Question
Question: Write the coordination number and oxidation state of platinum in the complex \(\left[ {{{Pt}}{{\left...
Write the coordination number and oxidation state of platinum in the complex [Pt(en)2Cl2].
Solution
Complex compounds are the compounds having complex ions. The given compound is an example of a complex compound. Coordination number defines the number of atoms or ligands which are directly bonded to the central metal ion or atom. The oxidation state defines the charge of the atom.
Complete step by step solution:
The structure of the given coordination compound is given below:
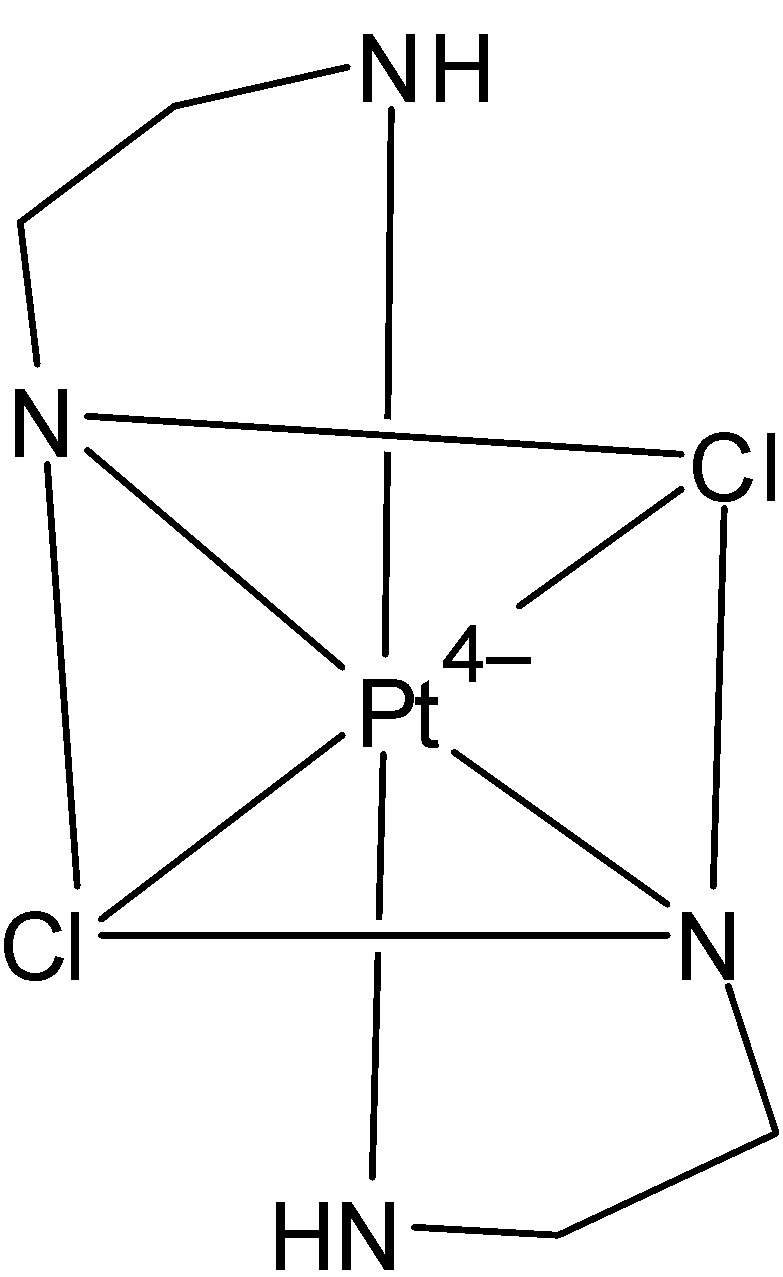
In the given compound, en represents the compound ethylene diamine. Its chemical formula is NH2CH2CH2NH2. Its structure is given below:
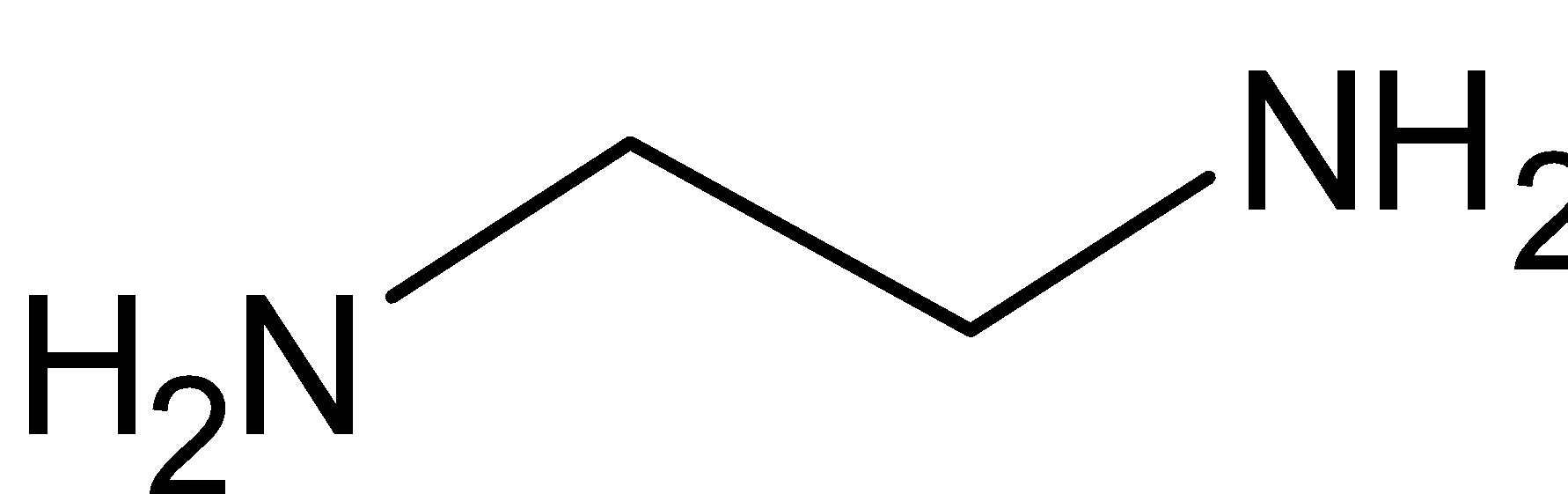
It is a bidentate ligand, i.e. it has two points of attachment or it can coordinate to metal at two points of the complex. Ethylene diamine has two nitrogen atoms which have two lone pairs of electrons. This is donated to the central metal ion. Also, the complex has two ethylene diamine ligands. Thus it donates a total of four electrons. And chlorine donates one electron each, so a total of two electrons from chlorine. Thus a total of six electrons are donated. So the coordination number of platinum is 6.
Now let’s find the oxidation state of platinum. Oxidations state can be determined by knowing the charge on the complex ion and the ligand.
So let’s consider the oxidation state of platinum as x and the charge on ethylene diamine is 0 since it is a neutral ligand. And charge on chlorine ligands is −1. Combining all these values, we get
x+0+−2=0⇔x=+2.
Thus the oxidation number or oxidation state of platinum metal is +2 and its coordination number is 6.
Note:
According to Werner’s theory, the primary valency is equivalent to the oxidation state while the secondary valency is equivalent to the coordination number. Primary valency can be varied. While secondary valency, for a certain oxidation, is fixed.
