Question
Question: Which one of the following occurs by an addition-elimination mechanism? A.Toluene, \(B{r_2},\,FeB{...
Which one of the following occurs by an addition-elimination mechanism?
A.Toluene, Br2,FeBr3→p− Bromo toluene
B.Benzene, HNO3,H2SO4→ nitrobenzene
C.Benzene, CO, HCl, AlCl,CuCl→ benzaldehyde
D.2,4 dinitrochlorobenzene, NaOH, heat, then H+→2,4− dinitrophenol
Solution
Elimination reaction is a type of reaction where several atoms either in pairs or groups are removed from a molecule. This removal usually takes place due to the action of acids and bases or action of metals. Moreover, in case of additional reaction, two or more reactants come together to form a larger single product.
Complete step by step answer:
Basically, elimination reaction is a type of reaction that is mainly used to transform saturated compounds i.e. organic compounds which contain single carbon-carbon bonds to unsaturated compounds i.e. the compounds which feature double or triple carbon-carbon bonds. Now, addition elimination reaction is a two-stage reaction process of an additional reaction followed by an elimination reaction.
In simple words, we can say that an additional reaction is a chemical reaction wherein two or more reactants come together to form a larger single product. Further, there are two types of addition reaction i.e. electrophilic addition and nucleophilic addition. In case of electrophilic addition, a reactant with multiple bonds has its π bond broken and forms two new σ bonds. Its mechanism is as shown:
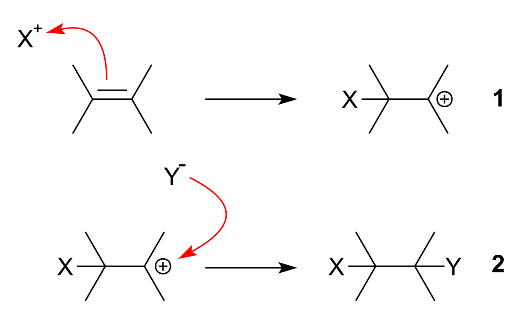
Now, in case of nucleophilic addition reaction, a chemical compound with an electron-deficient or electrophilic double or triple bonds, a π bond reacts with a nucleophile which is an electron rich reactant and then the double bond disappears and forms two new single bonds. Its mechanism is as shown:
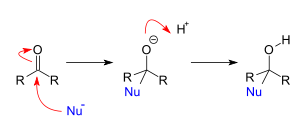
Now, among the given options, Toluene, Br2,FeBr3→p− Bromo toluene and 2,4- dinitrochlorobenzene, NaOH, heat, then dinitrophenol shows addition-elimination reaction. When 2,4- dinitrochlorobenzene is heated with sodium hydroxide, the hydroxide ion is first added to the carbon atom bearing the chloride atom. Further, this is followed by elimination of chloro groups in the form of chloride ions.
Hence, option A and option D both are correct.
Note: Another common example of addition elimination reaction is the reversible reaction of amines with carbonyls. In this process, imines are formed in the alkylamino-de-Oxo-bi substitution reaction. Moreover, the hydrolysis of nitriles to carboxylic acids is also a form of addition-elimination reaction.
