Question
Question: Within the nucleus, DNA is organized along with proteins into a material called (a) Nuclear lamina...
Within the nucleus, DNA is organized along with proteins into a material called
(a) Nuclear lamina
(b) Chromosome
(c) Chromatid
(d) Chromatin
Solution
DNA is grouped within the nucleus along with proteins in a macromolecular complex. This complex's function is to bundle long DNA molecules into more compact, denser structures. The nucleosome is the structural unit of this DNA-protein complex.
Complete step by step answer:
- DNA is arranged within the nucleus into a substance called chromatin along with proteins.
- Chromatin is a viscous, gelatinous material made up of histones or acidic proteins called nonhistones, DNA, RNA, and basic proteins.
- The term chromatin is derived from the word "color" meaning chroma and the suffix "in."
- Proteins called histones are bound to chromosomes in order to coordinate the vast amount of DNA within the nucleus; DNA is wrapped around these histones to create a structure resembling beads on a string. These complexes of protein-chromosomes are called chromatin.
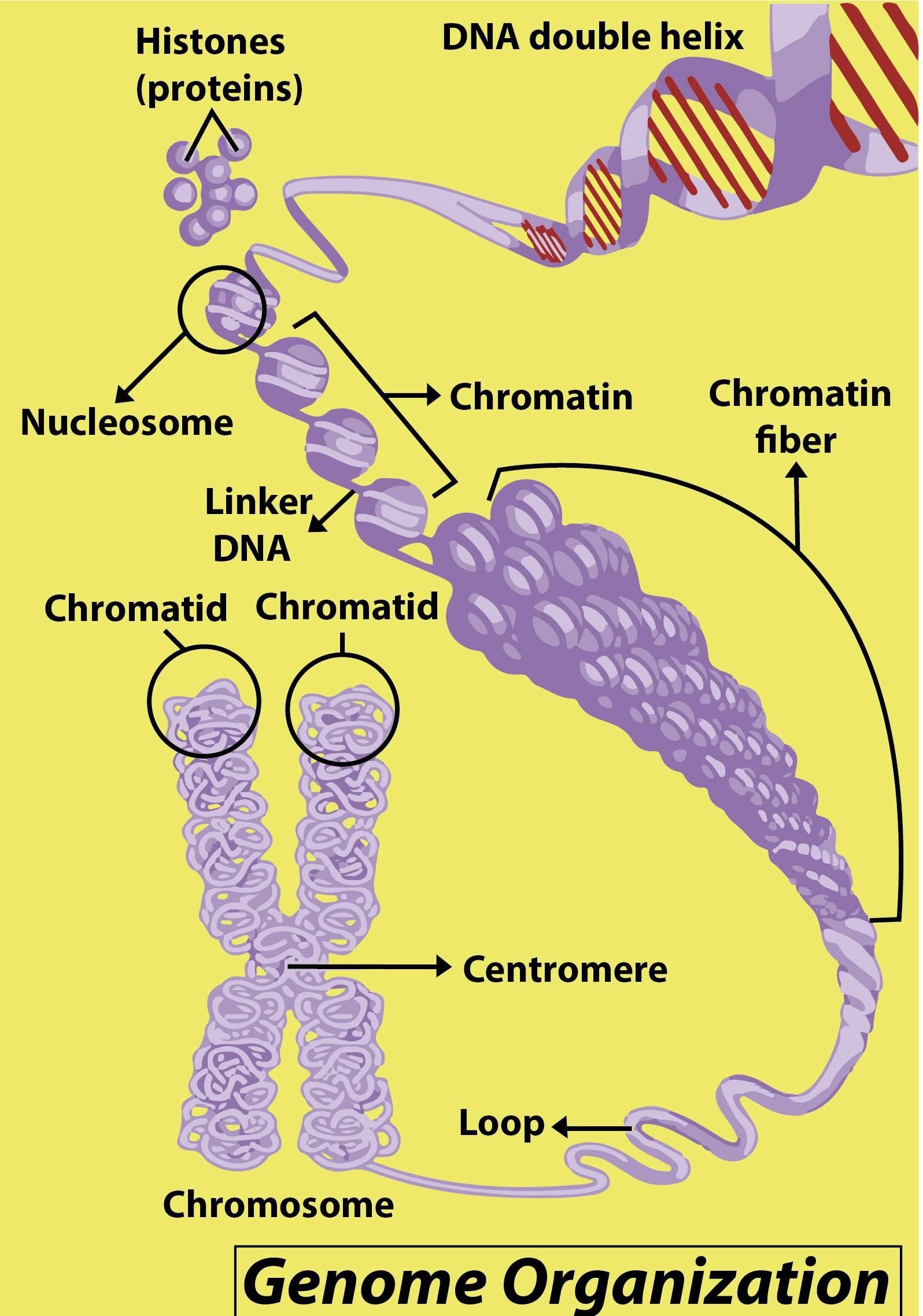
- Its primary role is to bundle long DNA molecules into denser, more compact structures. This prevents the tangling of the strands and also plays an important role in strengthening DNA during cell division, preventing damage to DNA, and controlling gene expression and replication of DNA.
So, the correct answer is, ‘Chromatin’.
Note:
- Chromatin is a DNA and protein complex that is present in eukaryotic cells.
- Chromatin promotes proper segregation of chromosomes in anaphase during mitosis and meiosis; the distinctive shapes of chromosomes evident during this stage are the consequence of coiling DNA into highly condensed chromatin.
- Chromatin's primary protein constituents are histones that bind to DNA and act as "anchors" through which the strands are wounded. There are usually three levels of chromatin organization.
- DNA wraps around histone proteins, forming nucleosomes and the structure (euchromatin) of so- called beads on a string. In their most compact form (heterochromatin), several histones wrap up into a 30-nanometer fiber composed of nucleosome arrays. The 30-nanometer fiber’s higher- level DNA supercoiling generates the metaphase chromosome (during mitosis and meiosis).
