Question
Question: Which one of the following compounds will give dimethyl glyoxal with \(Se{{O}_{2}}\)? A. Acetone ...
Which one of the following compounds will give dimethyl glyoxal with SeO2?
A. Acetone
B. Acetophenone
C. Ethyl methyl ketone
D. Propanaldehyde
Solution
Think about the structure of dimethyl glyoxal and what all are the functional groups involved. Think about the type of oxidation that uses selenium dioxide as a reagent and causes oxidation to form carbonyl carbon.
Complete answer:
The reaction that involves the oxidation of an alkyl carbon to a carbonyl carbon using selenium dioxide as a reagent is known as the Riley oxidation reaction. It acts on the enol tautomers of ketones on the double bonded carbon and turns it into a glyoxal compound. Let us look at the structure of glyoxal before determining which compound will be converted into dimethyl glyoxal after Riley oxidation. The structure of dimethyl glyoxal is as follows:
We can see here that we have two methyl groups attached to two different carbonyl carbons, or we can say that the methyl groups are attached to two ends of the glyoxal group. So, we will require a starting compound that has at least four carbon atoms. Let us look at the structures of all the compounds to determine whether they will form dimethyl glyoxal after Riley oxidation.
- Acetone
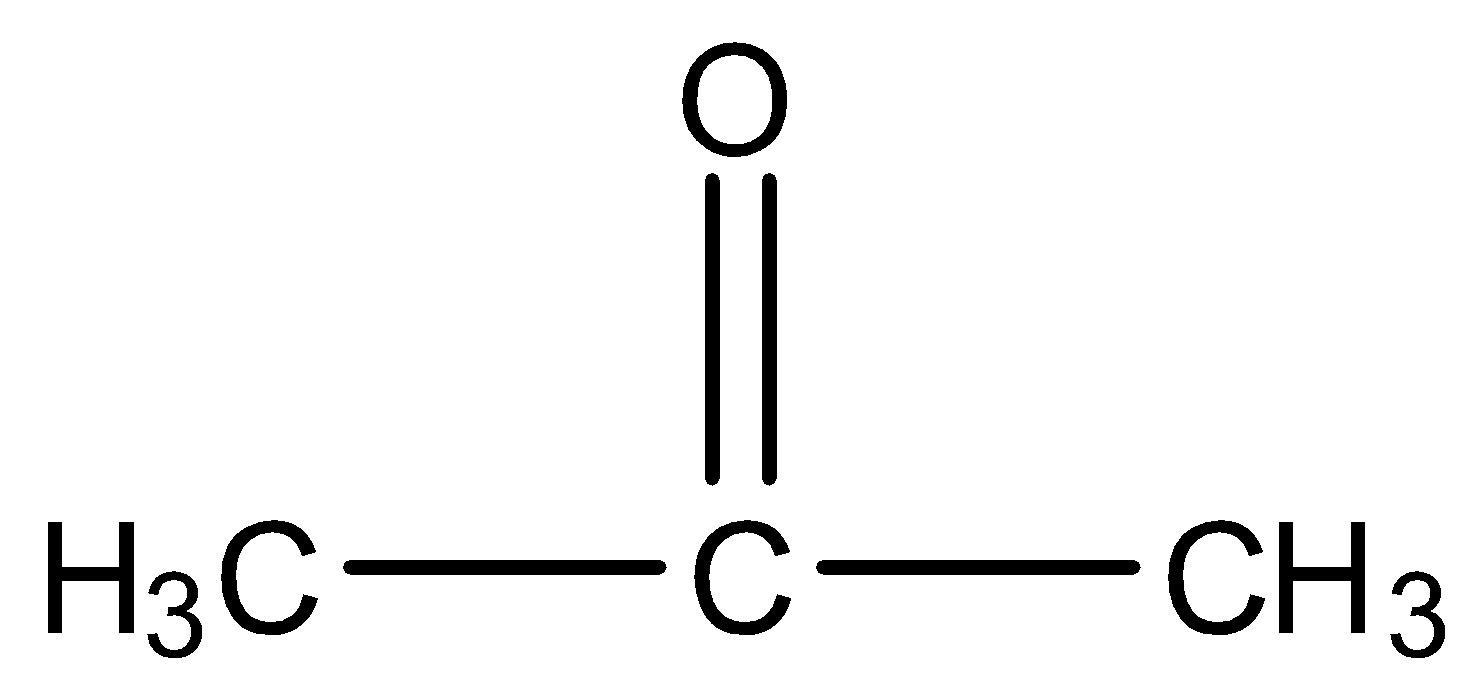
Here, we can see that it has only three carbon atoms so it will not be converted into dimethyl glyoxal.
- Acetophenone
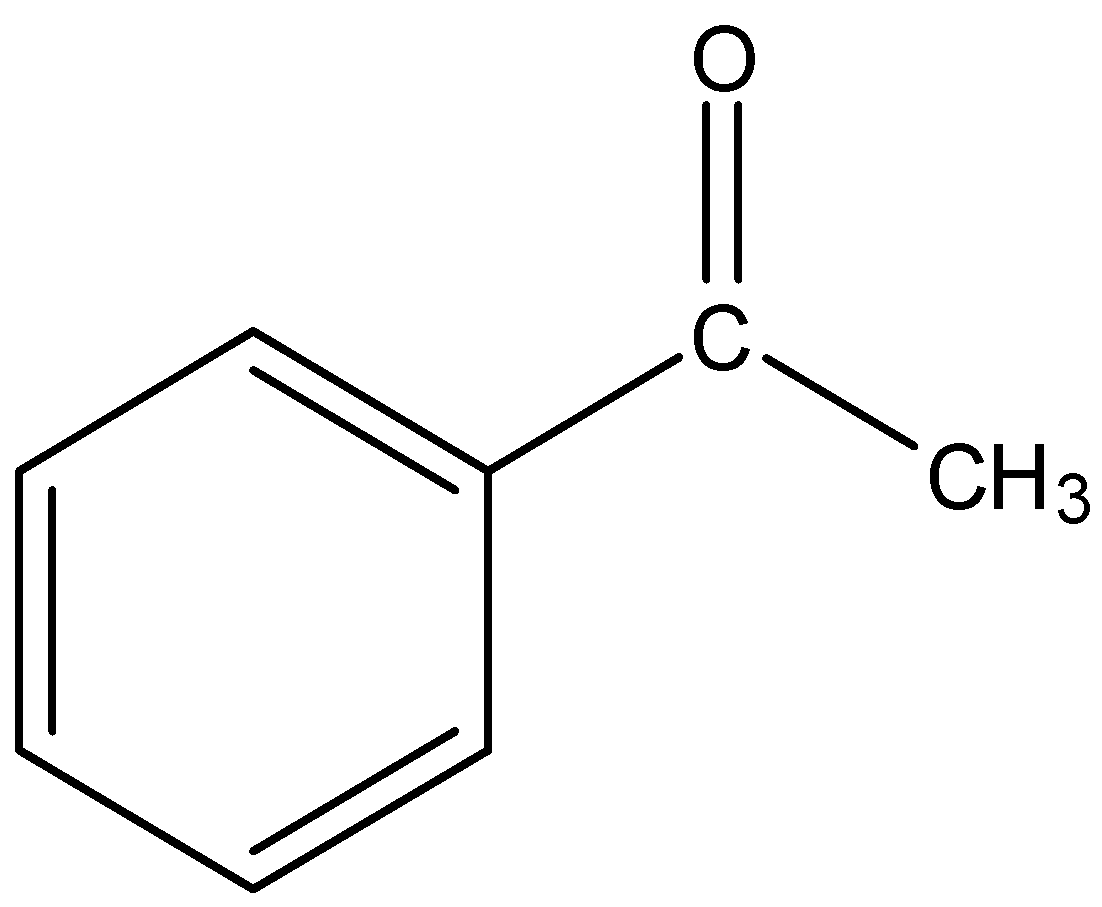
This is a cyclic structure and will not be converted into dimethyl glyoxal after riley oxidation.
- Ethyl methyl ketone
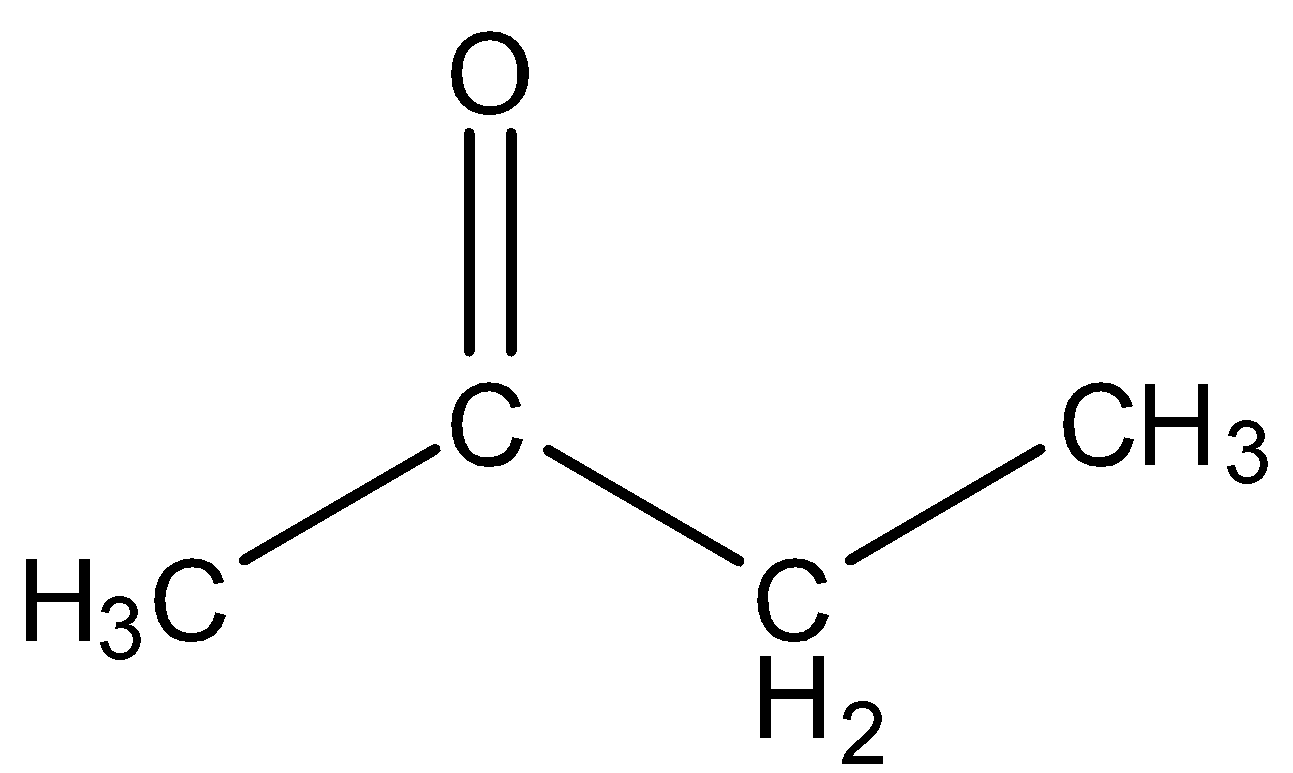
This has four carbon atoms and can be converted into dimethyl glyoxal in certain conditions.
- Propanaldehyde
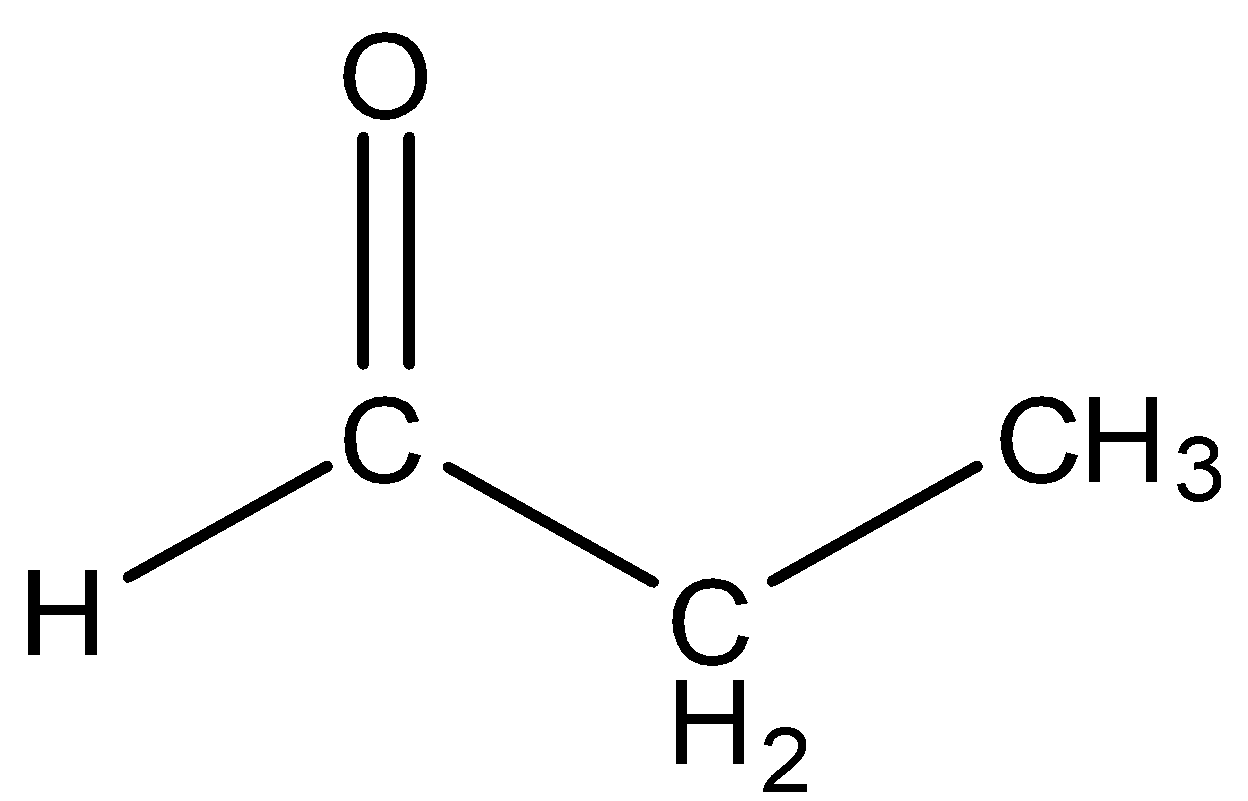
Even this molecule has only three carbon atoms so it cannot be converted into dimethyl glyoxal.
Now, let us look at the reaction mechanism of how ethyl methyl ketone is converted into dimethyl glyoxal.
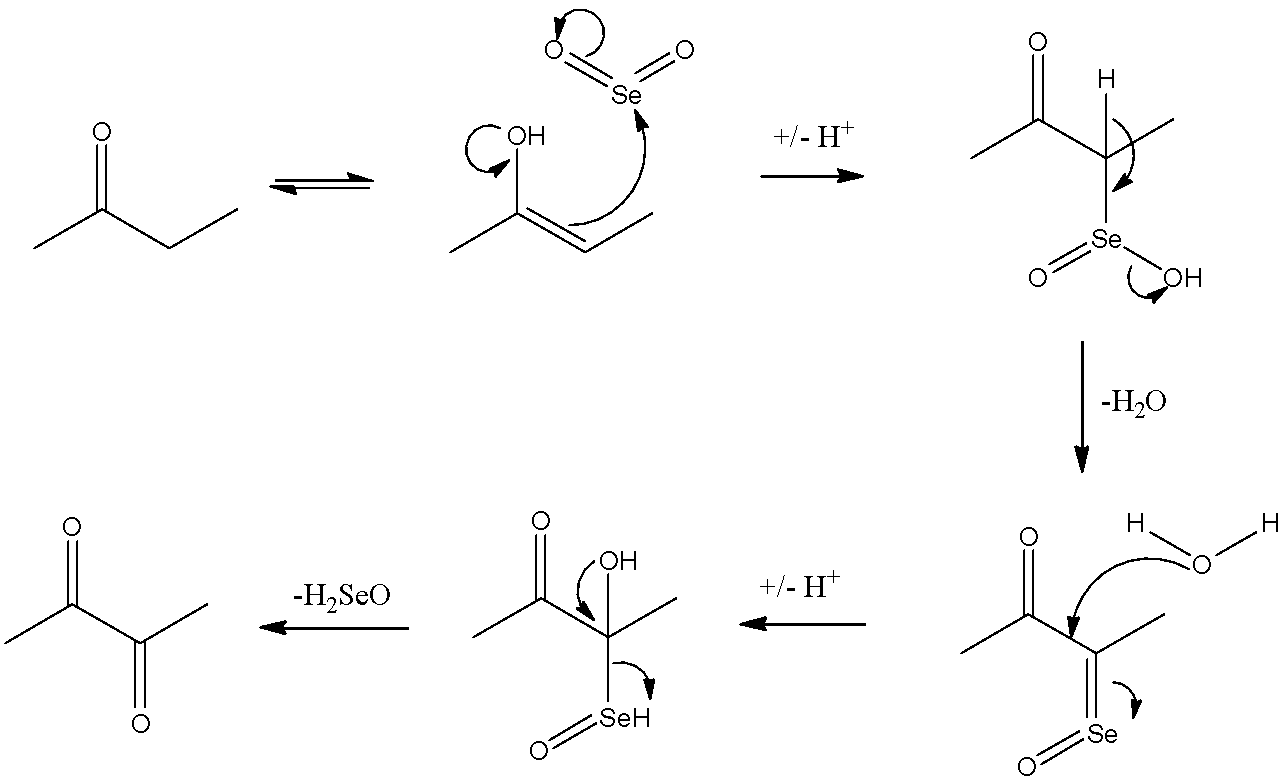
Here, we can see that ethyl methyl ketone gets converted to dimethyl glyoxal by the Riley oxidation.
Hence, the correct answer is ‘C. Ethyl methyl ketone’.
Note:
All the compounds given in the options do react with selenium dioxide but it is not necessary that they give a glyoxal compound. Any alpha carbon (carbon adjacent to carbonyl carbon) can undergo this oxidation.
