Question
Question: Write down all possible functional isomers of \( {C_4}{H_8}O \) ?...
Write down all possible functional isomers of C4H8O ?
Solution
In the question, it is asked to draw the possible functional isomers of C4H8O . The isomers are compounds which have the same chemical formula but they have different structural formulas. The phenomenon is termed as isomerism.
Complete answer:
We know that the compounds which are represented by the same molecular formula but arranged in different structures are called isomers and this phenomenon is called isomerism. In other words, we can say that the compounds which show isomerism phenomena are called isomers.
Isomers not only have different structures but they possess different physical and chemical properties as well. Isomerism can be classified into two categories i.e. structural isomerism and stereoisomerism.
Structural isomerism- The compounds which have differences in their structure come in the category of structural isomerism. The structural isomerism is further subdivided into chain, functional, positional, metamerism, tautomerism and ring- chain isomerism.
Stereoisomerism- The compounds which have differences in their spatial arrangement of atoms comes in the category of stereoisomerism. The stereoisomerism is further subdivided into two parts i.e. geometrical isomerism and optical isomerism.
Here, in the question we are asked to draw the functional isomerism. Let’s first understand functional isomerism.
Functional isomerism- The compounds which have the same chemical formula, but have different functional groups are called functional isomers and this phenomenon is called functional isomerism.
For the above chemical formula C4H8O there are a total of eight possible functional groups which include aldehyde, ketone, alcohol and ether.
The functional isomers possible from C4H8O are as follows:
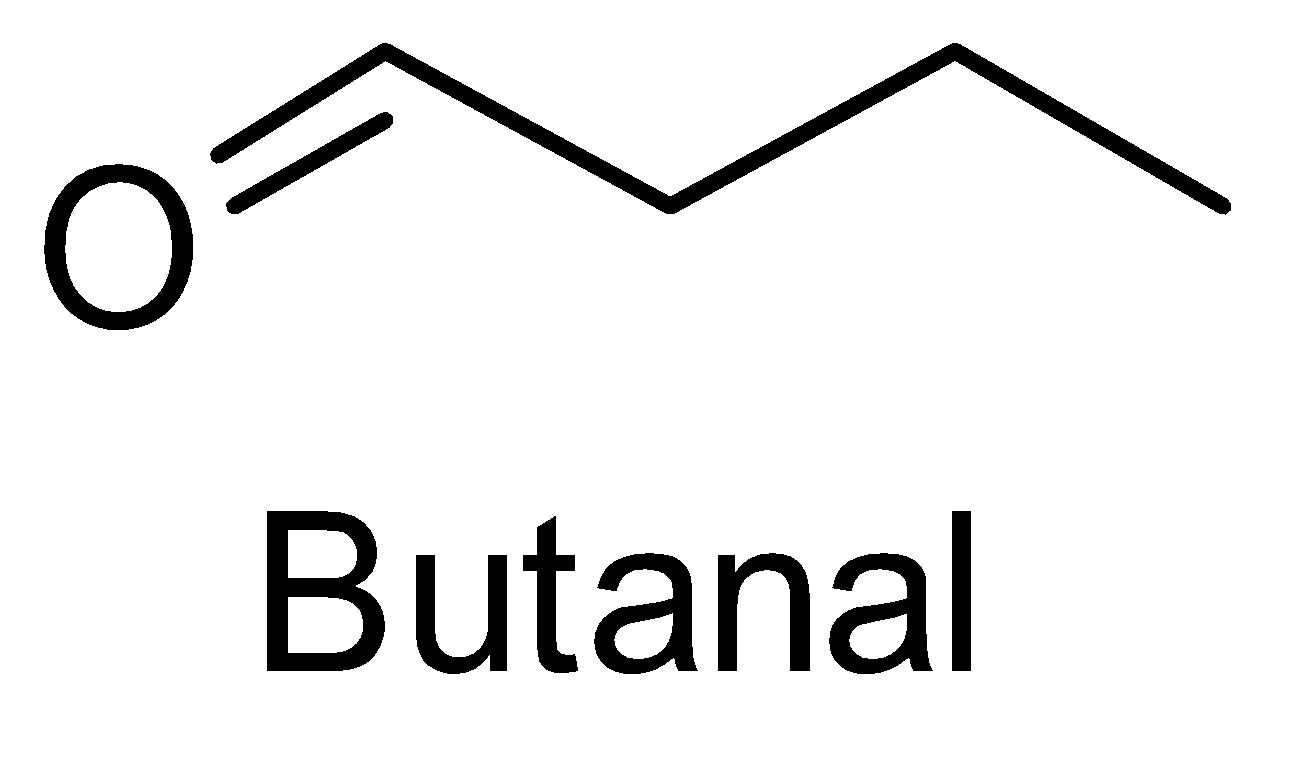
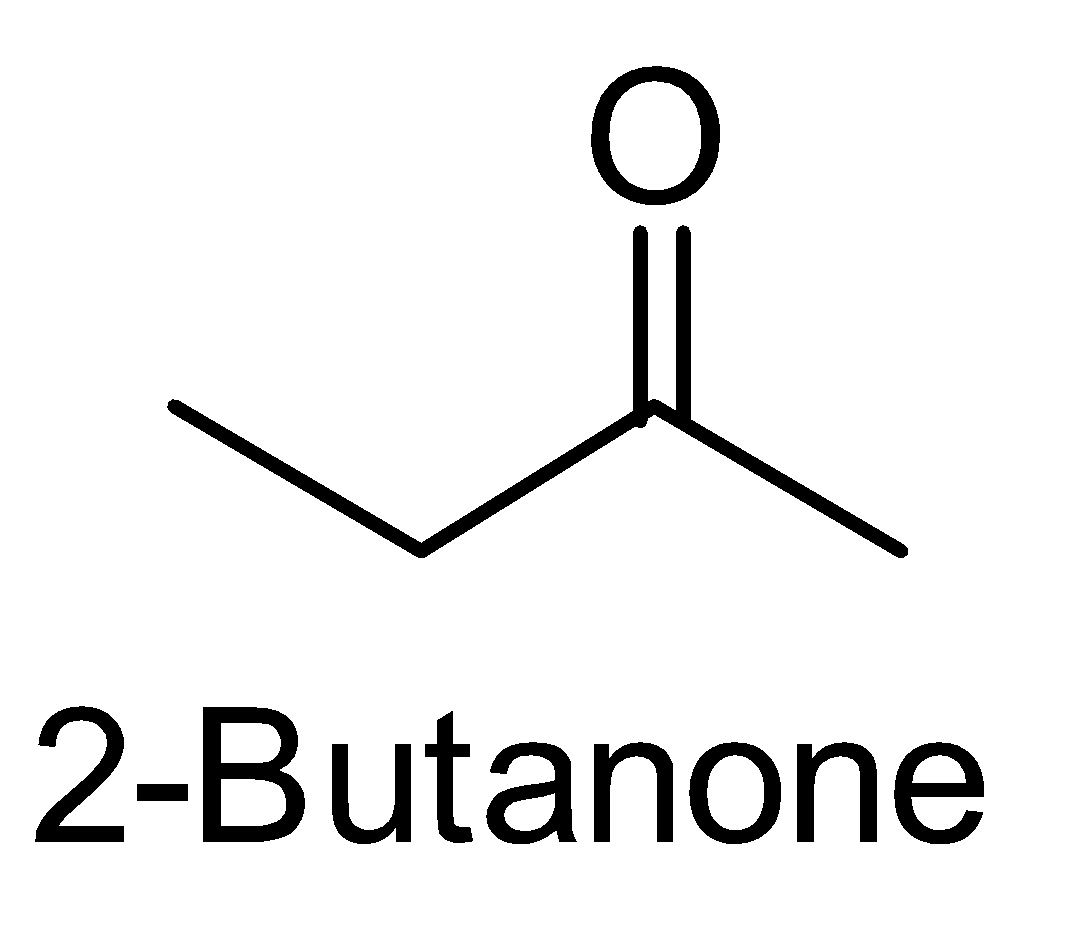
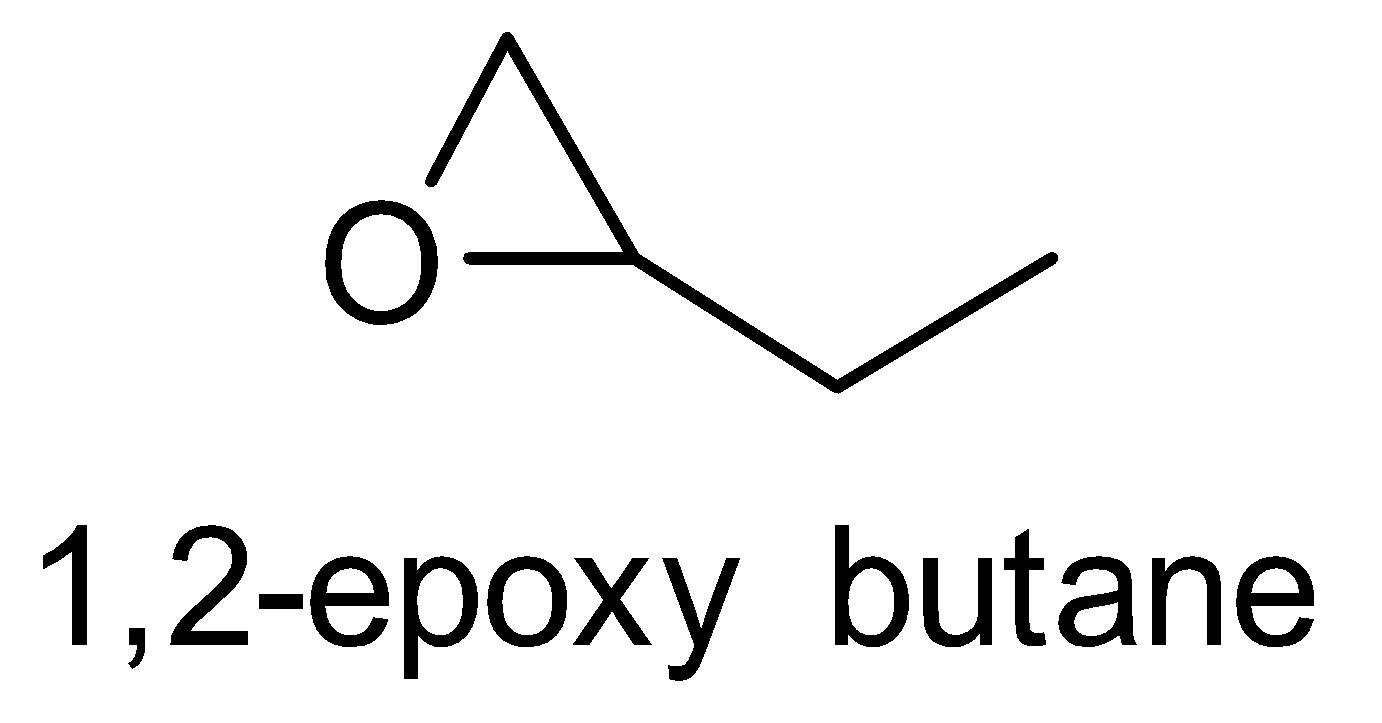
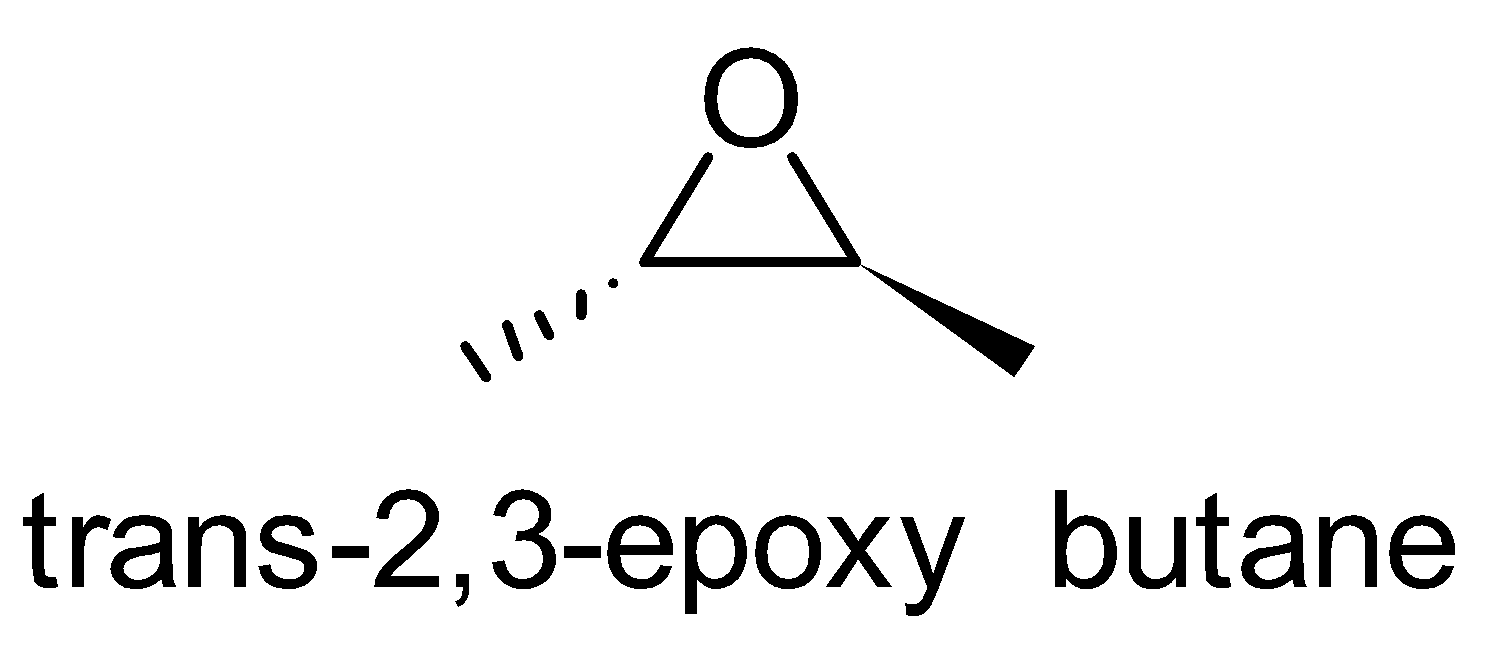
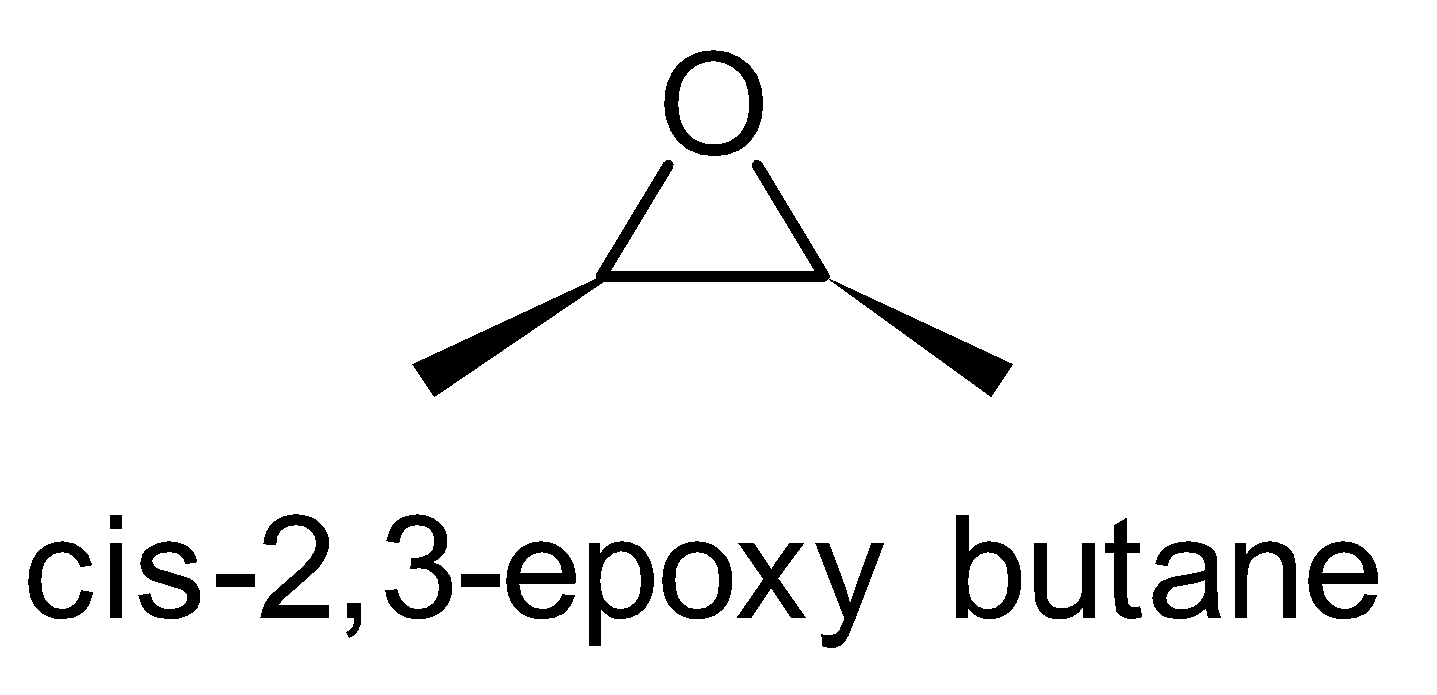
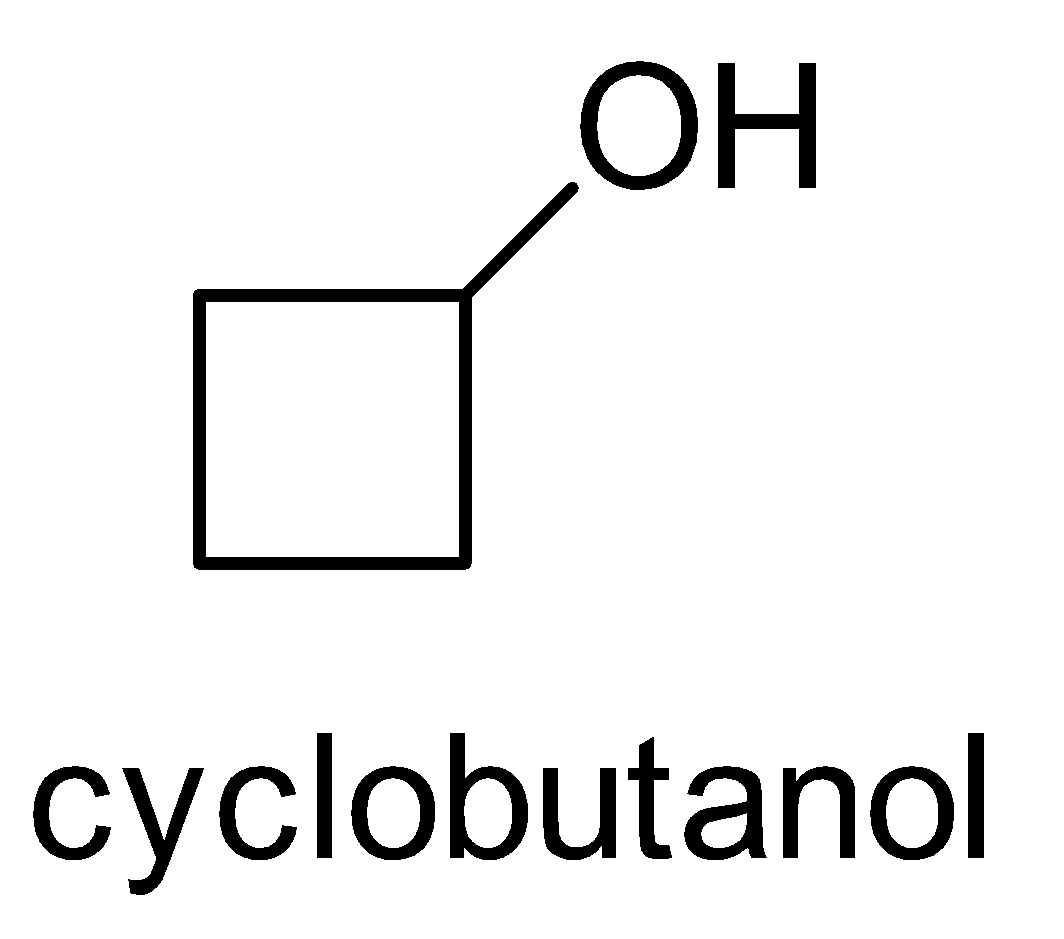
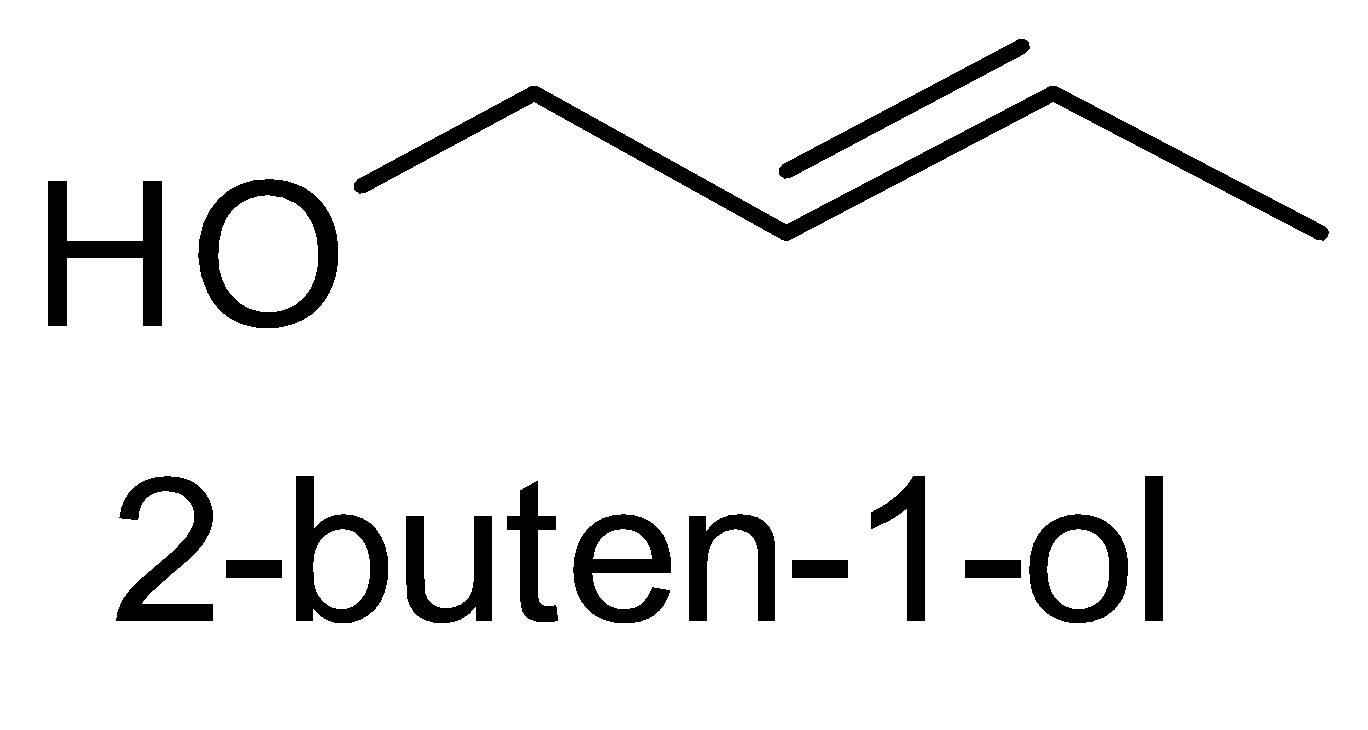
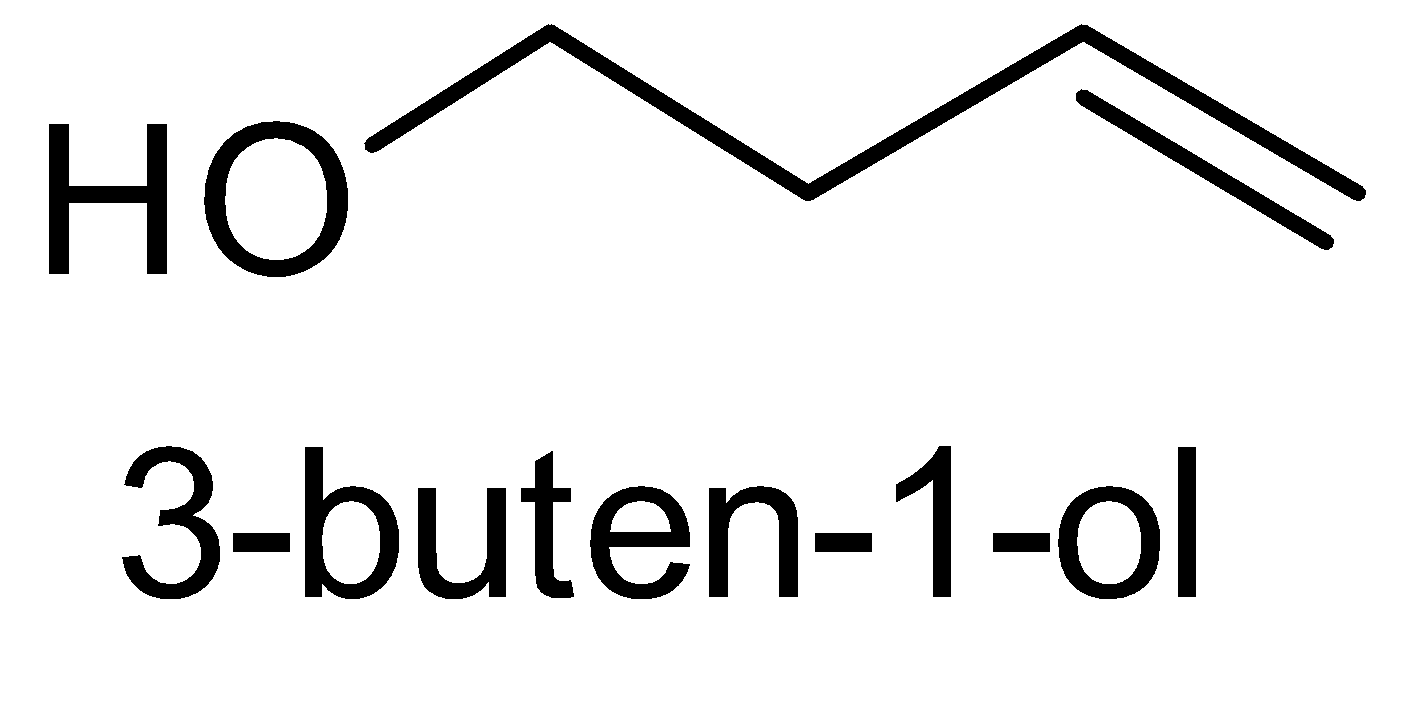
Hence there are eight possible functional isomers of C4H8O
Note:
Functional isomers are the sub part of structural isomers. Functional isomerism occurs when there is difference in the arrangement of functional groups. The repeated structural formula of the same compound does not count as isomers.
