Question
Question: Write the decreasing order of stability of following compounds. \[(i)\]  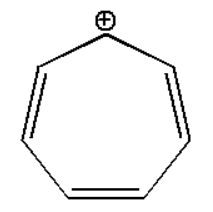
(ii) CH2=CH−+CH2
(iii) C6H5−+CH2
(iv) CH3−+CH−CH3
Solution
The stability of compounds depends on the delocalization of electrons. In resonance the electrons are delocalized over the entire structure and thus its stability is most. We will analyze stability in each compound and then predict the stability of compounds.
Complete answer:
(i):
The compound is stabilized due to resonance effect which can be shown as:
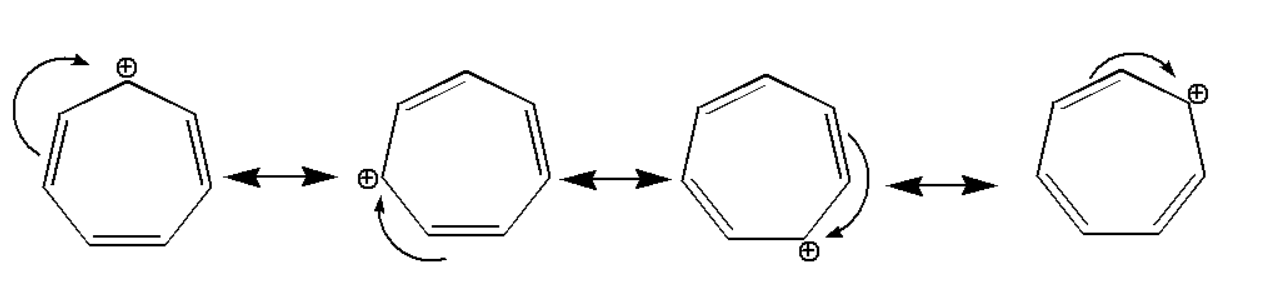
Hence we can observe that the above compound is stabilized by the resonance effect. The compound which is stabilized by resonance effect is most stabilized compound.(ii) CH2=CH−+CH2 :
Here also the above organic compound is stabilized due to resonance effect which can be shown as:
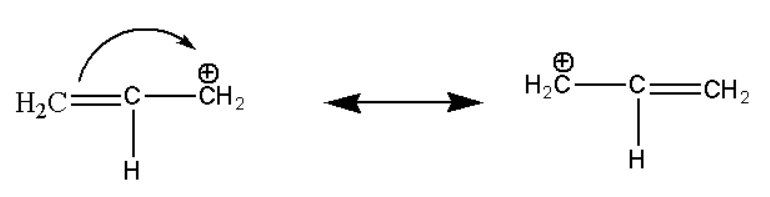
Hence the ethane molecule is stabilized by resonance effect but its stability is less as compared to stability of a ring.
(iii) C6H5−+CH2
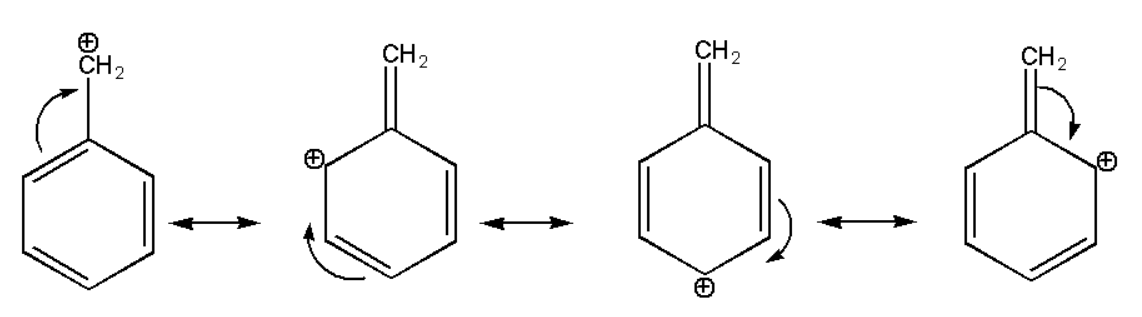
The above structure also gets stabilized due to the resonance effect of pi bonds but here the aromaticity of the benzene ring gets distorted. But its stability is also more than aliphatic compounds.
(iv) CH3−+CH−CH3
The above compound will be stabilized by the (+I) effect of the methyl group attached at both sides of carbocation. The two degree carbocation is more stable than one degree carbocation.
Since we know that the compound stabilized by the resonance effect has more stability than the compound stabilized by (+I) effect and hyperconjugation effect. Thus the order of stability will be as: (i)≻(iii)≻(ii)≻(iv).
Note:
It must be noted that a ring stabilized by resonance effect is much more stabilized than an aliphatic compound stabilized by resonance. Also due to presence of methyl group on benzene it disturbs the aromaticity of the benzene ring. The greater the delocalization of electrons, the more stable the compound will be.
