Question
Question: Write IUPAC names of the products obtained by the ozonolysis of the following compounds? i) Pent\(...
Write IUPAC names of the products obtained by the ozonolysis of the following compounds?
i) Pent - 2 - ene
ii) 3,4 - Dimethylhept - 3 - ene
iii) 2 - Ethyl But - 1 - ene
iv) 1 - Phenylbut - 1 - ene
Solution
Ozonolysis reaction has ozone as the main reagent. This reaction results in the formation of the carbonyl group at the carbon atoms at the double bond. Aldehyde and ketones are produced depending on the reactant molecule. One can apply this concept to form the products of the above reactants.
Complete step by step answer:
- First of all we will understand the reaction of ozonolysis. The ozonolysis reaction is the addition of oxygen atom to the carbon-carbon double bond which means there is the formation of a carbon-oxygen double bond which will give either aldehyde or ketone.
- Now let’s analyze each structure and see the products and then determine their IUPAC names,
i) Pent - 2 - ene:
CH3−CH=CH−CH2−CH3O3OzonolysisCH3−(CO)−H+H−(CO)−CH2−CH3
In the above reaction when Pent - 2 - ene is undergoes an ozonolysis reaction then there is the formation of two aldehydes as acetaldehyde and propionaldehyde which have IUPAC names as Ethanal and Propanal respectively.
ii) 3,4 - Dimethylhept - 3 - ene:
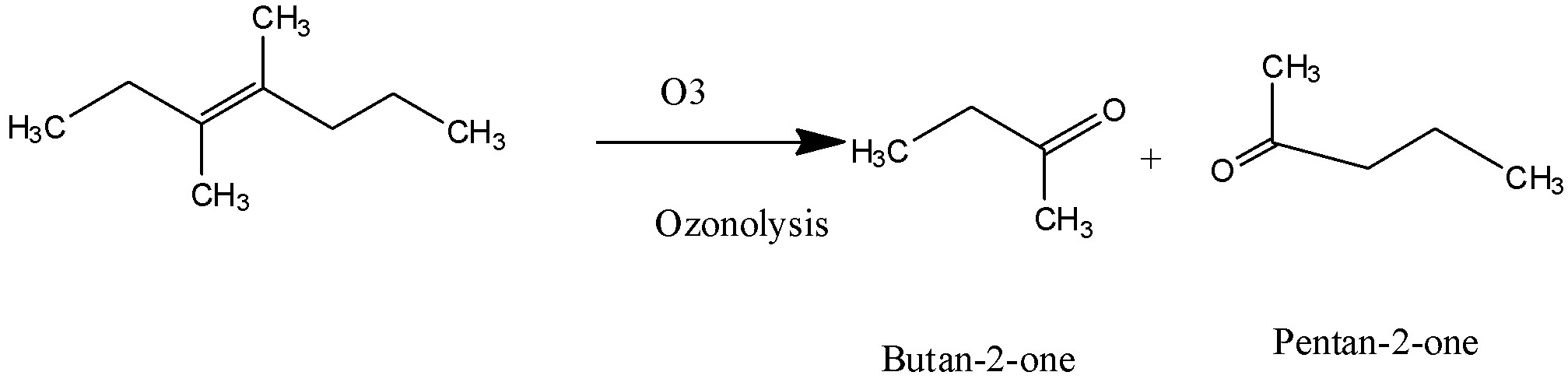
In the above reaction when 3,4 - Dimethylhept - 3 - ene undergoes an ozonolysis reaction and yields products which have IUPAC names as Butan-2-one and Pentan-2-one.
iii) 2 - Ethyl But - 1 - ene:
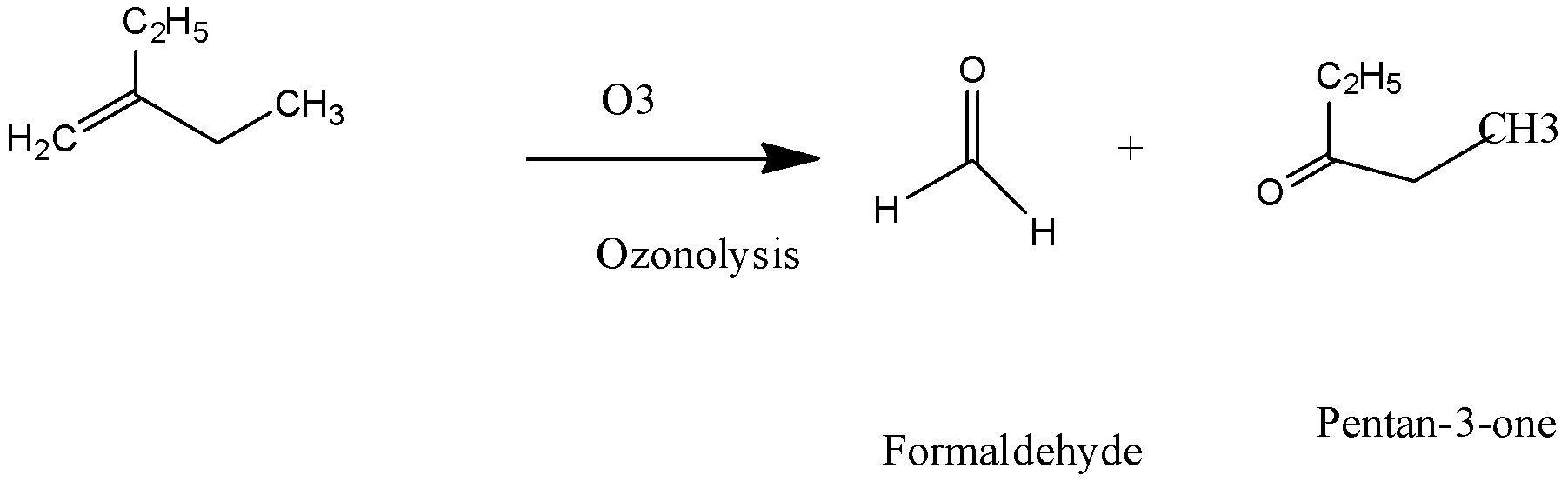
In the above reaction when 2 - Ethyl But - 1 - ene undergoes ozonolysis reaction and yields products which have IUPAC names as formaldehyde and pentan-3-one.
iv) 1 - Phenylbut - 1 - ene:
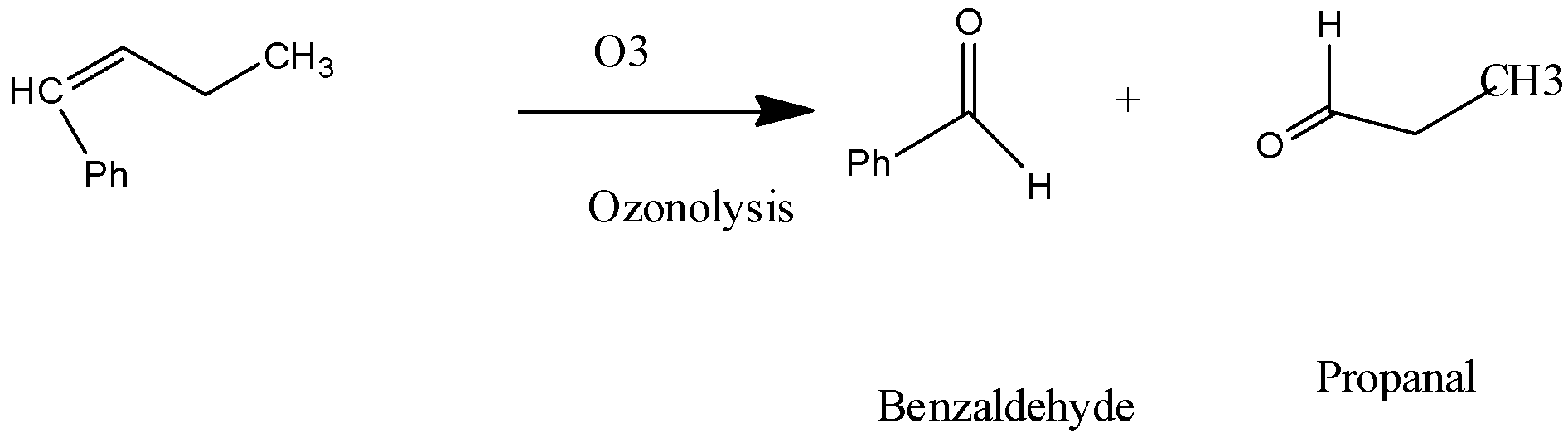
In the above reaction when 1 - Phenylbut - 1 - ene undergoes an ozonolysis reaction and yields products which has IUPAC names as benzaldehyde and propanal.
Note:
The reaction name Ozonolysis has -lysis suffix which means breaking of bonds in presence of ozone. Ozonolysis of double bonds gives aldehydes and ketone depending on the substituents present on carbon-carbon double bonds. This is a type of oxidation reaction where the addition of oxygen takes place.
