Question
Question: Write down the steps which involve the transformation of 1-bromopropane to 2-bromopropane....
Write down the steps which involve the transformation of 1-bromopropane to 2-bromopropane.
Solution
Hint: The first step involves the dehydrohalogenation of 1-bromopropane before adding the bromine atom being added to the second carbon atom due to a specific method of addition. Now, write down all of these steps in order for the transformation of this reaction.
Step-by-Step Solution:
Let us first look at what the processes of dehydrohalogenation of haloalkanes and Markovnikov’s addition really mean before moving on to how they can be applied to this reaction.
Dehydrohalogenation is an elimination reaction that eliminates (removes) a hydrogen halide from a substrate. The reaction is usually associated with the synthesis of alkenes, but it has wider applications.
When treated with a strong base like alcoholic KOH, many alkyl chlorides convert to corresponding alkene. It is also called a β-elimination reaction and is a type of elimination reaction. Some examples are shown below:
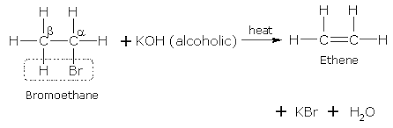
Let us now apply this to 1-bromopropane.
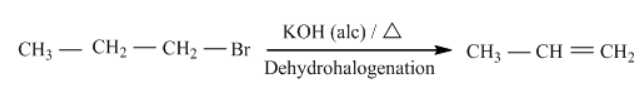
Now, let us look into the next step, which is Markovnikov’s addition.
Markovnikov's rule (Markovnikov addition) is an addition reaction of a protic acid HX (hydrogen chloride, hydrogen bromide, or hydrogen iodide) to an alkene or alkyne, the hydrogen atom of HX becomes bonded to the carbon atom that had the greatest number of hydrogen atoms in the starting alkene or alkyne.
Applying this to the obtained propene, we would then obtain 2-bromopropane as the major product and 1-bromopropane as the minor product.
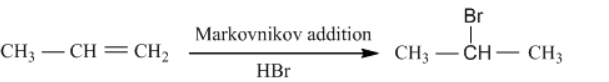
Note: The main difference between Markovnikov and Anti Markovnikov rule is that Markovnikov rule indicates that hydrogen atoms in an addition reaction are attached to the carbon atom with more hydrogen substitutes whereas Anti Markovnikov rule indicates that hydrogen atoms are attached to the carbon atom with the least hydrogen substitutes. Be very careful of this difference.
