Question
Question: Write the characteristics of the image formed by an object at the center of the curvature of a conca...
Write the characteristics of the image formed by an object at the center of the curvature of a concave mirror.
Solution
There are many types of image formation possible for different positions of an object according to the mirror. The different positions of the object can be at focus, between the focus and mirror, between the focus and center of curvature, at the center of curvature, and beyond the center of curvature. In a concave mirror, the image will be real. And, here the other characteristics of the image can be found by simply drawing the diagram of image formation in the correct process.
Complete step-by-step solution:
First, the following figure is drawn according to the position of the object in front of a concave mirror and forms the image maintaining the process of the image-formation of an extended object by spherical mirrors.
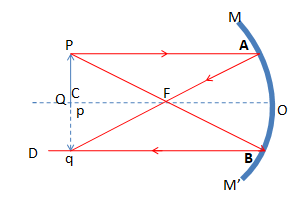
The object PQ is placed at the center of curvature of the concave mirrorC . from the point Pa ray PA parallel to the main axis, incidences on the point A , and after reflection goes along the path AF. Another ray PB , incidences on point B touching the point F and after reflection goes along the path BD (parallel to the main axis).
The reflected raysAF and BD intersect each other at a point p. Hence, at the point p the real image of the point P is formed. Now, a perpendicular line pq is drawn from p at the main axis. pq is the image ofPQ .
Here, the object and the image are placed at the same place i.e at the center of curvature. The image is real, inverted and of the same size as the object.
Note: The comparison between Real and Virtual images formed by the spherical mirrors:
Characteristics of real image:
The image is formed at the same side of the mirror at which the object is placed.
The real image is always inverted.
Characteristics of virtual image:
The image is formed at the opposite side of the mirror at which the object is placed.
The virtual image is always upright.
The shape of the image is smaller than or equal to the object for the concave mirror and bigger than or equal to the object for the convex mirror.
