Question
Question: Write chemical reaction of isobutylene which undergoes anti-Markovnikov addition of water to carbon-...
Write chemical reaction of isobutylene which undergoes anti-Markovnikov addition of water to carbon-carbon double bond.
Solution
According to the Markovnikov's rule of addition, when a protic acid (HX) is added to an alkene, the proton is bonded to the less alkyl substituted carbon atom. So, anti-Markovnikov's addition would mean that the protic acid is added to the more alkyl-substituted carbon atom. Using this rule, we can predict the chemical reaction of isobutylene which undergoes anti-Markovnikov addition of water to carbon-carbon double bonds.
Complete step by step solution:
Isobutylene is a hydrocarbon having formula (CH3)2C=CH2. It is also known as 2-methylpropene, and is an isomer form of butylene.
Isobutylene has a four-branched alkene structure:
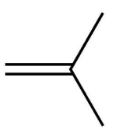
Now, when water is added, in the presence of a strong acid catalyst, to an alkene, alcohols or hydroxy-alkanes are formed.
We know that according to the Markovnikov's rule of addition, when water is added to an alkene in the presence of a strong acid, the standard carbocation mechanism is followed and the H+ ion from water (H2O) bonds with the carbon atom which is less alkyl-substituted or has more carbon-hydrogen bonds, while the hydroxyl group (OH−) bonds with the carbon atom which is more alkyl-substituted or has more carbon-carbon bonds.
So, when a reaction follows anti-Markovnikov's rule of addition, the H+ ion from water (H2O) bonds with the carbon atom which is more alkyl-substituted or has less carbon-hydrogen bonds.
By using this information, we can write chemical reaction of isobutylene undergoing anti-Markovnikov addition of water as follows:
Step 1: First we identify the carbon with least number of C-H bonds, or the most alkyl-substituted carbon.

Step 2: We use borane (BH3) and tetrahydrofuran (THF) as a catalyst, during the addition of water to isobutylene. So, the hydrogen atom will be added to the carbon identified in step 1, according to the anti-Markovnikov's rule.
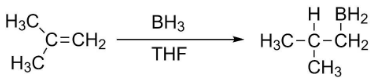
Step 3: Finally, addition of water will take place to form isobutyl alcohol.
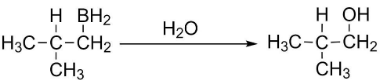
So, when isobutylene goes under anti-Markovnikov's addition of water to C=C, isobutyl alcohol ((CH3)2−CH−CH2−OH) is formed.
Note: Anti-Markovnikov's rule is also known as the Kharasch effect. It is important to note that both Markovnikov's rule and Anti-Markovnikov's rule are applicable only when there is presence of unsaturation and the alkene is asymmetrical in nature.
