Question
Question: Which type of respiration is involved in the process of fermentation?...
Which type of respiration is involved in the process of fermentation?
Solution
Respiration is a process that gives energy for completing activities. It's of two types, aerobic and anaerobic respiration which solely supported the presence and absence of oxygen. This leads to the release of energy within the sort of ATP by the breakdown of glucose. within the case of anaerobic respiration, a particular process is accompanied by the formation of ethanol, carboxylic acid, etc.
Complete answer:
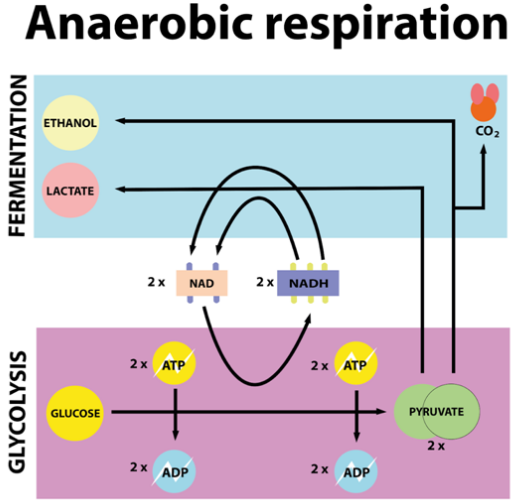
Fermentation is a kind of anaerobic respiration. This type of respiration is mostly carried out primarily by fungi and bacteria. Gay Lussac was the first to discover fermentation.
Fermentation is mainly of two types:
-Alcoholic fermentation
-Lactic acid fermentation
Both the process of fermentation is hazardous as either acid is produced or alcohol.
- During vigorous exercise, when the oxygen is inadequate for cellular respiration pyruvic acid is reduced to lactic acid by using the enzyme lactate dehydrogenase.
- The fermentation of alcohol results in the release of carbon dioxide with ethanol whereas lactic acid fermentation releases only lactic acid. In the case of alcoholic fermentation, the pyruvic acid formed at the end of the glycolysis is converted to alcohol by using two enzymes, pyruvic acid decarboxylase, and alcohol dehydrogenase. This is commonly seen in yeast and bacteria. Yeast poison to death when the concentration of alcohol reaches about 13%.
In lactic acid fermentation, homofermentative lactic acid bacteria reduces the lactic acid into pyruvic acid at the end of glycolysis.
Note:
-The gaseous exchange, i.e., intake of oxygen and release of carbon dioxide is called breathing while respiration involves the biological oxidation of organic molecules i.e., breaking up of C−C bonds by the different enzymes and results in the release of energy in the form of ATP.
-It is the common step in both anaerobic and aerobic respiration as all organisms retain the machinery to partially oxidize glucose without the help of O2.