Question
Question: Which one of the following is the electron deficient molecule? A.\({B_2}{H_6}\) B.\({C_2}{H_6}\)...
Which one of the following is the electron deficient molecule?
A.B2H6
B.C2H6
C.PH3
D.SiH4
Solution
We need to know that the term electron deficiency describes the atoms and molecules that have fewer number of electrons required for maximum stability. For each atom in a molecule, the main group atoms having less than eight electrons and for transition group atoms having less than eighteen electrons are described as electron deficient.
Complete step by step answer:
If we talk about electron deficiency in chemistry, then boranes and carboranes are widely used terms. The boron hydrides and other molecules which do not have enough valence electrons to form localized bonds joining all atoms fall in the category of electron deficient atoms or molecules.
B2H6 atom has three half-filled orbitals in an excited state. Two electrons of boron-hydrogen bond are involved in the formation of a three-centre bond also called the hydrogen bridge.
The chemical structure of B2H6 can be observed as,
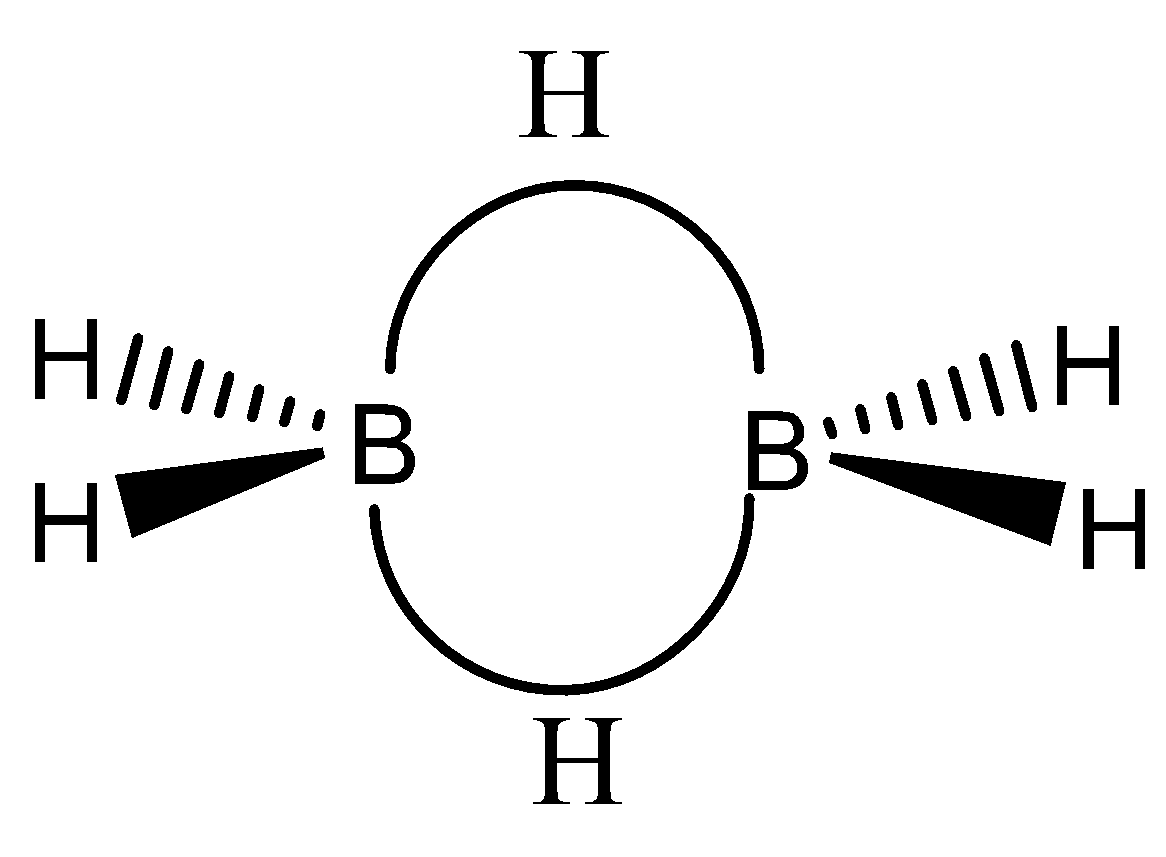
The valency of boron is 3, but in this particular structure, the two electrons of boron atom are shared with hydrogen atoms forming covalent bonding.
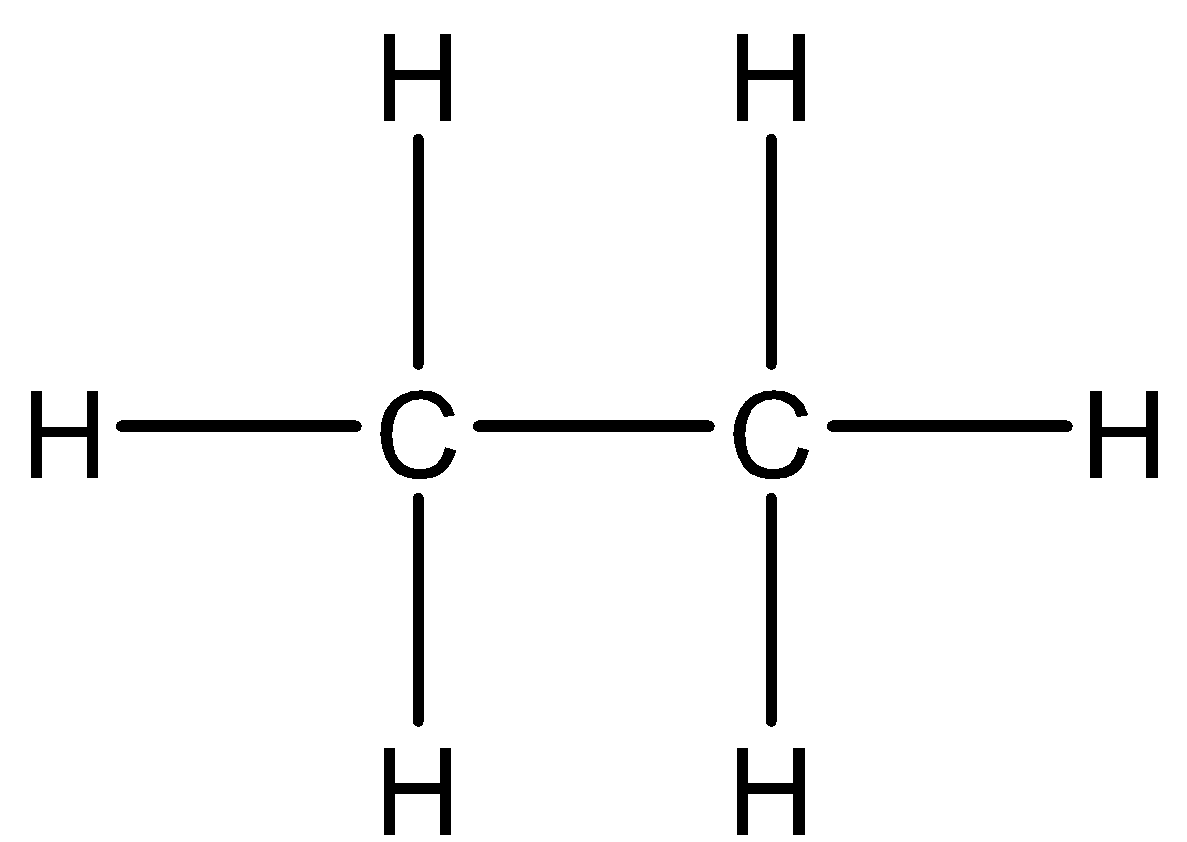
If we look at ethane - C2H6. There are two carbon atoms bonded with each other and each carbon atom is bonded with another three hydrogen atoms. Thus, there is no sharing of electrons and the structure is electron sufficient.
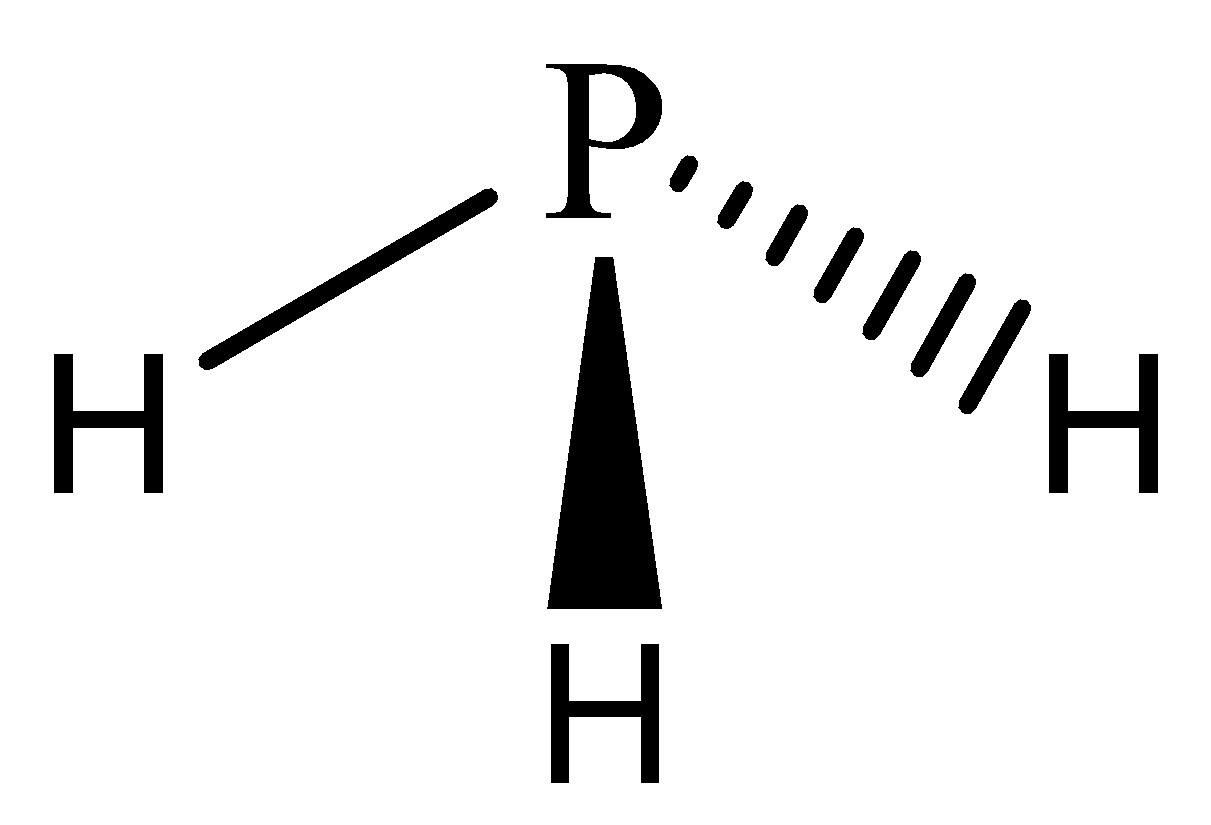
While in phosphine, one phosphorus atom is bonded with three hydrogen atoms, the valency of phosphorus being 3 is satisfied.
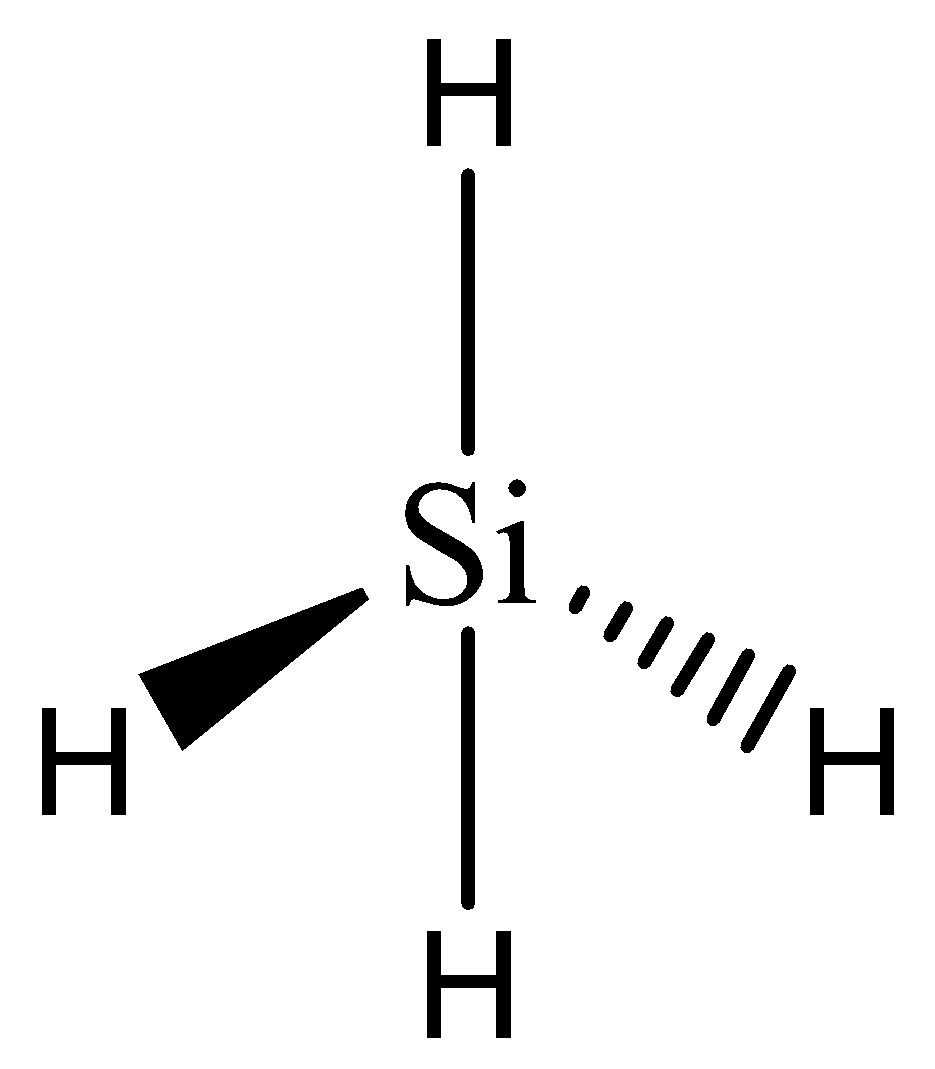
In silane, one silicon atom is bonded to four hydrogen atoms. The valency of silicon is 4 which has been satisfied with the adequate number of electrons in bonding.
Hence, the correct answer to the question is option A.
Note:
We have to know that in organic chemistry, electron deficiency is used to represent alkene or arene that have electron withdrawing groups attached. For example – nitrobenzene. The electron deficient pi-bonds may lead to electrophilic or nucleophilic attacks in substitution reactions like in nucleophilic aromatic substitution reactions. Boranes and carboranes are identified as electron deficient compounds in chemistry. As they are the best example that elaborates the term.
