Question
Question: Why did DNA fragments in the band ‘D’ moved further away in comparison to those in band ‘C’? 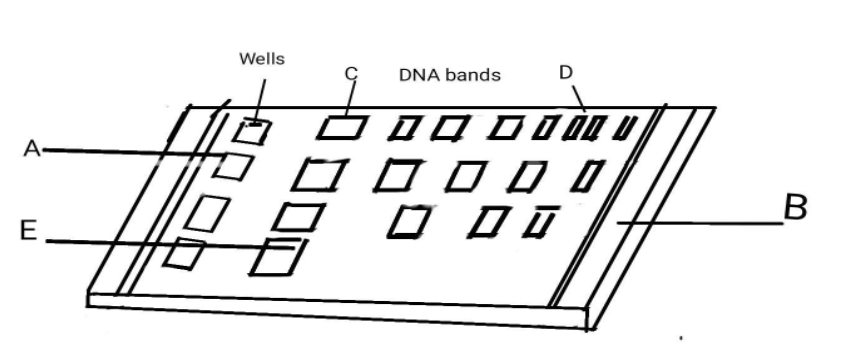
Solution
Here, the above-shown picture represents gel electrophoresis. It is used to separate macromolecules such as DNA or proteins in a gel matrix. The gel matrix is composed of agarose. The loaded DNA samples get separated by molecular weight and size.
Complete answer:
- The method of gel electrophoresis is used in biochemistry, genetics, and clinical biology to separate a mixture of macromolecules.
- Here, in the given question, the picture shows agarose gel electrophoresis of DNA. The DNA gets separated by applying an electric field to move macromolecules from anode to cathode through the gel matrix. Agarose gel when solidified has three-dimensional structures with pores and channels.
- This structure is held together by hydrogen bonds. When being applied to an electric field, the DNA moves from the negative to the positive side in the gel as DNA has a negative charge. Supercoiled or small DNA moves faster through pores present in the gel. While the large DNA collides with pores and that lowers their speed. Therefore, the molecules of different sizes can be separated by this sieving process.
- So, coming back to the question, we can say that DNA in the ‘D’ band has a small or supercoiled DNA and DNA in the ‘C’ band has a large size and higher molecular weight. Due to small size and lower molecular weight, DNA in the ‘D’ band has moved further away than DNA in the ‘C’ band.
Note: Always remember that agarose gel electrophoresis separate macromolecules based on size and weight. To measure the size of DNA that has been separated, the ladder is added in one well with samples DNA. Gel electrophoresis is widely used to identify the size of DNA.
