Question
Question: Why is adsorption always exothermic?...
Why is adsorption always exothermic?
Solution
The responsible factor is on the account of forces between the surface and the adsorbent. The heat of adsorption is the term used for the explanation of the exothermic process.
Complete step by step answer:
Let us first understand the adsorption phenomenon.
When there is attracting and retaining the molecules of a substance on the surface of a liquid or a solid forming into a higher concentration of the molecules on the surface is called adsorption.
The substance that is adsorbed on the surface is called the adsorbate and the substance on which it is adsorbed is called adsorbent.
The reverse process of adsorption i.e. removal of particles from the surface is called desorption.
Occlusion is the term used to define the adsorption of gases on the surface of metals.
Some examples of adsorption are:
To the solution of an organic dye such as methylene blue, add animal charcoal and stir, it is observed that the intensity of the color in the solution decreases showing that some amount of the dye being adsorbed.
Introduce finely divided solid into a closed vessel containing a gas at low pressure. The pressure of the gas decreases.
Adsorption- an exothermic process:
When adsorption takes place, the residual forces on the surface of the adsorbent decreases. In other words, surface energy decreases. This appears in the form of heat which is called heat of adsorption. Hence, adsorption is an exothermic process, i.e., ΔHadsorption is always negative.
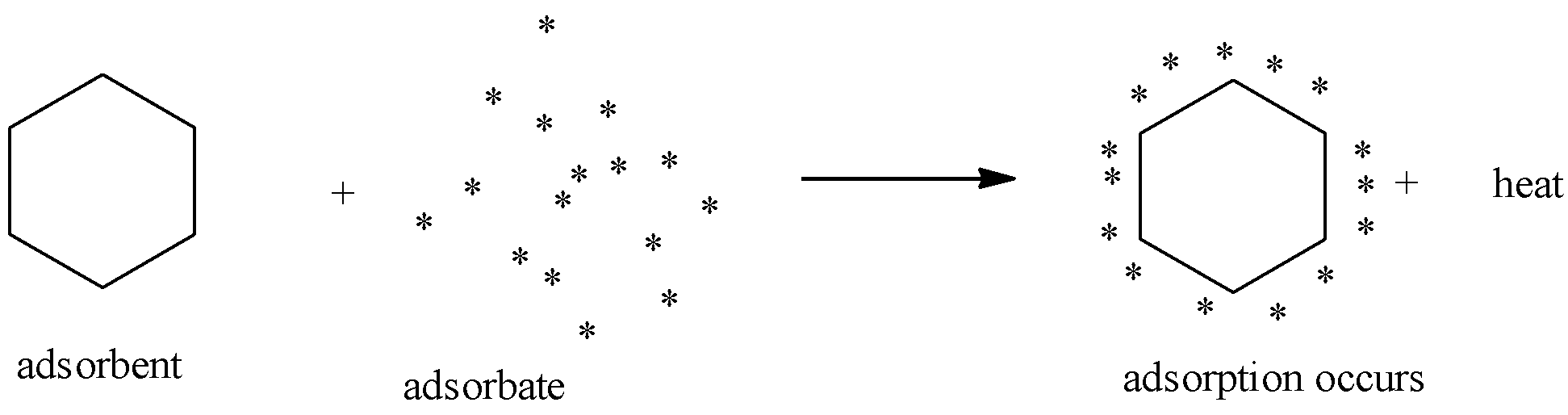
So, when the adsorbate gets attached to the adsorbent the heat is evolved making the reaction exothermic.
Note: As the area of the adsorbent increases the amount of adsorption increases and this would increase the heat of adsorption. Finely divided metals or the substances which have a porous surface, for example, charcoal, alumina gel, clay, etc. act as excellent adsorbents.
