Question
Question: Why do \(Be{F_2}\) molecules have zero dipole moment although the \(Be - F\) bonds are polar?...
Why do BeF2 molecules have zero dipole moment although the Be−F bonds are polar?
Solution
Dipole moments occur when there is a separation of charge. They can occur between two ions in an ionic bond or between atoms in a covalent bond; dipole moments arise from differences in electronegativity. The dipole moment is a measure of the polarity of the molecule.
Complete answer:
The bond dipole moment uses the idea of electric dipole moment to measure the polarity of a chemical bond within a molecule. It occurs whenever there is a separation of positive and negative charges.
We know, that the BeF2 is a linear molecule:
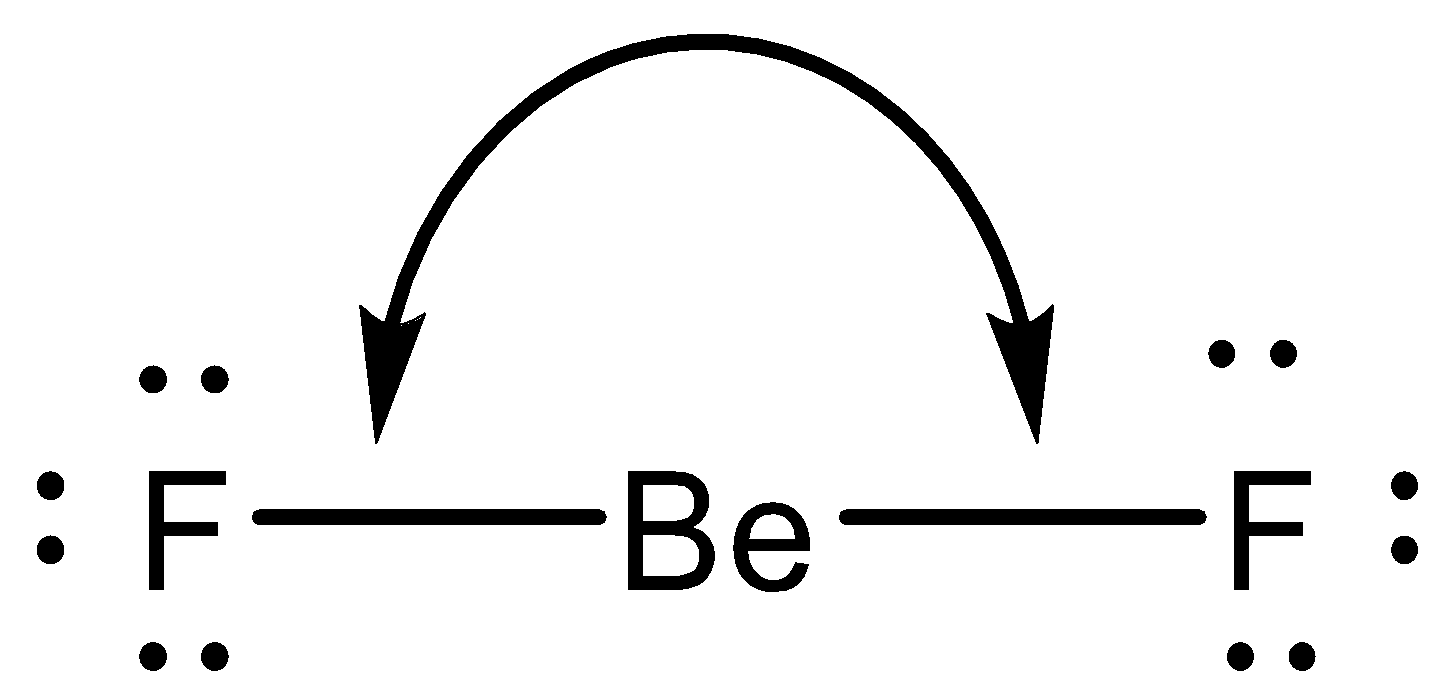
Fluorine is much more polar than beryllium, with an electronegativity difference of 2.41. So, fluorine will pull beryllium's electrons towards itself. However, there is an opposite fluorine atom on the other side, pulling at the same strength; if two balanced forces are pulling in different directions, then no movement happens.
So here, beryllium atoms are pulled at the same strengths in different directions, and so they do not move at all, thus canceling out the dipole moments.
Additional information:
For diatomic molecules there is only one bond so the bond dipole moment is the molecular dipole moment. For polyatomic molecules, there is more than one bond. The total molecular dipole moment may be approximated as the vector sum of the individual bond dipole moments. Often bond dipoles are obtained by the reverse process: a known total dipole of a molecule can be decomposed into bond dipoles.
Note:
Dipoles are caused when the positive and negative charges in an atom move to opposite ends. This means that at one end of the atom or molecule, there is a higher concentration of positive charge, and at the other end, there is a higher concentration of negative charge.
