Question
Question: Which type of restriction enzymes are used in recombinant DNA technology? A. Type-I B. Type-II ...
Which type of restriction enzymes are used in recombinant DNA technology?
A. Type-I
B. Type-II
C. Type-III
D. All of the above
Solution
Recombinant DNA technology is a technique used in Biotechnology that consists of removing the DNA of interest from the target and then inserting it in the host genome. Restriction enzymes are tools of recombinant DNA technology. These are molecular scissors that can cut specific strands of DNA. Different restriction enzymes have different functions.
Complete answer: Recombinant DNA technology is a technique that is used to change the phenotypic characters of host species. Some genetic alterations are done to modify the genotype of the host organisms by inserting a gene of interest into the host’s genome. The transfer of the gene of interest is mediated by a vector. The vector integrates the DNA segment from the target organism to the host organism’s genome, where the inserted gene expresses itself. The restriction enzymes play a major role in the cutting of the DNA segment of interest. They very specifically bind to recognition sequences and make the cut at that site giving a free segment of the gene of interest. These are mainly of two types. Endonucleases are used to cut the DNA segment from within the sequence. But the exonucleases cut the DNA strand from its ends.
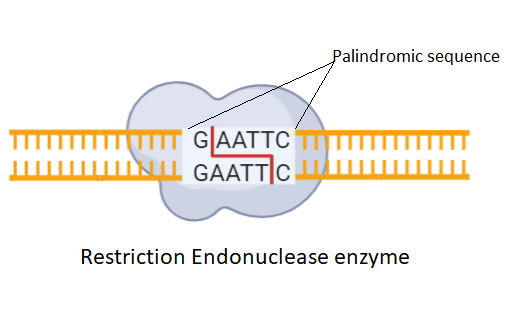
Let us understand each type of restriction enzyme types based on their activity to know which of them is used in recombinant DNA technology.
-The type-I recognizes specific sequences in the DNA of interest but at non-specific sites. It cuts at more than 1,000 bp away from the gene of interest. Thus, it is incompatible to be used.
-Type –II recognizes the palindromic sequences as their recognition sites. These sequences read the same from both the left and right sides. The enzyme cuts within these palindrome sequences with precision and specificity.
-The type-III recognize the specific sequences of 5 to 7 base pairs. It cuts 24 to 27 base pairs downstream of the recognition site. Thus, it is also not feasible to use to get accurate results.
Therefore, from the above discussion, we can conclude that type-II restriction enzymes are used in recombinant DNA technology. So, the right answer is option B.
Note: Restriction mechanism is an inherent property inside the bacterial cells. The bacteria use this mechanism to cut off the viral genomes that infect the bacterial cells. The restriction enzyme in bacteria recognizes the viral genome, then binds to it, and cuts it into segments. This inactivates the viral activity of the virus. The bacteria protect their genome from restriction endonucleases by methylation reactions.
