Question
Question: Why the blue color of copper sulfate solution in water changes to yellow when treated with concentra...
Why the blue color of copper sulfate solution in water changes to yellow when treated with concentrated hydrochloric acid?
Solution
Hint: Color can be changed because of the change in ligands. It is due to crystal field splitting. The number of unpaired electrons in the last subshell is counted.
Complete step by step answer:
Copper is a d-block element and most of the transition metal compounds are colored both in the solid-state and in aqueous solution.
Color is due to the presence of incomplete d-subshell. Further, when the anion or the ligands approach the transition metal ions, their d-orbitals do not remain degenerated. They split into two sets, one consisting of lower energy orbitals (t2gwhich includes dxy,dyz, and dzx) and the other consisting of higher energy orbitals (egwhich includes dx2−y2, and dz2). This is called crystal field splitting.
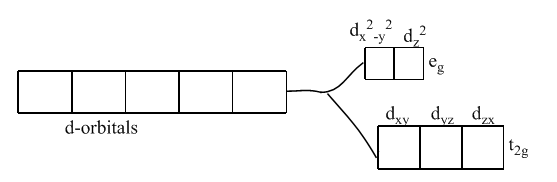
Thus, the electron can jump from lower energy d-orbital to higher energy d-orbital. The required amount of energy to do this is obtained by absorption of light of a particular wavelength in the region of visible light. The transition metal ion has the property to absorb such radiations from the visible light and appears colored due to the emission of the remainder as colored light.
In hydrated copper sulfate, four water molecules are present as ligands. In the presence of these ligands, d-orbital are no longer degenerate in energy. Hence, the d-d transition takes place absorbing red wavelength. The complementary color, viz., blue is reflected.
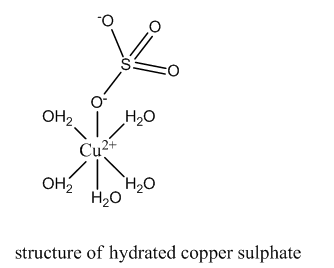
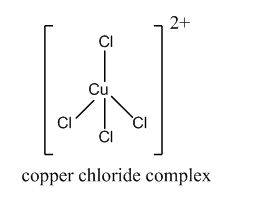
But when concentrated hydrochloric acid is added to the hydrated copper sulfate, the water ligands are replaced by chloride ligands. This forms the copper chloride complex. The d-d transition takes place by absorbing the violet wavelength. Hence, the reflection is yellow.
Hint: There are specific colors of specific ligands that they will impart. Don’t get confused between the wavelength absorbed and wavelength emitted. The color of the compound will always be complementary to the color of the wavelength absorbed.
