Question
Question: Why is nitrogen \( s{p^3} \) hybridized even when it bonds to only three other atoms?...
Why is nitrogen sp3 hybridized even when it bonds to only three other atoms?
Solution
Hybridization is defined as the mixing of atomic orbitals to form new hybrid orbitals suitable for the pairing of electrons to form chemical bonds in valence bond theory with different energies, shapes, etc. than the component atomic orbitals.
Complete answer:
The atomic number of nitrogen is seven, so the electronic configuration is 1s22s22p3 . According Hund's rule, every orbital in a subshell is filled with one electron before any one orbital is doubly filled; moreover all electrons which are singly filled in orbitals should have the same spin. So that 3p electrons will occupy 3 degenerate p orbitals, i.e. x , y and z which are as follows:
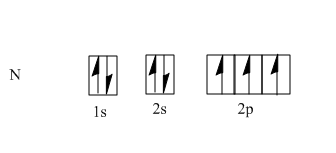
One s orbital and three p orbitals are hybridized to form four hybrid orbitals with equivalent characteristics. These hybrid orbitals are known as sp3 hybridized. In the case of N , we have four orbitals filled with five electrons as nitrogen has five electrons in its valence shell.
By following Hund's rule, each of the four hybrid orbitals take one electron each, leaving us with one more electron.
fillingofelectronbyHundrule:
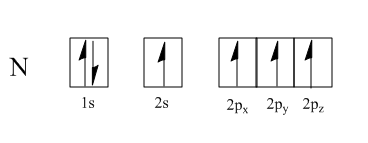
This electron then fills into one of the sp3 hybrid orbitals that is already filled with one electron, making a total of two electrons.
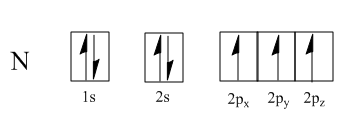
These pairs of electrons are usually shown as “lone pairs” on a Lewis diagram.
Lone pair in nitrogen:
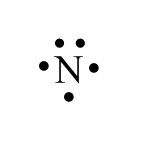
According to Molecular Orbital Theory, this lone pair is in a non-bonding orbital. So, there are only three electrons in the bonding orbital and two electrons in the antibonding orbital because of which three electrons will take part in bond formation and those in the non-bonding orbital do not participate. Therefore, nitrogen form sp3 hybridized even forming only three bonds with atoms.
Note:
For sp3 hybridized central atoms , only possible molecular geometry is tetrahedral. In order to be in sp3 hybridized, an atom must have one s orbital and three p orbitals. Because of tetrahedral shape, the bond angle is approximately equal to 109.5∘ .
