Question
Question: Write the angles of incidence at the faces AB and AC of the prism. 
(A) At the face AB, i=60∘and at the face AC, i=0∘.
(B) At the face AB, i=0∘and at the face AC, i=0∘.
(C) At the face AB, i=60∘and at the face AC, i=60∘.
(D) At the face AB, i=0∘and at the face AC, i=60∘.
Solution
Hint : The angle of incidence is the angle between incident ray and normal. The total internal angle of a triangle is180∘. So the complete ray diagram will give us the answer.
Complete step by step answer
A ray that strikes the surface separating the two optical media is called the incident ray. The angle which the incident ray makes with the normal at the point of incidence is called angle of incidence. The angle which the reflected ray makes with the normal at the point of incidence is called the angle of reflection.
Furthermore, the incident ray, reflected ray and a line perpendicular to the wall at the contact point lie in the same plane. We can calculate the amount of refraction using Snell’s law, which shows the relationship between the incident light and refracted light.
In the diagram, the ray of light approaching the prism is known as the incident ray (labelled PQ in the diagram). At the point of incidence where the ray strikes the prism, a line can be drawn perpendicular to the surface of the prism. This line is known as a normal line, since it is drawn normal to the surface. The normal line divides the angle between the incident ray and the reflected ray into two equal angles. The angle between the incident ray and the normal is known as the angle of incidence.
As we can see from the image given, a ray of light PQ is incident normally on the face AB of an equilateral glass prism. Since the incident ray and the normal of surface AB coincides, the angle formed by the incident ray with the normal is given by i=0∘, where i is the angle of incidence.
Since the prism is equilateral, the angles of the prism are all 60∘. The angle between the ray and the surface AB is 0∘ (total internal angle of a triangle is 180∘) and hence the angle the ray makes with the normal to surface AC is 60∘which is the angle of incidence.
So the correct answer will be option D.
Note
The complete ray diagram showing the emergence of the ray PQ as ST is shown in the figure below.
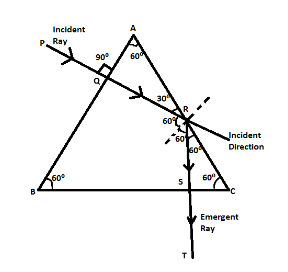
At the face AB, the ray suffers refraction. At the face AC, it suffers total internal reflection since the critical angle of a glass prism is 42∘, and the angle of incidence is greater than 42∘. Finally at the face BC it is again refracted. The ray is refracted whenever it passes from one medium to another.
