Question
Question: Which product is formed when diethyl ether is exposed to sunlight and air for a long period? A.Pe...
Which product is formed when diethyl ether is exposed to sunlight and air for a long period?
A.Peroxide
B.Ethyl alcohol
C.Diethyl ketone
D.Ethane
Solution
Ether is a compound where two alkyls or aryl or one alkyl and one aryl group is bonded with oxygen. It can be formed by the dehydration of alcohols by emitting water molecules using dehydrating agents like Conc. H2SO4
Complete step by step answer:
Ether is a volatile, flammable, colorless liquid with a distinctive odor. It belongs to the large functional group of organic compounds called ethers. Its IUPAC name is alkoxy alkane. Ether is synthesized by dehydration (removal of a water molecule) of alcohol using sulfuric acid. For example, the reaction of synthesis of diethyl ether shown below,
2CH3CH2OH+2H2SO4→(CH3CH2)2O+H2SO4+H2O
Ether undergoes combustion reaction, reacts with oxygen, and forms carbon dioxide and water. It is highly flammable and reacts with halogens like chlorine or bromine to form halogen-substituted ether that undergoes substitution reaction in the absence of sunlight.
In presence of sunlight ethers form peroxides. The reaction is shown below,
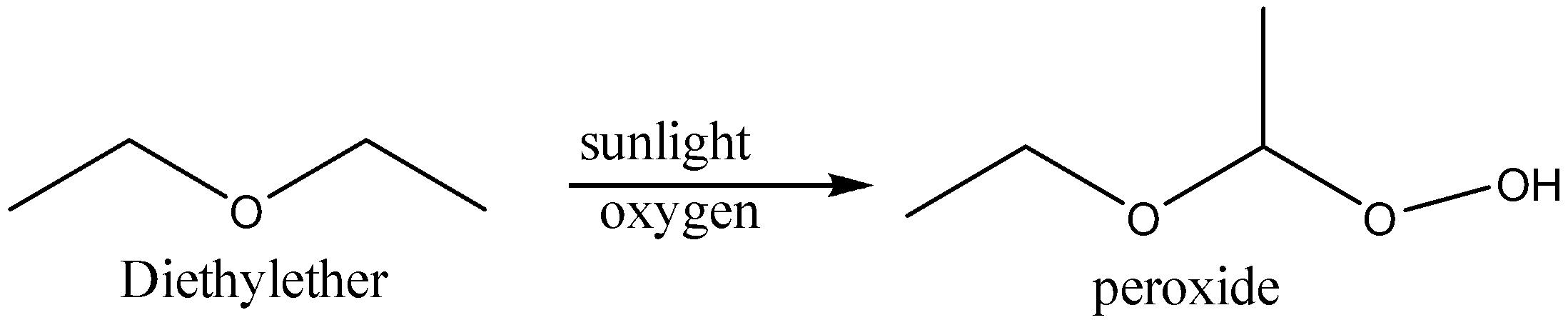
So, the correct option is A.
Additional information:
In presence of an acid, ether can be dissociated. For example, in the presence of HI, it dissociates by the following mechanism.
ROR′HIROH+R′IHIRI+R′I
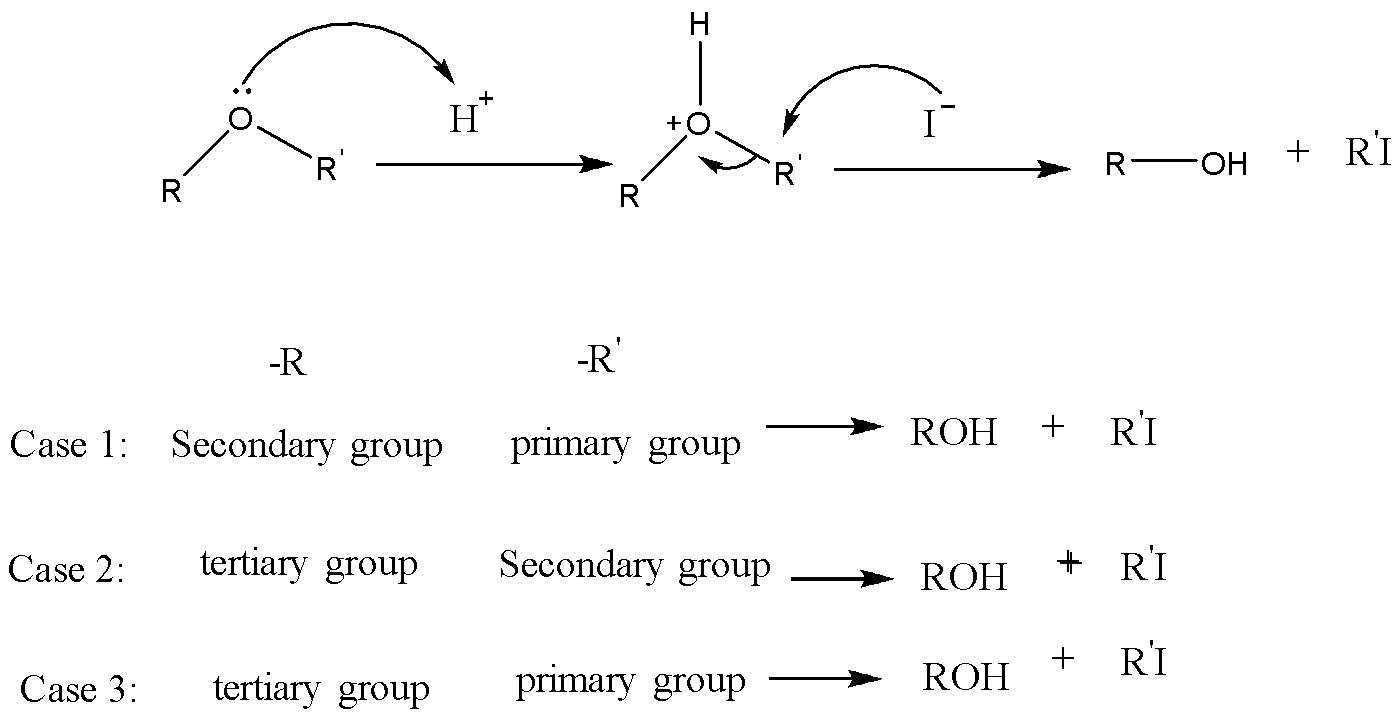
This mechanism is theSN2 mechanism. The formation of alkyl iodide and alcohol depends upon the group attached to the oxygen. Between secondary and Primary alkyl groups, the primary alkyl group favors the SN2 attack at the iodide nucleophile to form corresponding alkyl iodide. Between secondary and tertiary alkyl groups, the secondary alkyl group favors the SN2 attack at the iodide nucleophile to form corresponding alkyl iodide. And between tertiary and Primary alkyl groups, the primary alkyl group favors the SN2 attack at the iodide nucleophile to form corresponding alkyl iodide. In between the vinyl or benzyl group and an alkyl group, the alkyl group favors the SN2 attack at the iodide nucleophile to form corresponding alkyl iodide. Because vinyl and benzyl groups do not participate in theSN2 reaction.
Now for the phenyl methyl ether in presence of HI, it will dissociate in the following manner,
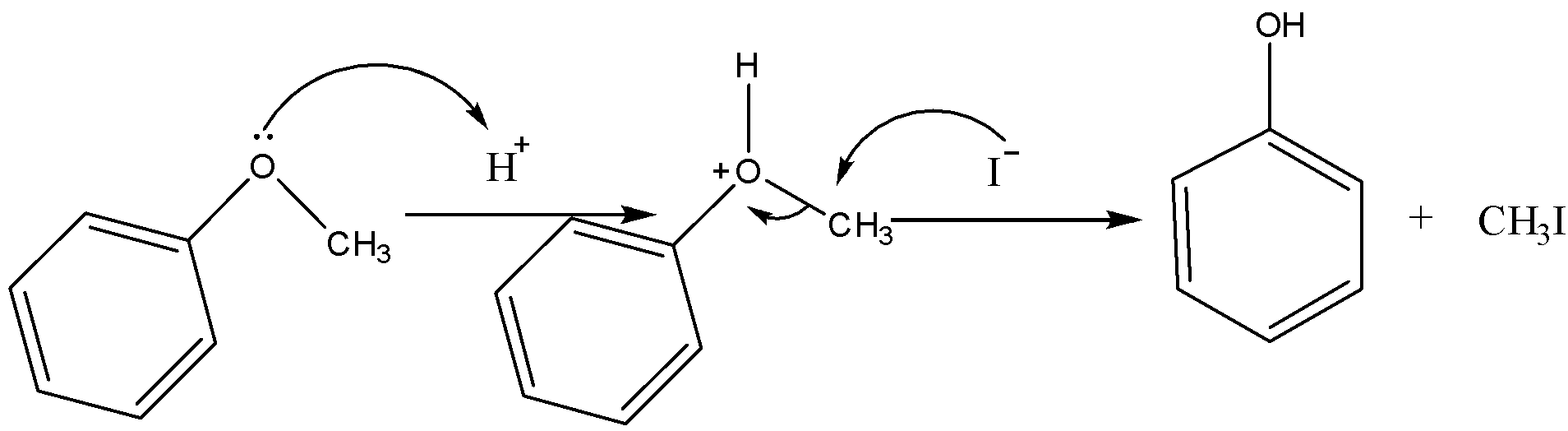
Therefore, on the heating of phenyl methyl ether in presence of phenol is formed with methyl iodide.
Note: From the structure, we get that ethers do not have a hydrogen-bonding network that needs to be broken up to dissolve the solute. It is a nonpolar molecule similar in structure to alcohol, and both ethers and alcohols are similar in structure to water.
