Question
Question: Which statement(s) is/are WRONG? A) Acetylene is insoluble in conc. \[{H_2}S{O_4}\] due to the non...
Which statement(s) is/are WRONG?
A) Acetylene is insoluble in conc. H2SO4 due to the non-formation of vinyl carbocation(H3C−C⊕H2)(HSO4−)
B) Ethylene is soluble in conc. H2SO4 due to the formation of vinyl carbocation (H3C−C⊕H2)(HSO4−)
C) But-2-yne dissolves in conc. H2SO4 due to the formation of vinyl carbocation (Me−C⊕=CH−Me)(HSO4−)
D) More the s-character in the positively charged C, the more stable is the carbocation and more likely is its formation.
Solution
Solubility follows the rule “like dissolves like”. If a molecule is polar, it will dissolve in a polar solvent like concentrated H2SO4. That is, H+from H2SO4will attack the carbon atom to form carbocation only if there is some degree of polarity. Further, s-character increase means a lesser number of electron donating groups on the positively charged carbon.
Complete step-by-step answer:
Hydrocarbons (saturated or unsaturated) are insoluble in water as they are non-polar in nature. Water is a polar solvent and dissolves polar solutes. So, you can make unsaturated hydrocarbons water soluble, by protonation of them with strong acid such as sulphuric acid.
Statement A is correct because acetylene is a highly symmetrical and non-polar molecule and does not get affected by conc. H2SO4. In fact, conc. H2SO4is used as a drying agent in the preparation of acetylene.
Statement B is also correct because ethylene is a slightly polar molecule and H+from conc. H2SO4attacks one of the doubly bonded carbon-atoms to form a carbocation which forms a bond of ionic nature with and hence, is soluble in conc. H2SO4.
Statement C is also a correct statement as methyl groups may be unsymmetrically distributed around doubly-bonded carbon which makes H+ from conc. H2SO4 to attack it and form a relatively stable carbocation whose combination with HSO4− makes But-2-yne soluble in conc. H2SO4
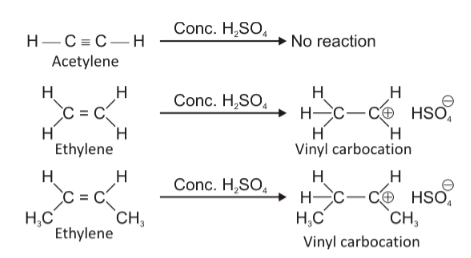
Statement D is a wrong statement because with increasing s-character, the stability of carbocation decreases. This happens because as the s-character increases, unsaturation increases, making electron donating alkyl groups less and less. Thus, the positive charge if acquired by such a carbon remains intensified on it and does not distribute or spread itself as happens in sp3carbon. So, as the s-character increases, carbocation stability decreases because of intensification of positive charge.Thus option D is the wrong statement while all the above three statements are correct.
Hence, the correct answer is option ‘D’.
Note: London forces or weak van der Waals forces do not impact the dissolution process of a compound in conc. H2SO4 as these forces are negligible as compared to strong polar forces that exist between H2SO4molecules. Further, the s-character increase, stabilizes the carbanion and not carbocation.
