Question
Question: With a decrease in temperature, oxyhaemoglobin curve will become (A) straight (B) most steep ...
With a decrease in temperature, oxyhaemoglobin curve will become
(A) straight
(B) most steep
(C) parabola
(D) all the above
Solution
The red blood cells contain a pigment known as haemoglobin. Each haemoglobin protein binds four oxygen molecules and forms Oxyhaemoglobin. Oxygen molecules are transported to individual cells in the body tissue where they are released.
Complete Answer:
- When blood flows into our lungs, oxygen is transferred to our haemoglobin, which forms oxyhemoglobin. Oxyhemoglobin is like a supply truck that delivers oxygen to our tissues. Oxyhaemoglobin has a close relation with temperature difference.
- Many people consider that the average body temperature is 37 degrees Celsius. Although this may be true, the temperature of the body is not the same anywhere in our body. For example, temperatures in our metabolising tissues will rise a few degrees when the heat is released from the cells as they function.
- Okay, so the temperature in our tissues is rising, so what does this have to do with the transport of oxygen? If the temperature decreases the affinity of haemoglobin to oxygen increases leading to increased binding of haemoglobin to oxygen. In fact, the rise in temperature lowers the affinity of haemoglobin to oxygen.
- When oxyhemoglobin is subjected to elevated temperatures in the metabolic tissues, affinity reduces and haemoglobin releases oxygen. This is really significant since only free oxygen will reach the cells. In other words, it needs to be released from the haemoglobin so it can reach our cells. Owing to the higher concentration of oxyhaemoglobin and the reduced dissociation, the curve gets steeper and the left curve change is noticeable.
So the answer is option B.
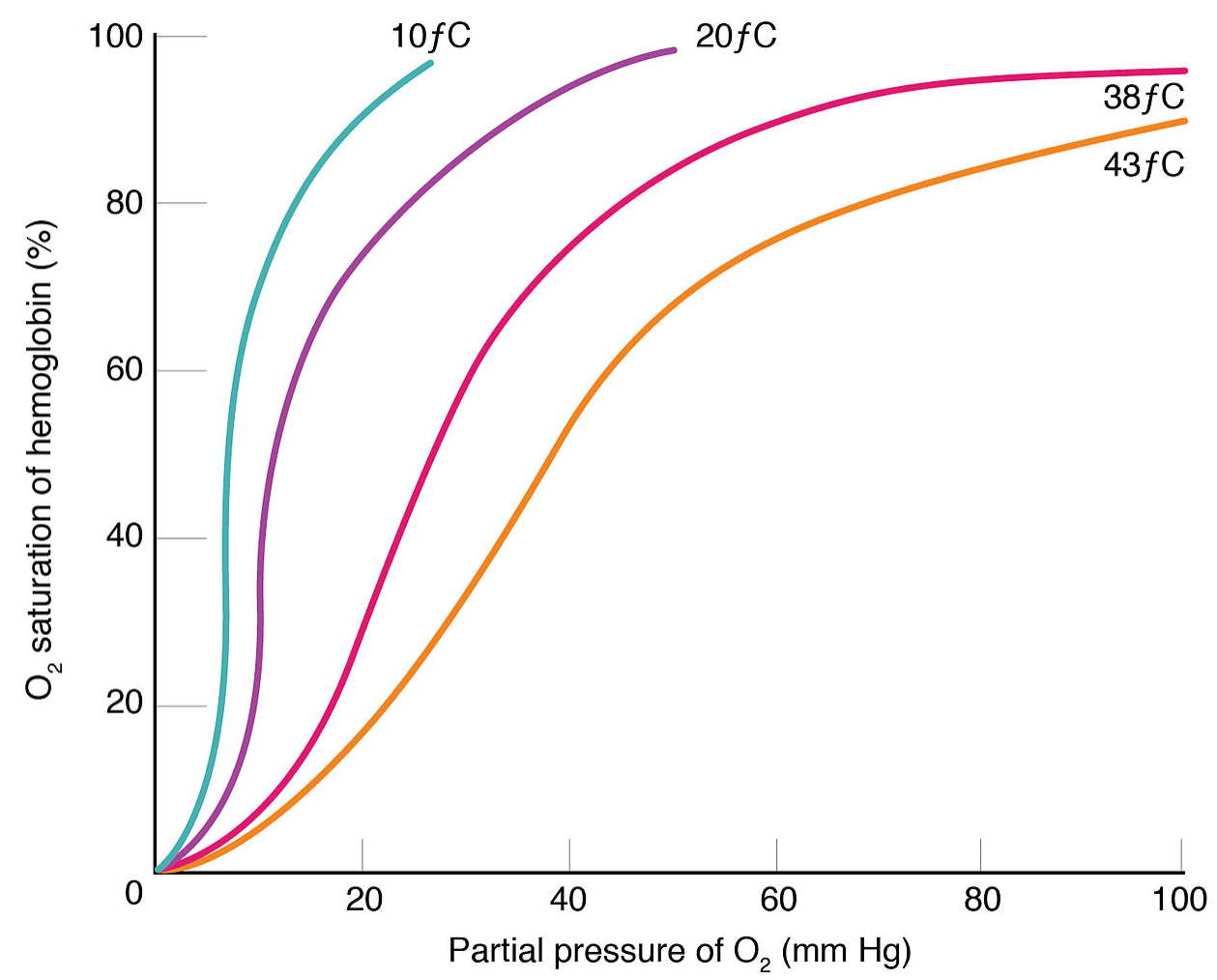
Note: It is called oxyhemoglobin in its oxygenated state and is light red. It is called deoxyhemoglobin in a diminished state and is purple-blue. Each haemoglobin molecule is made up of four heme groups in the globin community. Hemo group provides haemoglobin with the ability to bind oxygen due to the presence of iron atoms. It also adds to the red pigment that is present in muscles and blood.
