Question
Question: Which one of the following statements is correct, with reference to enzymes? A. holoenzyme= coenzy...
Which one of the following statements is correct, with reference to enzymes?
A. holoenzyme= coenzyme cofactor
B. apoenzyme=holoenzyme+coenzyme
C. holoenzyme=apoenzyme+coenzyme
D. coenzyme=apoenzyme+holoenzyme
Solution
Enzymes are the substances in our body that help in a reaction by speeding up the process. They do so by decreasing the activation energy of the reaction. Sometimes the enzymes are inactivated and these inactivated enzymes are called apoenzymes. To activate them we need some non-protein component which helps inactivation of these enzymes. These non-protein components are called cofactors.
Complete answer:
Cofactors - these are non-peptide molecules of an enzyme that helps in the activation of an enzyme.
There are various enzymes that require activation by these cofactors. For example: DNA polymerase requires magnum ion for its activation, RNA polymerase requires a sigma factor and Carbonic anhydrase is activated by zinc.
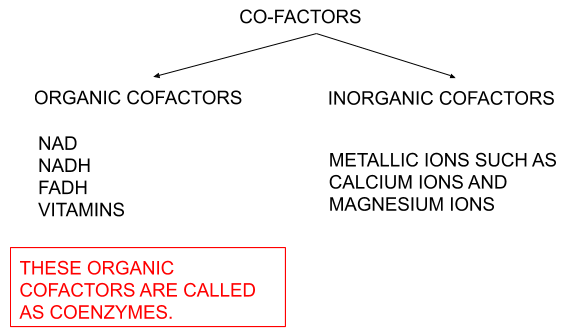
These cofactors can be organic and inorganic. An organic cofactor is called a coenzyme. Coenzymes are further divided based on their bondage with the enzymes. Some enzymes bind to enzymes very tightly and are known as a prosthetic group and some cofactors are loosely bound to these enzymes and usually referred to as coenzymes only.
-Apoenzyme: the inactivated enzymes are called the apoenzyme. They require cofactors for their activation.
-Holoenzyme: together these apoenzymes and cofactors are called the holoenzyme. We can also say an apoenzyme attached to its cofactor.
There might be confusion between cofactors and coenzyme. But remember cofactors include other non-protein factors(such as metallic ions and prosthetic groups ) which can bind covalently to apoenzyme. While the term coenzyme is specifically used for organic cofactors. And these coenzymes bind transiently to apoenzyme that forms holoenzyme for catalysis. After the reaction, they get detached.
Hence, the correct answer is option (C).
Note: Many coenzymes are derivative of vitamins so if vitamin intake is low there will be non-availability of coenzymes. Various water-soluble vitamins such as Vit C and B-complex helps in the formation of various coenzymes such as NAD and coenzyme A.
