Question
Question: Which one of the following is a correct set? A.\[{H_2}O,\;s{p^3}\],angular B.\[{H_2}O,\;s{p^2}\]...
Which one of the following is a correct set?
A.H2O,sp3,angular
B.H2O,sp2,Linear
C.NH4+,dsp2,Square planar
D.CH4,dsp2,Tetrahedral
Solution
We need to find the geometry and hybridization of a given molecule. We can find the hybridization by knowing the number of sigma bonds and lone pairs. Geometry of a molecule can be explained by the arrangement of lone pair and bond pairs.
Complete step by step answer:
Hybridization is the concept of mixing atomic orbitals into new hybrid orbitals with different energies, shapes etc, that are suitable for the pairing of electrons to form chemical bonds in valence bond theory.
z=no.ofσbond+l.poncentralatom
Where, No. of σ bond means single bond and l.p is the lone pair present on the central atom.
| Z | Hybridisation |
|---|---|
| 2 | Sp |
| 3 | Sp2 |
| 4 | Sp3 |
| 5 | Sp3d |
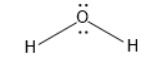
H2O have two lone pairs and two bond pairs.
So, z H2O for will be four.
z=4
Hybridisation of H2O is Sp3 and there are two lone pairs present there. Geometry will be angular or bent because of the electron-electron repulsion.
Geometry for NH4+ and CH4 is tetrahedral and they both don’t have lone pair of electrons and dsp2 type of hybridization is generally seen in transition metal ion.
Therefore, Option A is the correct and correct set is H2O,sp3, angular.
Note: Geometry of a molecule can be explained by the arrangement of lone pair and bond pairs while shape can be explained by the arrangement of atoms around the atoms, it is not linked with lone pair and hence only deals with bond pairs.
-The molecules which do not have lone pairs of electrons tend to have the same shape as geometry, because the geometry of a molecule is affected by the lone pairs.
