Question
Question: Which one of the following molecules contains no \[{{\pi }}\] it bonds? A. \[{{C}}{{{O}}_{{2}}}\]...
Which one of the following molecules contains no π it bonds?
A. CO2
B. HO2
C. SO2
D. NO2
Solution
Sigma and pi bonds are two covalent bonds. They differ in the overlapping of atomic orbitals. Sigma bonds are formed by the head-to-head overlapping of atomic orbitals and pi bonds are formed by the lateral overlap of two atomic orbitals.
Complete step by step answer:
Sigma bonds are the strongest covalent bonds, due to the direct overlapping of the orbitals. All single bonds are called sigma bonds. They can be formed by the combinations of atomic orbitals ie., S-S Overlapping S-P Overlapping a P-P Overlapping.
The sidewise positive overlap of atomic orbitals along a direction perpendicular to the internuclear axis generates pi bonds. The axes of the atomic orbitals are parallel to one another during the formation of π bonds, and the overlapping is perpendicular to the internuclear axis. These π Bonds are weaker than sigma bonds, due to lesser degree of overlapping. Double bonds are one sigma and one pi bond, and a triple bond is two π bonds and one σ bond.
Lewis dot structures show electronic structures of the elements, along with their pairing. Here, each dot shows an electron. A bond is represented by a pair of dots between the chemical symbols of atoms.
Structure of CO2: Lewis structure has a total of 16 valence electrons, it is doubly bonded to each of the oxygen atom.
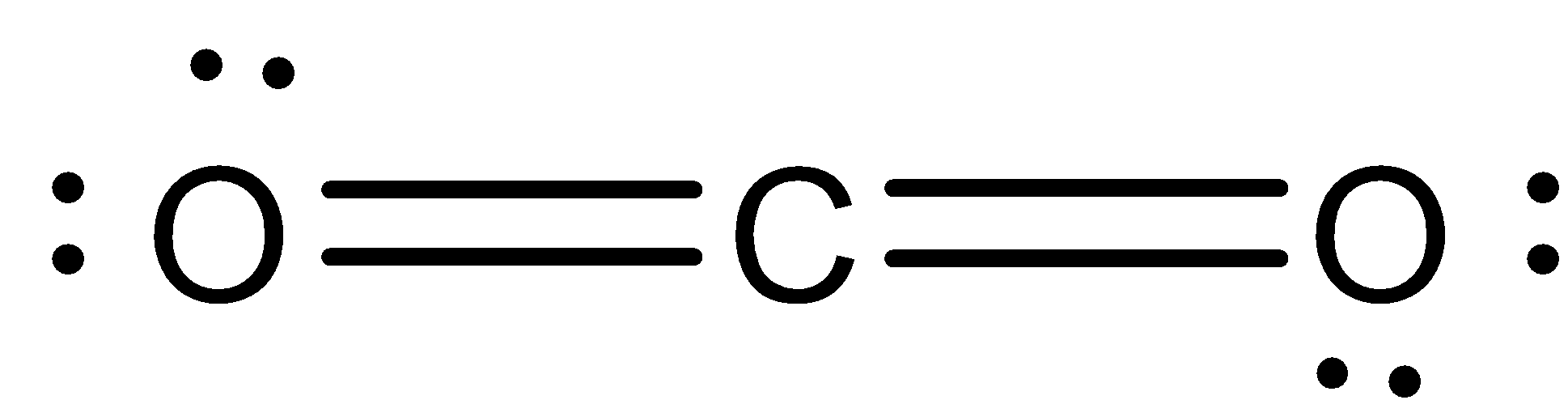
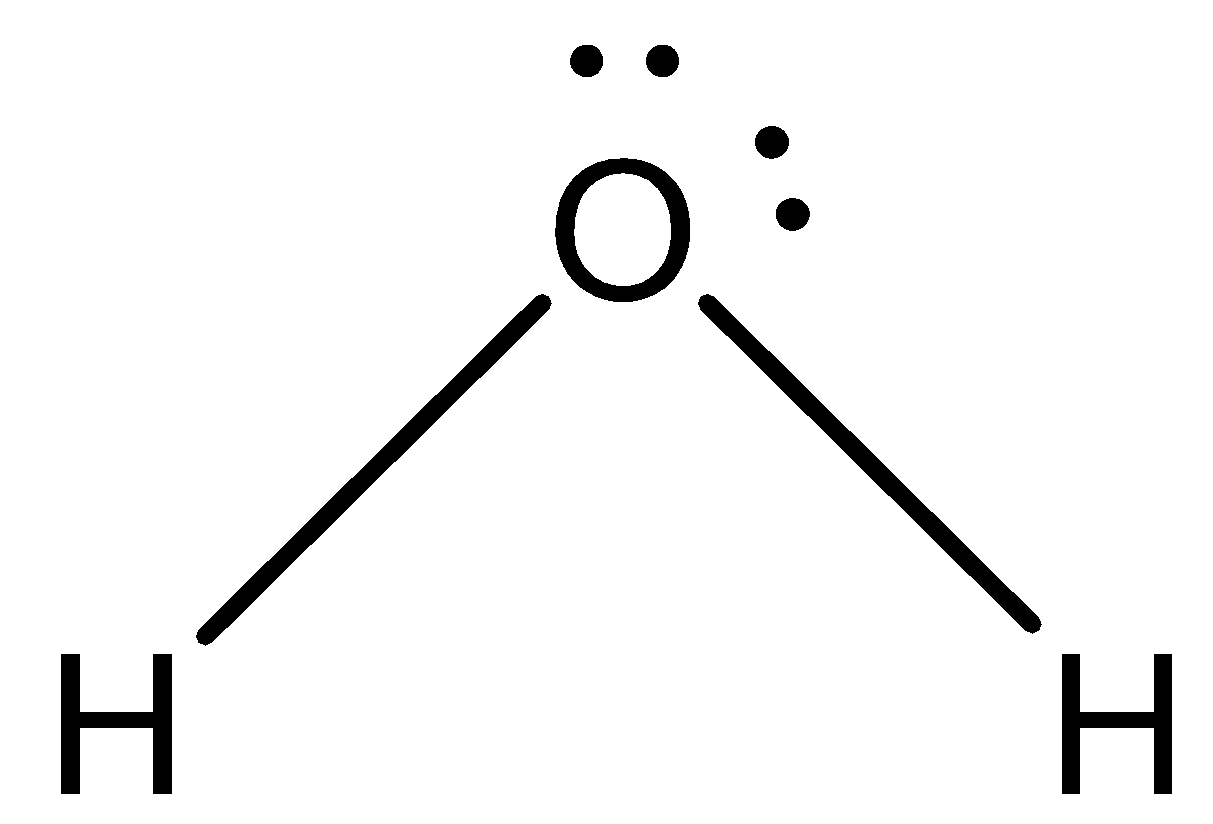
Structure of H2O: Lewis structure has a total of 8 valence electrons they are singly bonded to the oxygen atom.
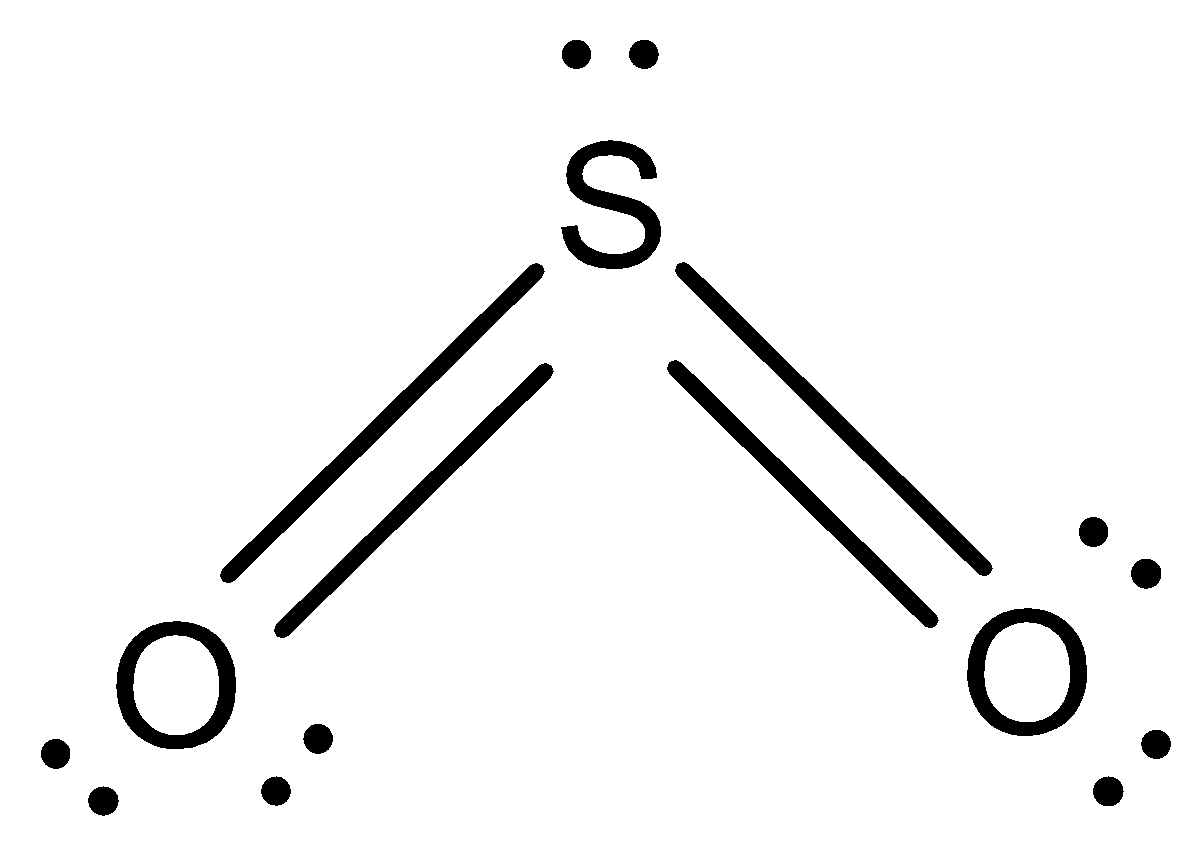
Structure of SO2 : Lewis structure has a total of 18 valence electrons. An oxygen sulphur double bond and oxygen sulphur single bond is obtained.
Structure of NO2: The NO2 Lewis structure has a total of 17 valence electrons. The structure is represented as,
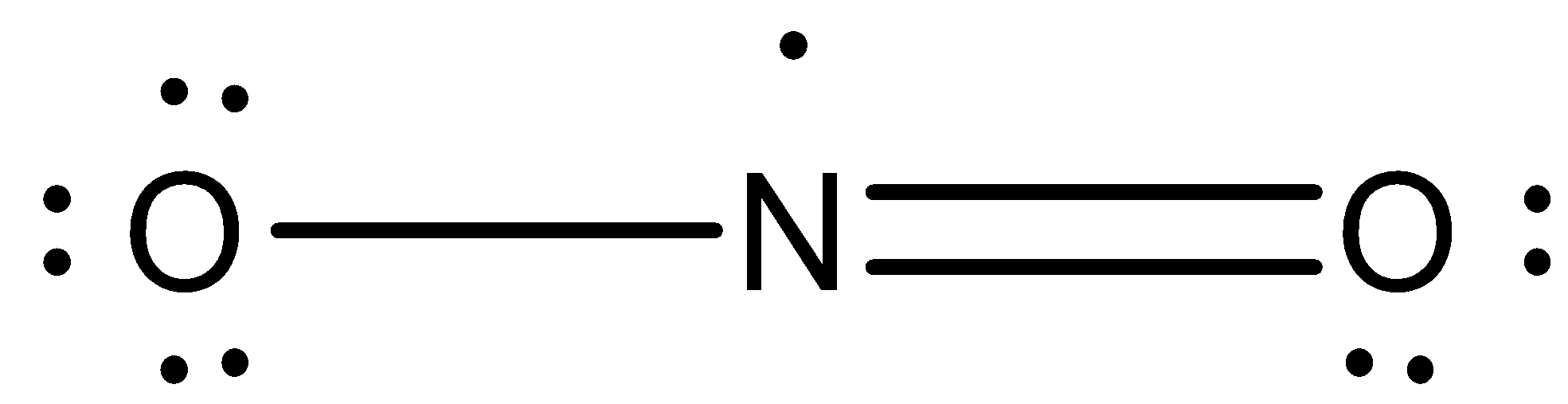
So, the correct answer is Option B.
Additional information:
The major drawback of Lewis structure is that it does not include the geometry of molecules, bonds formation, or how the electrons are shared.
Note: According to VSEPR theory (valence shell electron pair repulsion theory), is that electron pairs and lone pairs repel each other. The geometry formed is such that the electron pairs as far apart from each other as possible.
