Question
Question: Why do walls of trachea not collapse when there is less air in it?...
Why do walls of trachea not collapse when there is less air in it?
Solution
The trachea, commonly known as the windpipe. It is a pipe that carries oxygen rich air into lungs. The trachea divides further into smaller bronchi, the bronchi in turns divides into bronchioles and bronchioles finally terminates into alveoli.
Complete answer:
The alveoli is a balloon like sacs. They provide surface area for exchange of gases. Alveoli are provided with blood vessels. Each lung is provided with millions of alveoli.
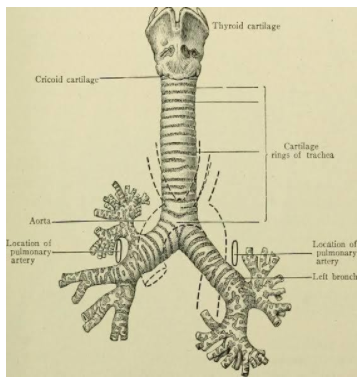
The trachea is covered by incomplete C- shaped cartilaginous rings . The trachea is composed of about 20 rings of tough cartilage. The back part of each ring is made of muscle and connective tissue. This ring prevents trachea from collapsing when there is less air in it.
The trachea is composed of rings of tough cartilage. The back part of each ring is made of muscle and connective tissue.
The tracheal cartilages help support the trachea while still allowing it to move and flex during breathing.
Note: Leucoplasts are of three types:
Amyloplasts – they store and synthesize starch.
Portionless – portionless helps in storing the proteins
Leucoplasts -Leucoplasts helps in storing fats and oils that are needed by the plant.
