Question
Question: Why is hyperconjugation called no bond resonance?...
Why is hyperconjugation called no bond resonance?
Solution
Hyperconjugation is a special case of resonance which involves the delocalization of sigma electrons of the C−H bond of any alkyl group. To answer the above question one must understand the term first.
Complete answer:
Resonance is the delocalisation of electrons in a molecule from bond pairs to lone pair or vice-versa.
The delocalisation of σ -electrons or lone pairs of electrons into adjacent π -orbital or p-orbital is called hyperconjugation. It occurs due to overlapping of σ -bonding orbital or the orbital containing a lone pair with adjacent π -orbital or p-orbital. The displacement of σ –electrons towards the multiple bond occurs when there are hydrogens on the α−carbon which is adjacent to the multiple bond. This results in polarisation of the multiple bond.
For a hyperconjugation there requires a condition which is, there must be an α−CH group or a lone pair on atom adjacent to sp2 hybrid carbon or atoms like nitrogen
Let's understand why hyperconjugation is called no bond resonance with the help of propene
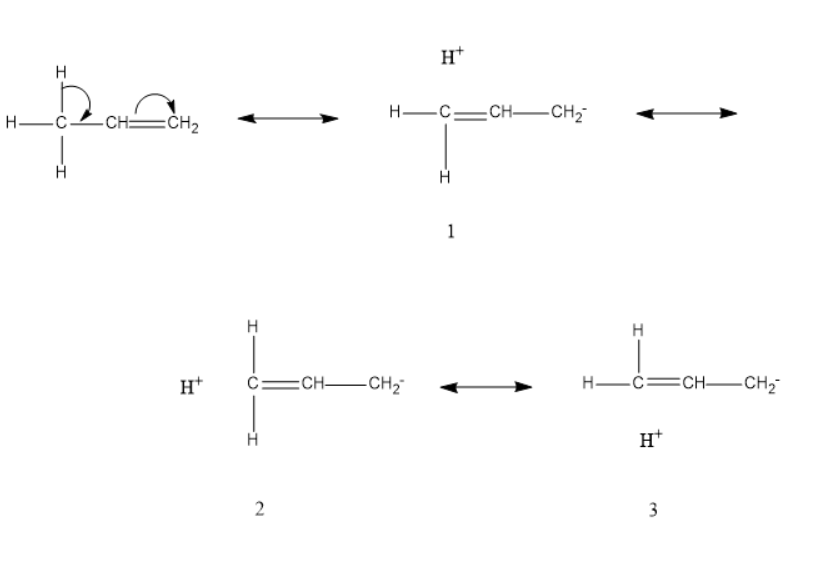
As we can see in hyperconjugative structure 1,2,3 that there is no bond between carbon and hydrogen atoms, hyperconjugation is called no bond resonance. As there is no bond between hydrogen and other atoms, therefore the bond broken is responsible for the possibility of the conjugation. There is no bond present from where the electrons are shifted. When the number of terminal hydrogen is more then the number of hyperconjugative structures are also more.
Note:
Hyperconjugation is an extension of resonance. Hyperconjugation involves delocalization of sigma bond electrons along with pi-bond electrons whereas resonance causes the delocalization through interaction between pi-bonds.
