Question
Question: Write definition of electric field intensity. Obtain an expression for electric force and electric...
Write definition of electric field intensity.
Obtain an expression for electric force and electric pressure on the surcharge of a charged conductor.
Draw necessary diagrams.
Solution
- Hint: Electric field intensity can be determined by finding the strength of the electric field at that point. For calculating electric force and electric pressure, we will use the relation between electric field vectors and the surface density of a conductor.
Complete step-by-step solution -
Electric field intensity is expressed as the strength of an electric field at any point. This value is equal to the electric force per unit charge experienced by a test charge placed at that point.
The unit of electric field intensity is metervoltorCoulombNewton.
Every element of a charged conductor experiences some normal mechanical force. This force is the result of repulsive force from a similar charge present on the rest of the surface of the conductor.
Let’s consider a small element ds on the surface of a charge conductor. If σis the surface density and the charge carried by the element ds is dq.
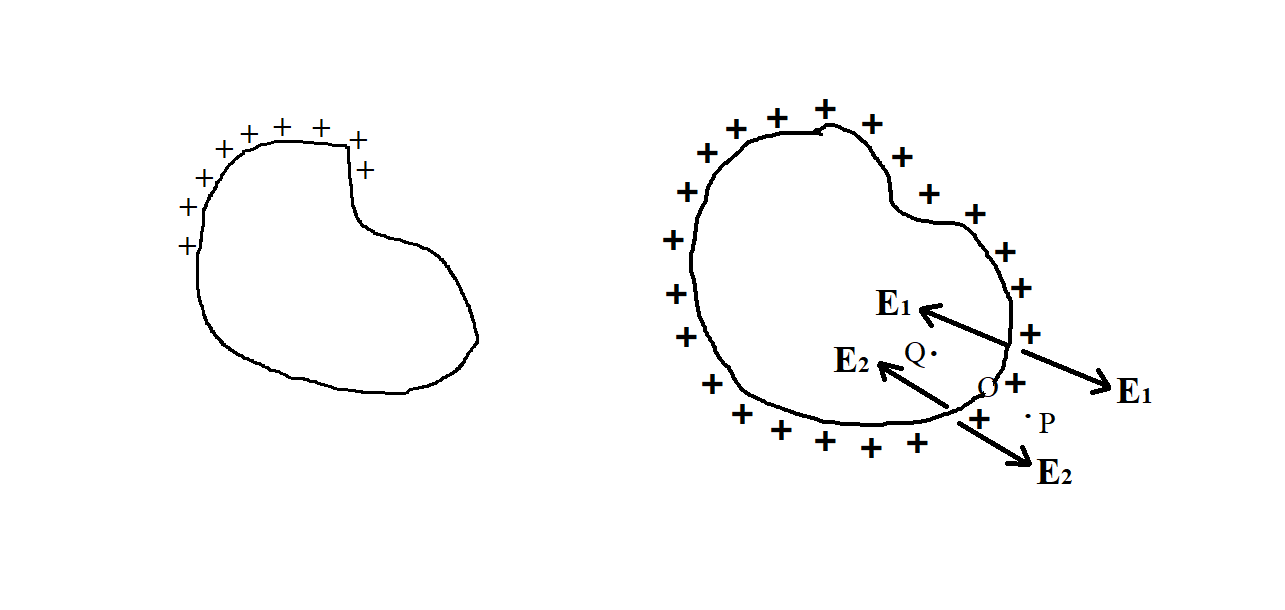
Consider a point P just outside the surface near the conductor near the element ds. The electric field intensity at a point is given by:
E=εoσ
The direction of the intensity is normally outwards.
The intensity consists of two components E1+E2=εoσ
Now consider a point Q inside the conductor. The electric field vectorsE1andE2at this point are oppositely directed. The electric field intensity inside a charged conductor is zero.
E1−E2=0E1=E2
As E1+E2=εoσ
For point inside charged conductor E1=E2
Therefore, 2E2=εoσ
E2=2εoσ
E2 is the electric field due to the charge on the rest of the conductor. Therefore, repulsive force experienced by element ds carrying charge dq is given by:
f=E2⋅dq
F=2εoσdq
f=2εoσ×σ⋅ds
F=2εoσ2ds
The electric pressure on surface ds will be
pressure = areaforce
pressure =ds 2εoσ2ds
P=2εoσ2Nm−2
Electric force experienced by ds on a charged conductor is, F=2εoσ2dq
Electric pressure on ds of a charged conductor is, P=2εoσ2Nm−2
Note: While calculating the electric field at any point, direction of the vector should be considered very carefully. Also remember that the electric field inside a conductor is zero because free charges in a conductor reside only on the surface.
