Question
Question: Which point defect in its crystal units increases the density of a solid?...
Which point defect in its crystal units increases the density of a solid?
Solution
Defects in the crystals around an atom or particle are termed as point defects. These happen only at or around a single lattice point. These defects do not expand in space in any dimension. They are alternatively known as zero dimensional defects.
Complete answer:
Interstitial defect is the point defect in which crystal units increase the density of a solid.
Additional information:
The point defects are further divided into following types:
• Stoichiometric defects
• Non- Stoichiometric defects
Stoichiometric is further divided into:
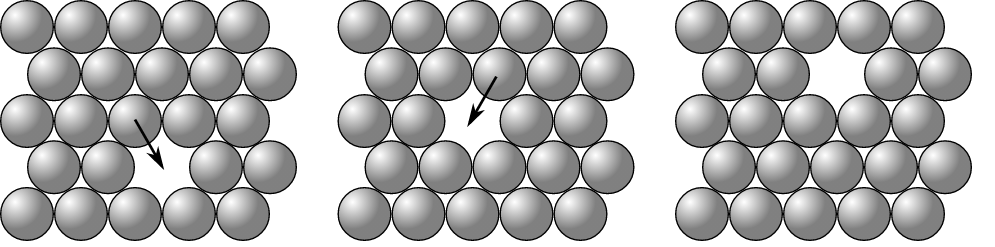
• Vacancy Defect: When an atom goes missing from its original lattice site, then this point defect is known as a vacancy defect. It results in the decrease of the density of the substance. It generate vacancy in the lattice site as shown in the figure:
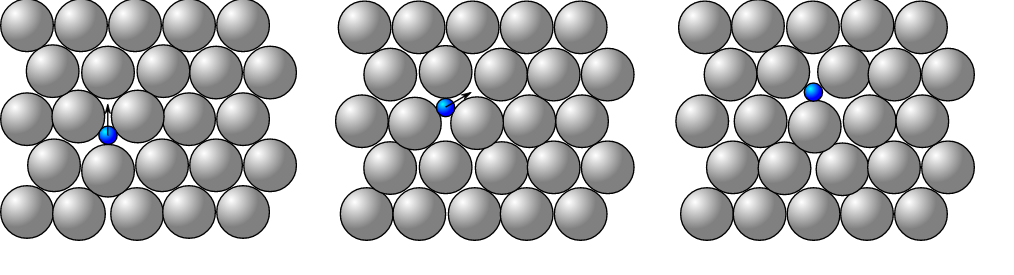
• Interstitial Defect: When an atom takes the interstitial position of the lattice structure then this point defect is known as an Interstitial defect. The atom can be of the same crystal or other crystal. If it is of the same crystal then it will be termed as a self-interstitial defect. In this defect the density of the crystal increases and causes atomic distortion. The diagram of interstitial defect is:
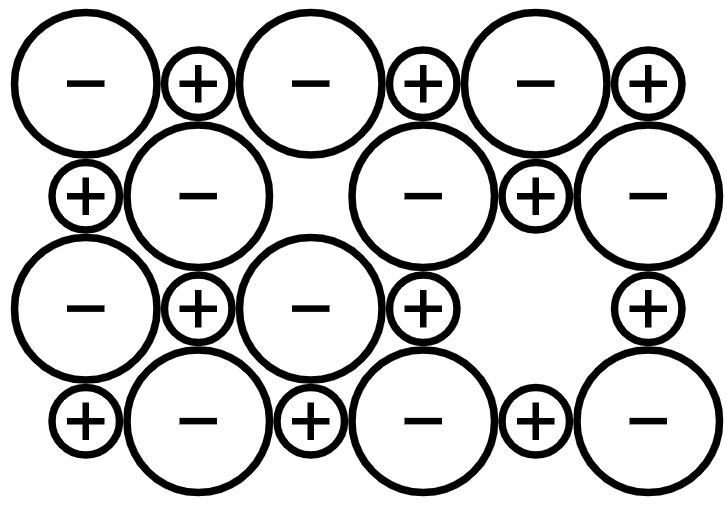
• Schottky Defects: This defect can be observed in various crystals. In this defect, the size of cation and anion is similar. This defect occurs when heat is sought to the ionic compound crystal. When heat raises the temperature, the thermal vibration occurs within the crystal. This creates gaps in the crystal pattern. Schottky defect reduces the density of the ionic compounds as ions leave the crystals which reduce the overall mass. The schottky defect is shown below:
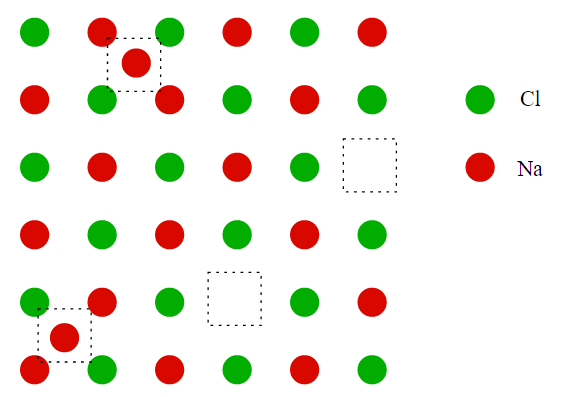
• Frenkel Defect: This type of defect is usually seen in the ionic compounds. When cation displaces interstitial voids then this point defect is known as Frenkel defect. In this defect cation is displaced because of its smaller size than anion. The density of the crystal does not change because of this defect. the Frenkel defect is shown in the below image for NaCl:
Note:
Frenkel Defect is different from Schottky defect in the terms of its occurrence and the characteristics. Frenkel defect generally occurs in the ionic compounds in which ions are of different sizes. Whereas Schottky defect occurs in ionic crystals where the size of the cation and anion is the same.
