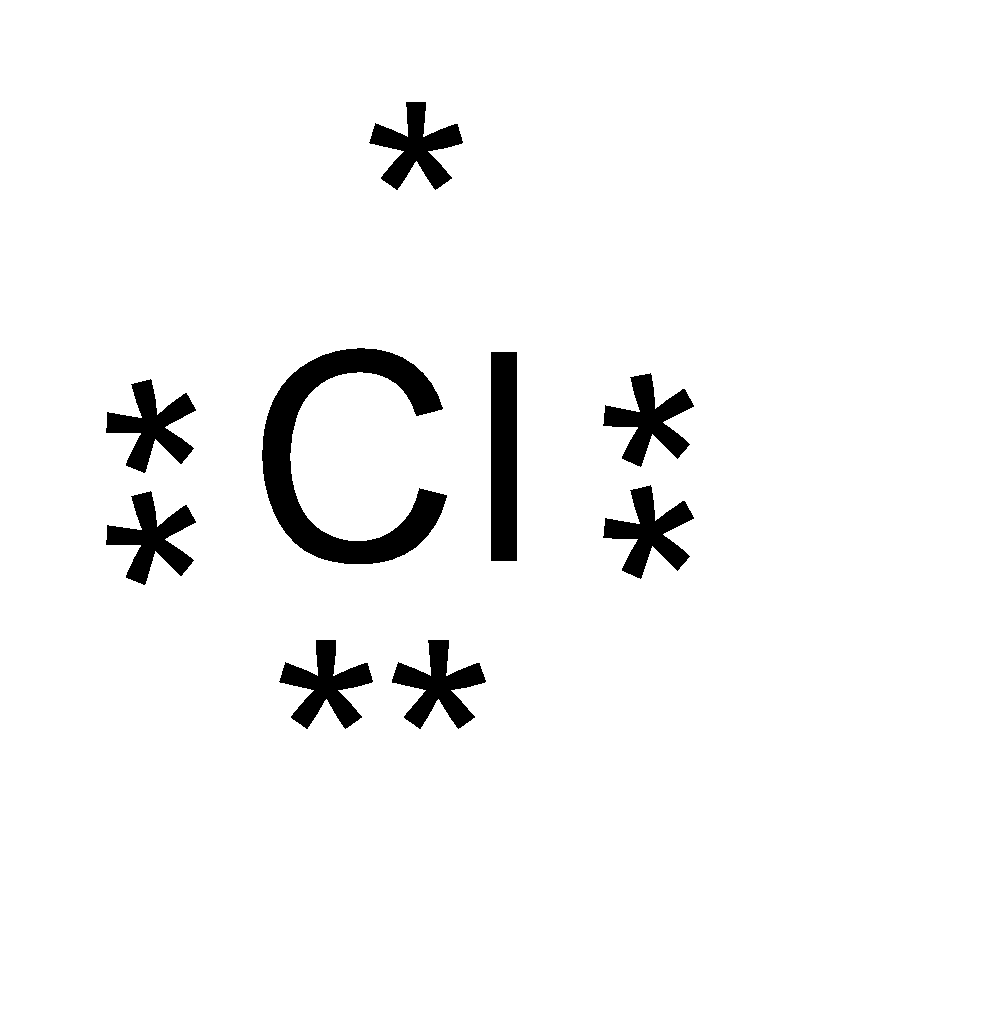
The chemical bond formed by Na and Cl atoms is due to the complete transference of electrons from sodium to chlorine atoms. Hence, we can say that it forms an ionic bond.
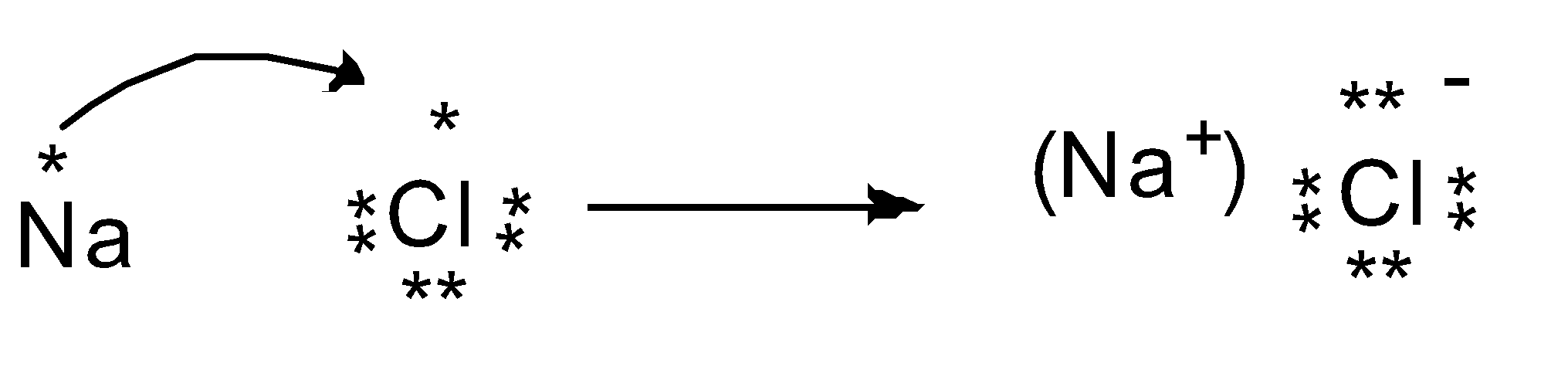
In order to attain a stable and completely filled valence shell, Na has to lose the outermost electron and Cl acquires one more electron to complete the valence shell.
When sodium ( Na ) loses one electron, it becomes Na+ cation and chlorine ( Cl ) accepts one electron and becomes an anion ( Cl− ). The oppositely charged ions that are ions attract each other and form NaCl . They are held together by electrostatic forces of attraction, so the bond existing between them is called an ionic bond.
Also, ionic bonds have high melting points because they have strong forces of attraction due to which it requires a large amount of energy to break the bond. Hence, ionic compounds have melting points.
Note:
Remember the electrostatic forces of attraction which hold the two oppositely charged ions together is called the ionic bond. They are considered as the strongest bond. It is also called an electrovalent bond.
