Question
Question: Which type of epithelium is found in the oesophagus, buccal cavity, cornea, vagina, and cervix? A....
Which type of epithelium is found in the oesophagus, buccal cavity, cornea, vagina, and cervix?
A. Transitional epithelium
B. Columnar epithelium
C. Non-keratinized stratified epithelium
D. Keratinized stratified epithelium
Solution
Epithelium tissue is the tissue covering the surface of the whole body. It is also the body's outer covering. It's the body's thin, defensive layer. Epithelial tissues throughout the body are prevalent. They are the main tissue in glands and constitute in forming the covering of all body surfaces, line body cavities, and hollow organs.
Complete answer: The outer surfaces of the organs and blood vessels of the body and the inner surfaces of the cavities in certain internal organs are covered by epithelial tissue.- There are three other types of epithelial tissue: squamous, columnar, and cuboidal.- The stratified epithelium type is non-keratinized. The tissues covering the inner and outer surfaces are this type of epithelial tissue. This epithelium is found in the oesophagus, pharynx, buccal cavity, vagina, etc. Thus, the correct response is that non-keratinized stratified epithelium exists in the vagina, cervix, buccal cavity, and anal cavity. Epithelial tissue's role in secretion, absorption, transport, defense, and taste and olfaction receptor. Microvilli is a finger-like extension. Non-keratinized surfaces consist of stratified squamous epithelium tissue, such as the cornea or conjunctiva of the skin, the oral cavity, the esophagus, the anal canal, the vagina, and the inner portion of the lips, and must therefore be kept moist by the body's secretions in order to avoid drying out. There, only one layer is in contact with the membrane, and also to maintain structural stability, other surfaces conform to each other.
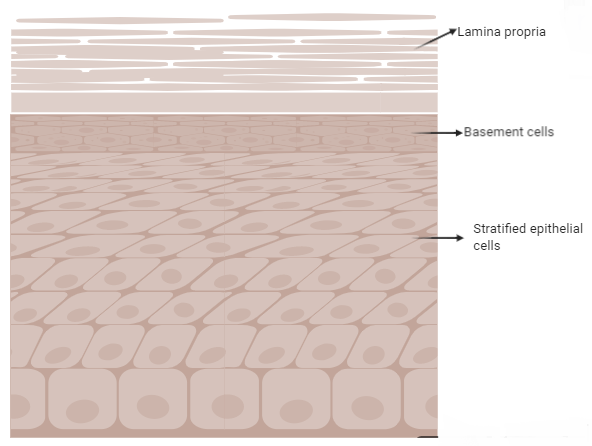
Therefore, choice (C), 'Non-keratinized stratified epithelium' is the appropriate response.
Note: There is only one layer of cell in-plane epithelium tissue that differs from stratified multilayer tissue. A type of stratified epithelium is a non-keratinized stratified epithelium. Just one layer is in contact with the basement membrane in the case of the non-keratinized stratified squamous epithelium, and the other layers are firmly attached to each other in order to retain structural stability. Likewise, until the basement membrane is exposed, the layer may be consecutively sloughed off (removed) and replaced.
