Question
Question: With reference to photosynthesis, what is the A. \[{\text{C}}{{\text{F}}_{\text{0}}}{\text{ - C}}...
With reference to photosynthesis, what is the
A. CF0 - CF1 complex?
B. ATP synthetase
C. Ferredoxin-NADP reductase
D. Cytochrome b6f complex
E. RuBP carboxylase
Solution
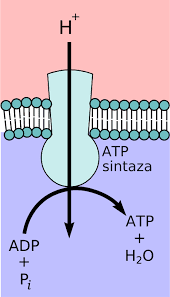
Photosynthesis is a process used by the plants to sustain their life. They do so by converting light energy into chemical energy. CF0 - CF1 complex is an important component of the proton channel. It directly has a role in the translocation of protons across the membrane. CF1 is the catalytic core and CF0 is the membrane proton channel.
Complete Answer:
The CF0 - CF1complex is a protein. Its function is the catalysis of the formation of the energy storage molecule called ATP (adenosine triphosphate). ATP is made by using ADP (adenosine diphosphate) and PI (inorganic phosphate). It is classified under ligases.
RuBP Carboxylase is an enzyme which is part of the first main step of carbon fixation. This is the process through which the atmospheric carbon dioxide is converted by plants through photosynthesis into energy rich molecules like glucose.
Cytochrome b6f complex is an enzyme that is found in the thylakoid membrane of chloroplasts in plants, cyanobacteria, and green algae. It acts as a catalyst for the transfer of electrons from plastoquinol to plastocyanin.
Ferredoxin-NADP Reductase acts as a catalyst to the reaction which converts reduced ferredoxin, NADP+, and H+ to oxidized ferredoxin and NADPH. This enzyme is a type of oxidoreductase enzyme.
The proton – linked ATP synthetase of chloroplasts is known as CF0 - CF1 complex. The catalytic part is known as CF1 and the membrane bound part is known as CF0. It interacts with CF1 and contains a proton channel.
So, the correct answer is option A, ATP synthetase.
Note:
In plants, the synthesis of ATP does not take place in the mitochondria even though they are the powerhouse of the cells. It happens in membrane bound sacs known as thylakoids. They are arranged in the form of stacks and are called the grana of chloroplast. Mitochondria’s division is accelerated by the body's increased demand for energy and they divide independently by fission.
