Question
Question: Write a short note on immunoglobulin....
Write a short note on immunoglobulin.
Solution
Immunoglobulin M (IgM) is an antigen receptor on B cells and the first antibody produced in an immune response.
Complete answer: Immunoglobulins are glycoprotein molecules that are produced by plasma cells in response to an immunogen and which function as antibodies.
1. Immunoglobulins bind specifically to one or a few closely related antigens. Each immunoglobulin actually binds to a specific antigenic determinant.
2. Antigen binding by antibodies is the primary function of antibodies and can result in the protection of the host. The valency of an antibody refers to the number of antigenic determinants that an individual antibody molecule can bind.
3. Frequently the binding of an antibody to an antigen has no direct biological effect.
Rather, the significant biological effects are a consequence of secondary “effector functions” of antibodies. The immunoglobulins mediate a variety of these effector functions.
4. Its fragments produced by proteolytic digestion have proven very useful in elucidating structure/function relationships in immunoglobulins. It can be divided into five different classes, based on differences in the aminoacid sequences in the constant region of the heavy chains.
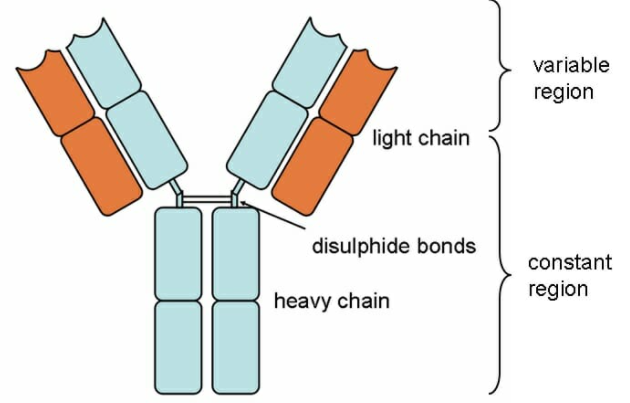
5. All immunoglobulins within a given class will have very similar heavy chain constant regions. It is present both on B cells, and as a soluble molecule in the blood because of its large size, IgM is found primarily in the intravascular space i.e. in the bloodstream and also lymph fluid.
6. The various antibodies produced by plasma cells are classified by isotype, each of which differs in function and antigen responses primarily due to structure variability.
7. A light chain has two successive domains: one constant domain and one variable domain. The ratio of these two light chains differs greatly among species, but the light chains are always either both kappa or both lambda, never one of each.
Note: Determination of individual subclasses is relevant in assessing primary immunodeficiencies or immune responses, especially if the total IgG or IgA concentration is not altered or elevated. They act as a critical part of the immune response by specifically recognizing and binding to particular antigens, such as bacteria or viruses, and aiding in their destruction.
