Question
Question: Why is nucleic acid a polymer?...
Why is nucleic acid a polymer?
Solution
Nucleic acid is an important macromolecule found in all cells and DNA. The information is encoded by DNA to make the proteins. Ribonucleic acid comes in different forms that participate in protein synthesis.
Complete answer:
A polymer is a large molecule that is built up from multiple smaller building blocks in a repetitive manner.
Polymer is mainly a large molecule that is built up from small building blocks in a repetitive manner. The main building block of nucleic acid is DNA and RNA. The nucleotides have a phosphate group, a sugar group and a nitrogenous base.
Consequently a nucleic acid is a segment of nucleic acid that specifically recognises and binds to its target nucleic acid. The interaction is based on the formation of stable hydrogen bonds between the two nucleic acids.
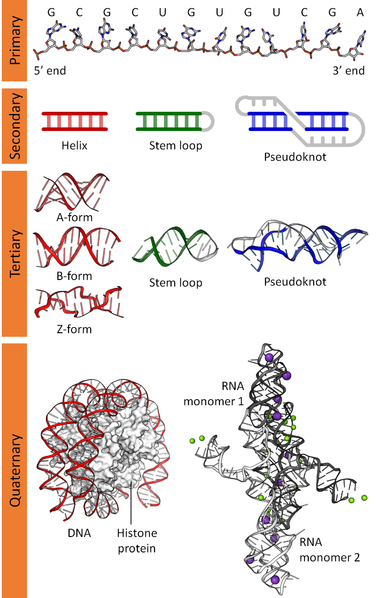
The nucleic acids are of two types: natural and synthetic nucleic acids. The natural nucleic acids are DNA and RNA. The pentose sugar in RNa is ribose while DNA has deoxyribose. The nitrogenous bases adenine, guanine and cytosine are found in both DNA and RNA , thymine is found only in DNA while uracil is found in RNA.
Note:
Nucleic acids are molecules that transfer genetic information from one generation to another generation. These macromolecules store the genetic information that determines the traits and make protein synthesis.
