Question
Question: Which one of the following materials cannot be used to make lenses? A. Water B. Glass C. Plast...
Which one of the following materials cannot be used to make lenses?
A. Water
B. Glass
C. Plastic
D. Clay
Solution
Hint: We use the refraction phenomenon to construct lenses. When light falls on one of the surfaces, it undergoes refraction and enters into the lens. After travelling through the lens, the light goes out of the lens with another refraction. Hence, lenses need to be made of a transparent material.
Complete step by step answer:
The lens is an essential instrument in optics. It is used in eyeglasses, contact lenses to correct the errors in our eyes.
We need to understand the working principle of the lens to answer this question.
Lenses are used to make images of objects by focusing or diverging the true path of light. The surfaces of the lens are curved, and it gives a focusing effect of the light. There can be two types of surfaces depending on the shape - Convex (bulging) or Concave (depressed).
A convex lens will focus the light beams, and a concave lens will make the light beam diverge. Look at the following figure of the convex lens to understand the internal mechanism of the lens.
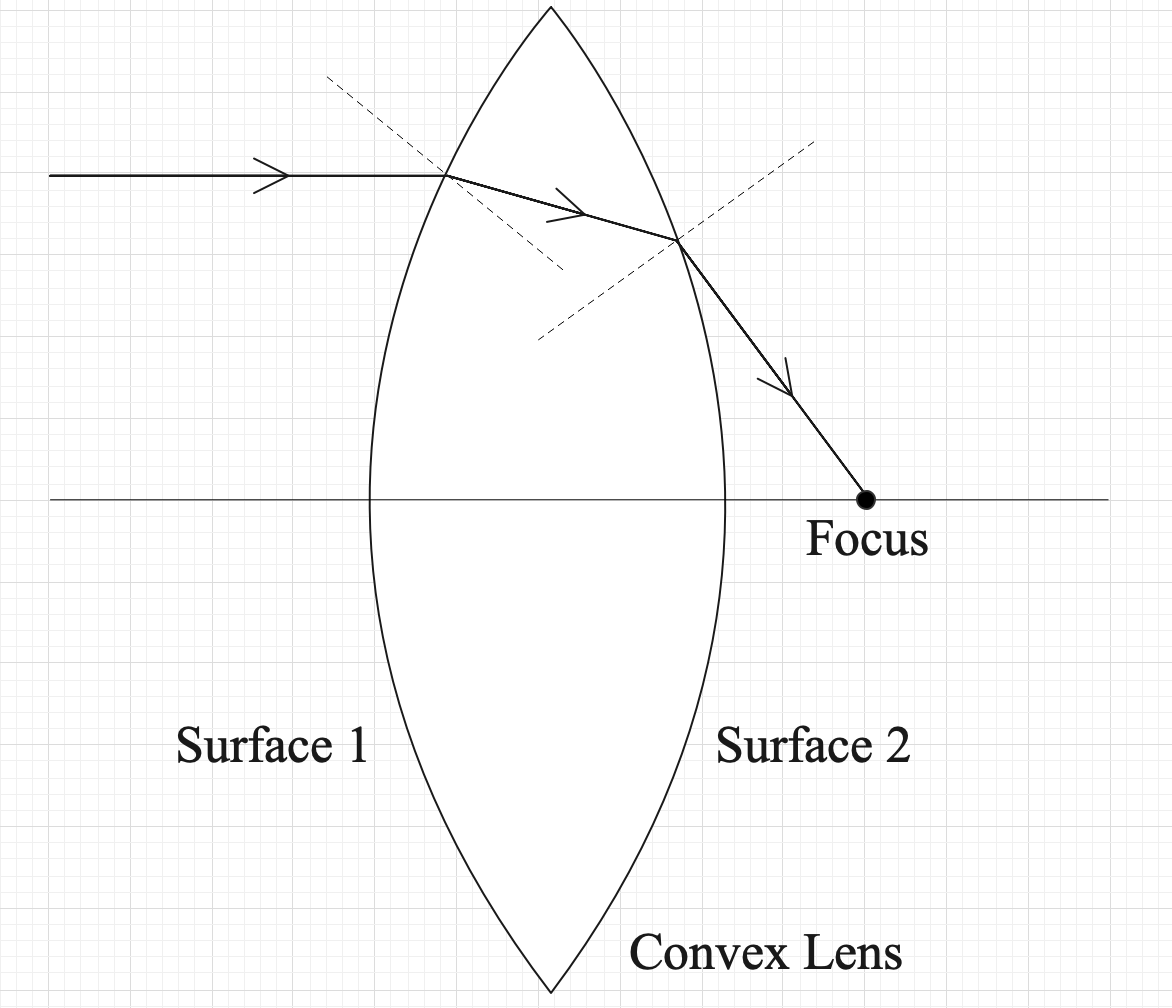
This figure shows the working principle of a convex lens. Both the surfaces need to be bulged out to be a convex lens. A light ray, parallel to the axis of the lens, falls on Surface 1 and undergoes refraction. This points the ray towards the axis. Now, it undergoes another refraction on surface 2. It further deviates the light from its original path.
The point at which the light meets the axis is called the focal point of the lens.
Now, it should be clear that the material should be transparent for the successful working of a lens.
Hence, an obstructive material cannot be used to make lenses.
Amongst the options, only Clay is not transparent.
The correct option is (D).
Note: There’s a famous formula which can be used to determine the focal length of the lens. We call it The Lens Maker’s Formula. It is given by,
f1=(n−1)(R11−R21)
Where,
f is the focal length of the mirror
n is the refractive index of the material
R1 is the radius of curvature of surface 1
R2 is the radius of curvature of surface 2.
Here, we are assuming that the width of the lens is negligible.
